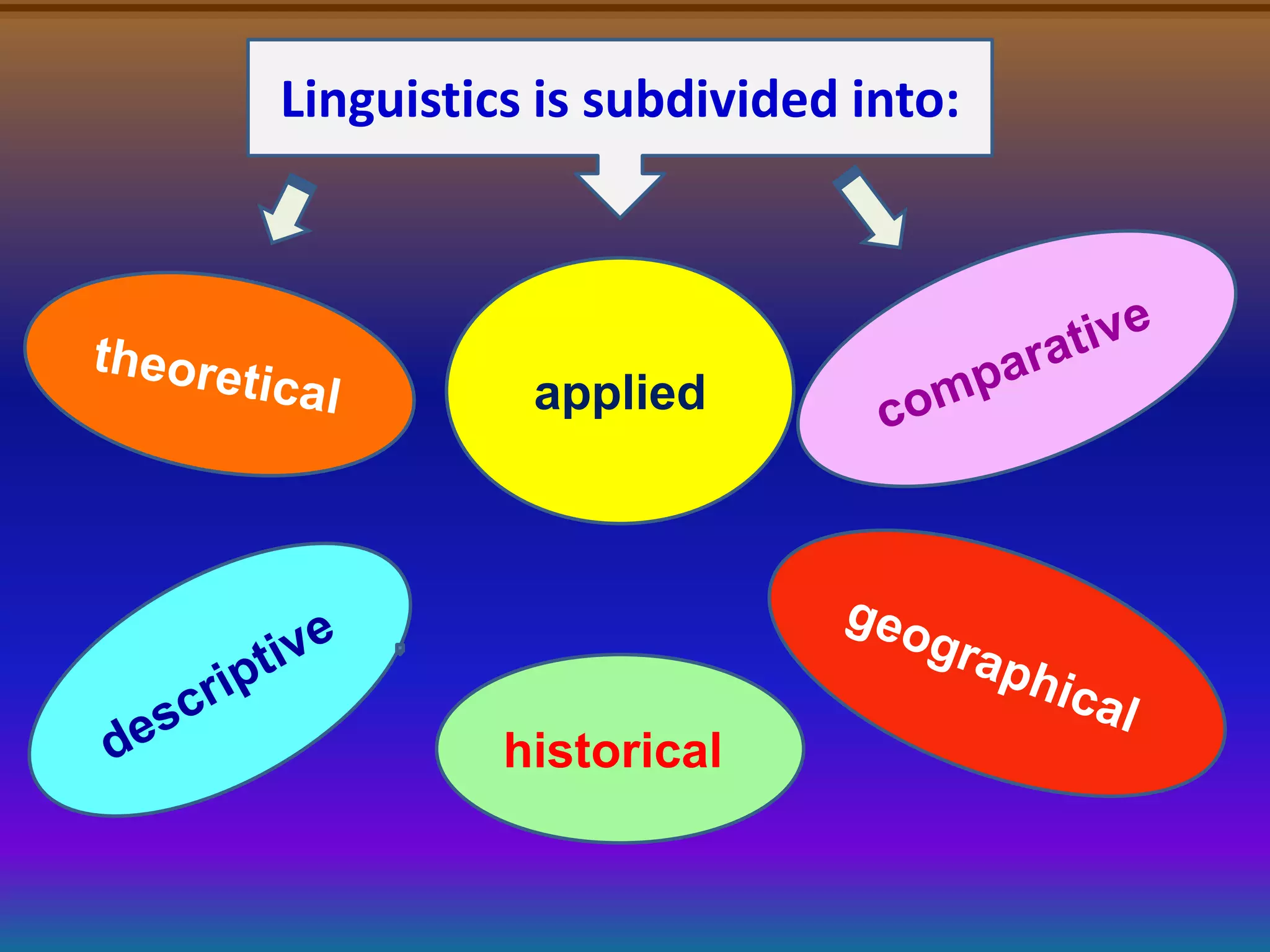
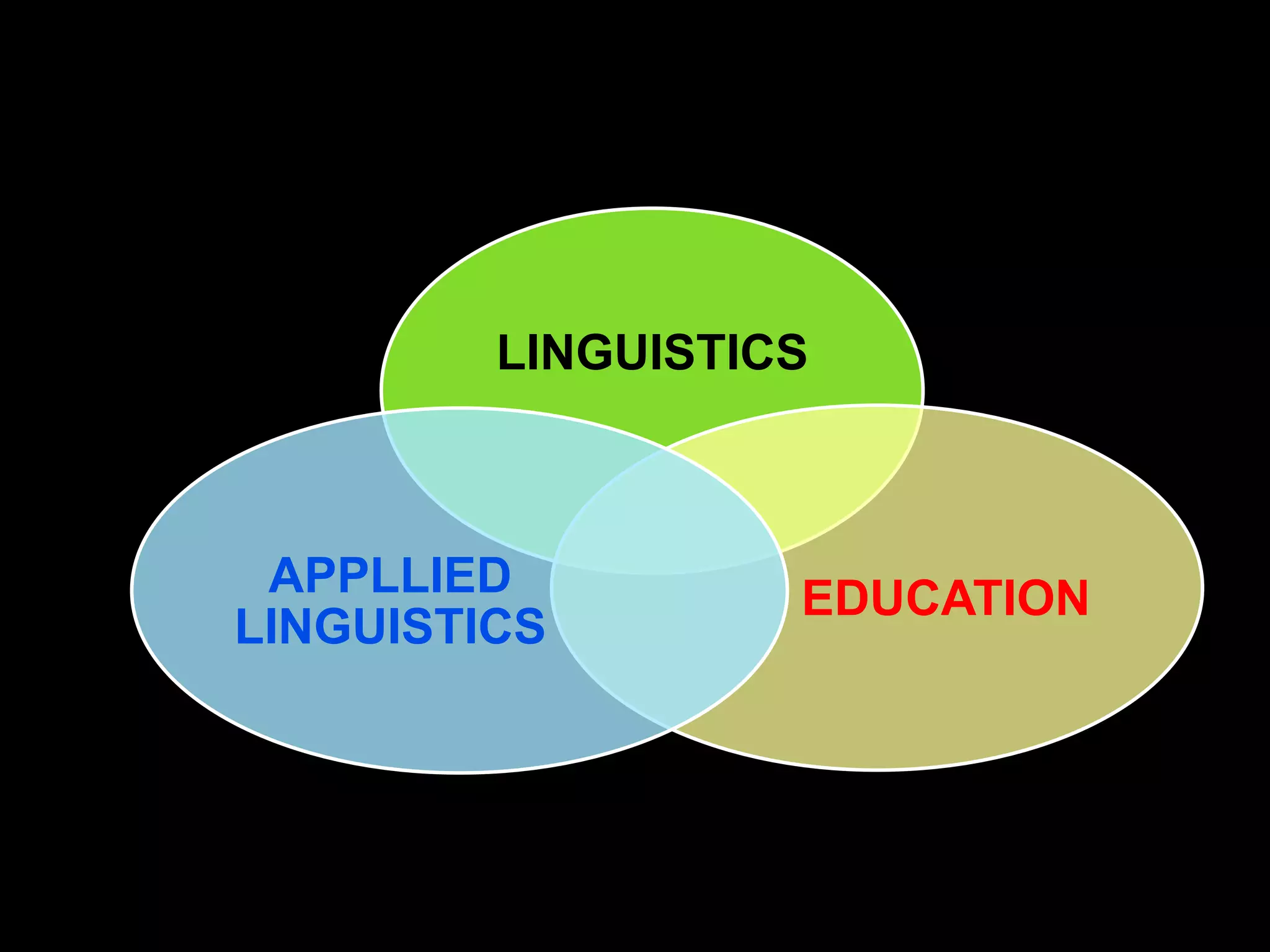
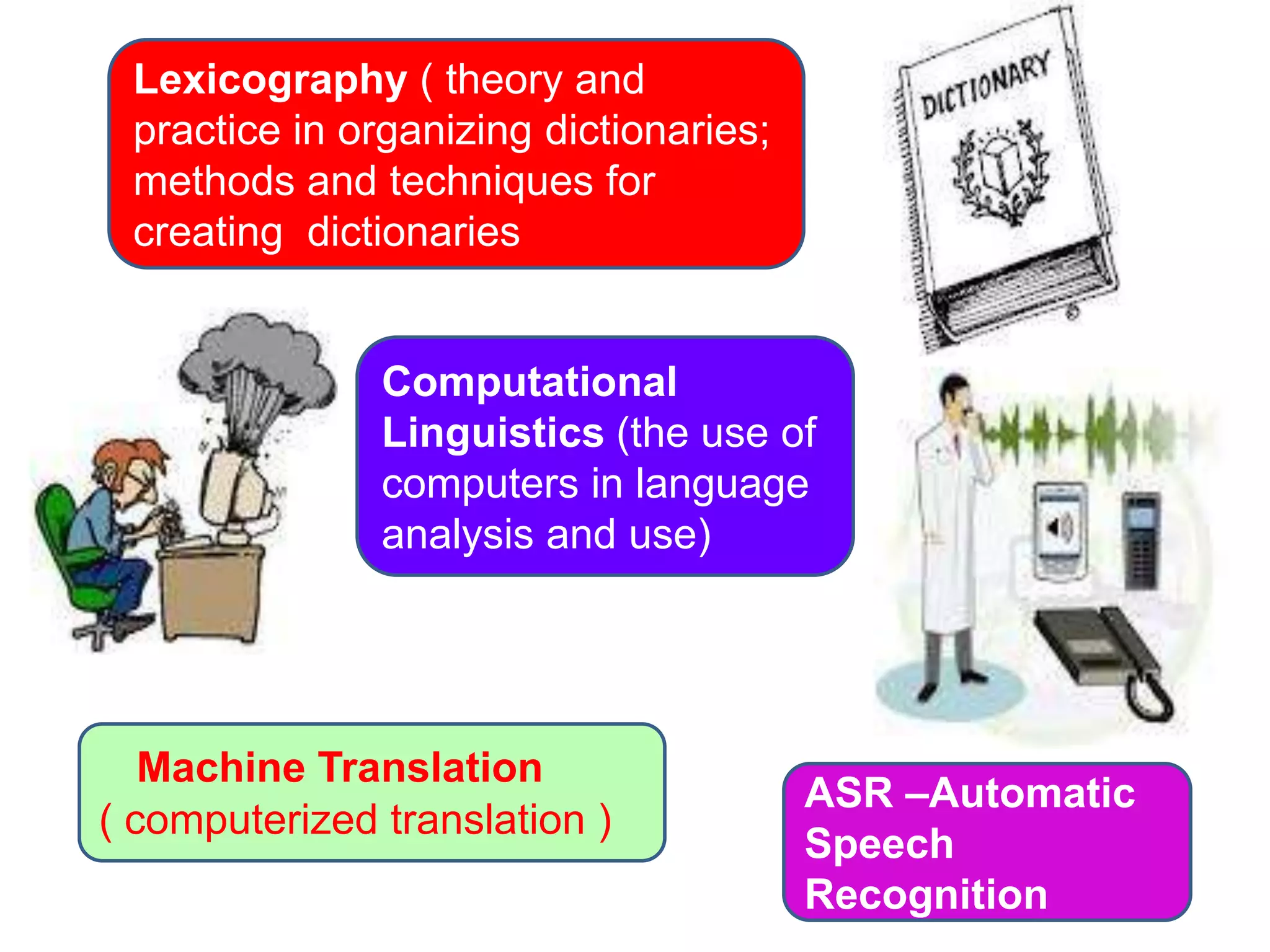
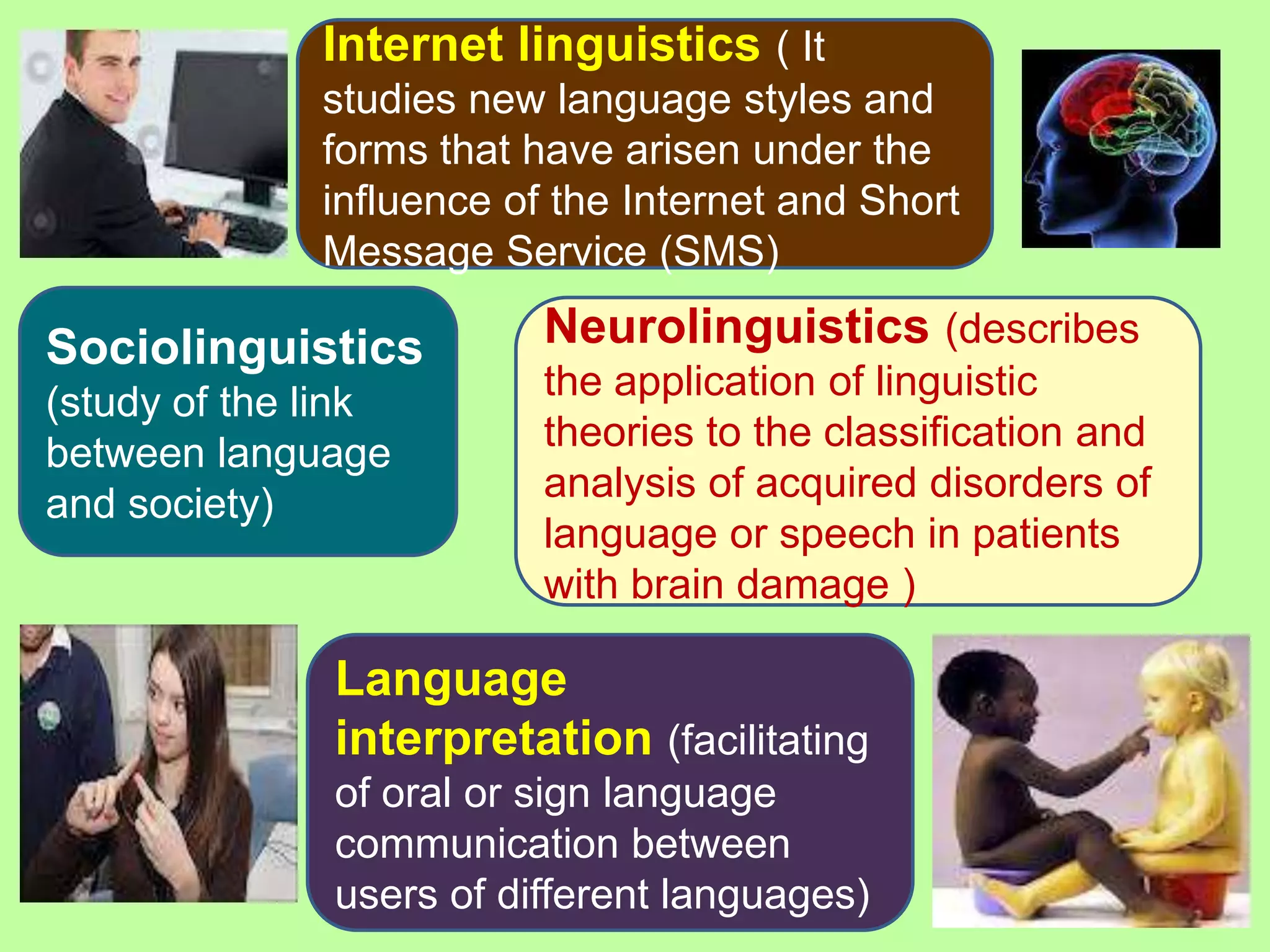
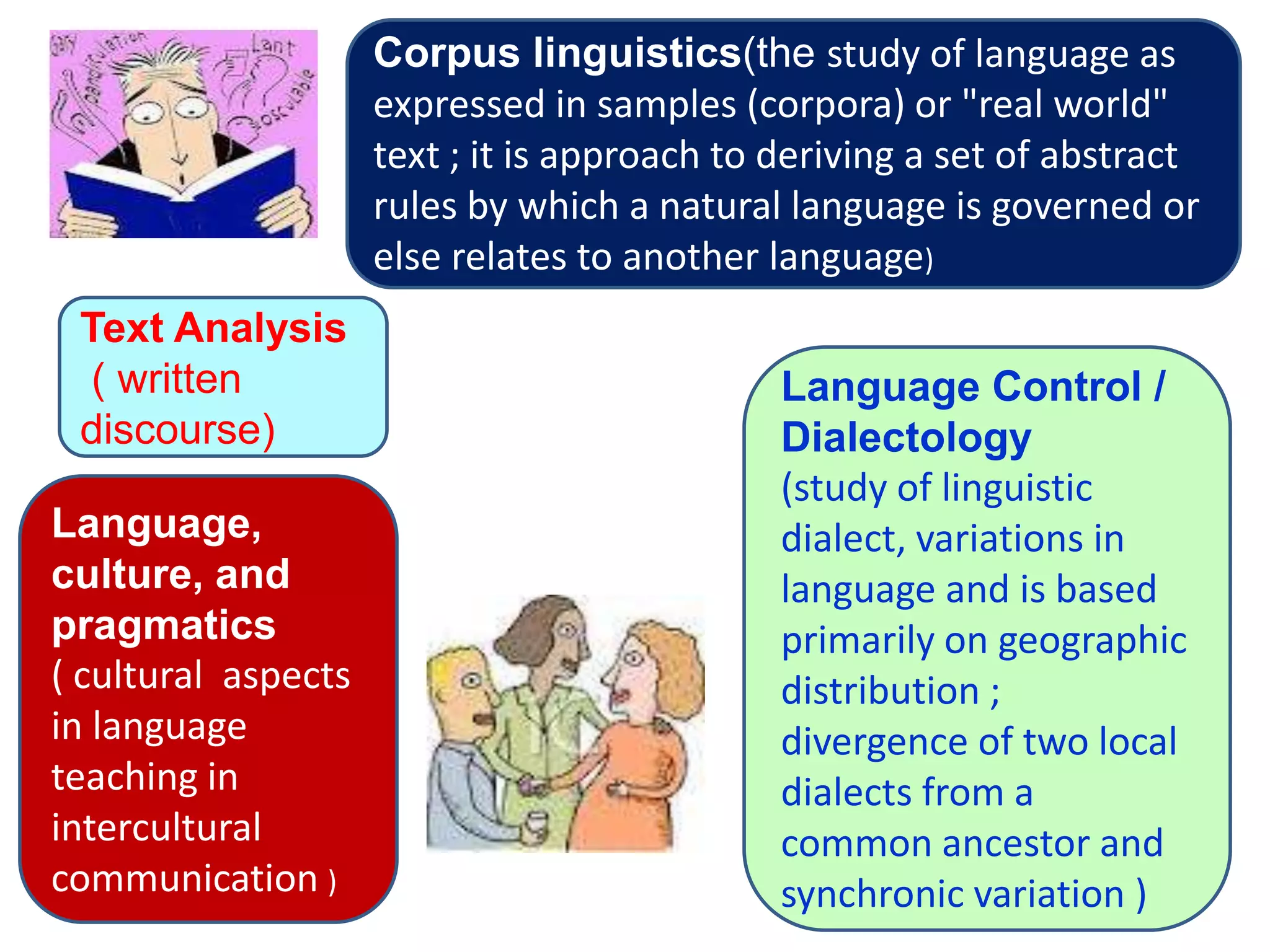
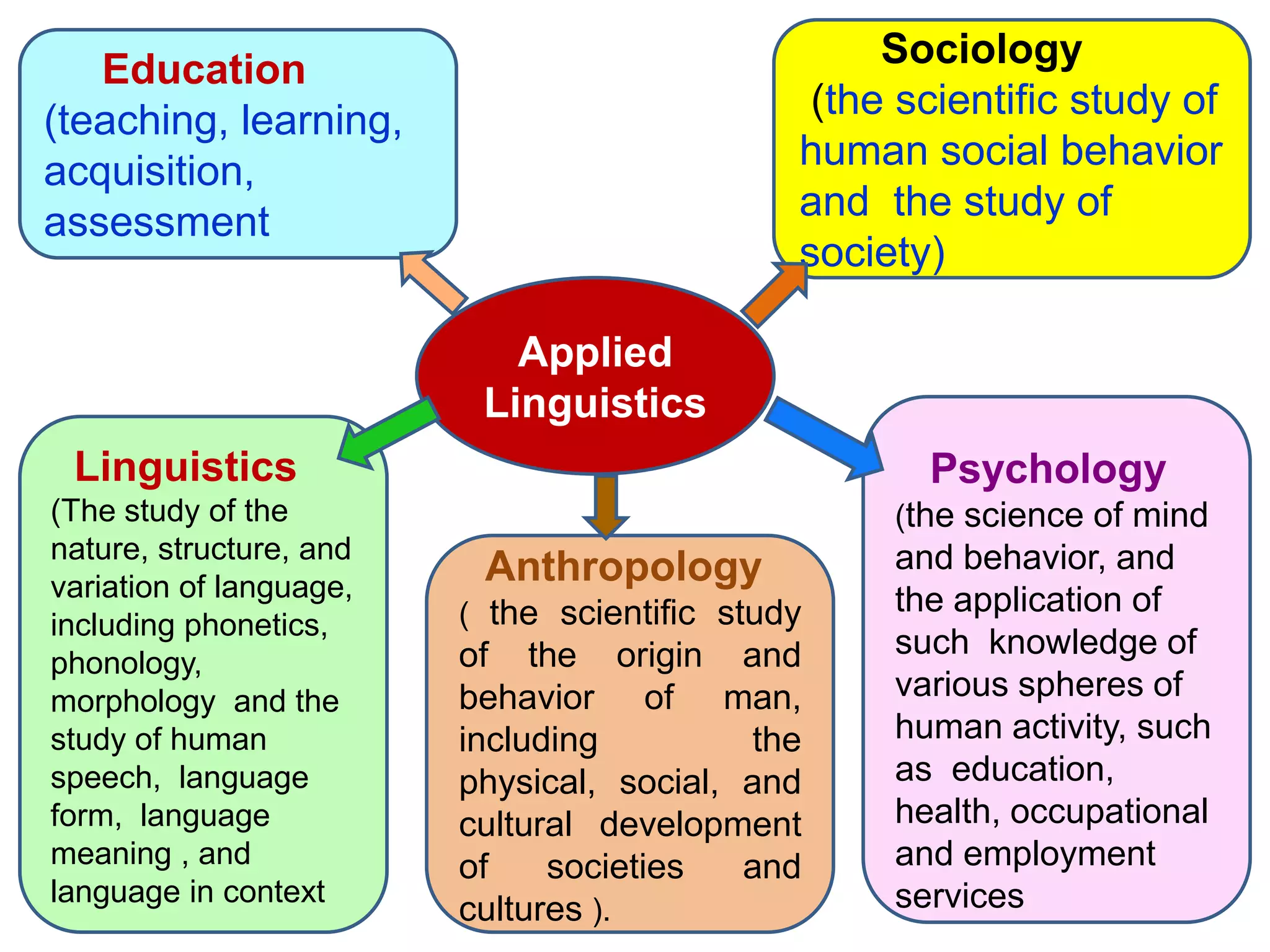
Linguistics is the scientific study of language, including areas like phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, and semantics. Applied linguistics [1] identifies and addresses language-related problems, [2] can be applied to all aspects of language use such as acquisition of first, second, and foreign languages, and [3] extends into practical fields including clinical linguistics, language teaching, lexicography, and computational linguistics. The key difference is that linguistics studies language itself, while applied linguistics examines the relationship between language and other domains.