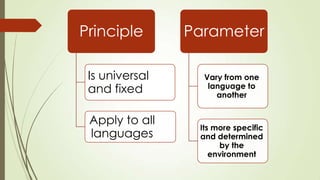
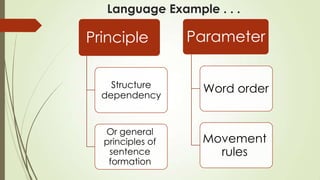
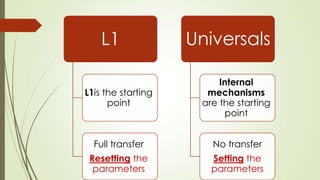
The document discusses key issues in Second Language Acquisition (SLA) focusing on the initial state that L2 learners bring to the acquisition process. It presents two basic positions: one where learners transfer all properties of their first language (L1) to the task, and another where they start with universal language principles without any L1 influence. The prevailing view in the literature supports the notion of L1 as the initial state, indicating a common agreement on the importance of L1 properties in SLA.