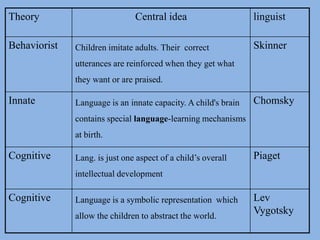
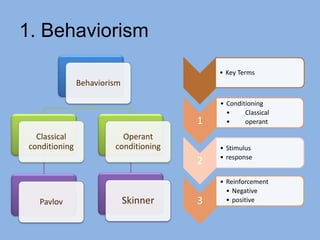
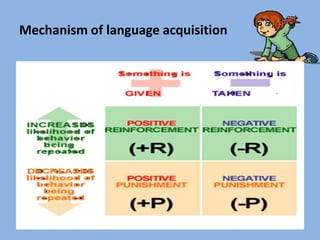
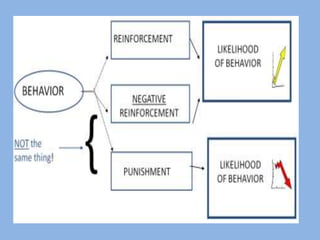
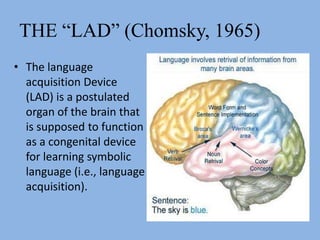
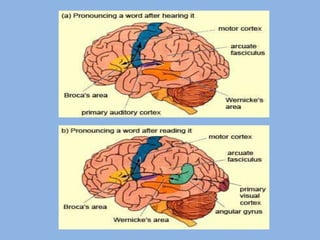
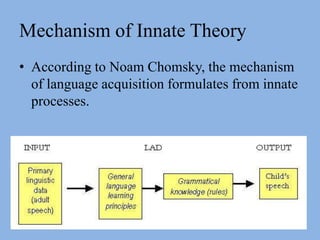
The document summarizes three main theories of first language acquisition: behaviorism, innatism, and cognitivism. Behaviorism, proposed by Skinner, views language learning as a process of habit formation through imitation, repetition, and reinforcement. Innatism, proposed by Chomsky, posits that children are born with an innate language acquisition device and universal grammar that allows them to learn the rules of any human language. Cognitivism incorporates aspects of both by recognizing the importance of cognitive processes and environmental influences in language development.