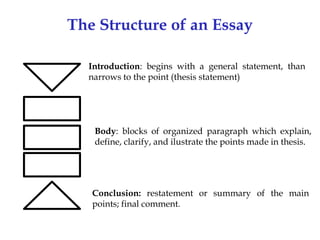
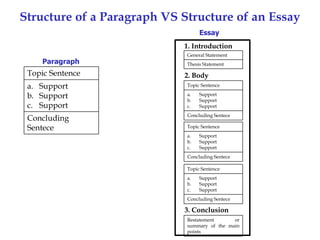
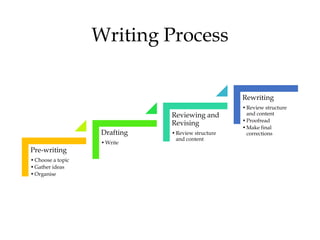
An essay is a group of paragraphs that discusses a single topic and central main idea. It typically contains at least three paragraphs, with five paragraphs being a common academic length. The structure of an essay includes an introduction with a general statement and thesis, body paragraphs that explain and support the thesis with evidence, and a conclusion that restates the main points. An outline is used to organize the information and structure of an essay in an ordered format using Roman numerals, capital letters, and Arabic numerals to denote the introduction, main ideas, supporting points, and details.