1. The document discusses the typical stages of first language acquisition in children from 0-30 months. These stages include pretalking, babbling, holophrastic, two-word, and telegraphic stages.
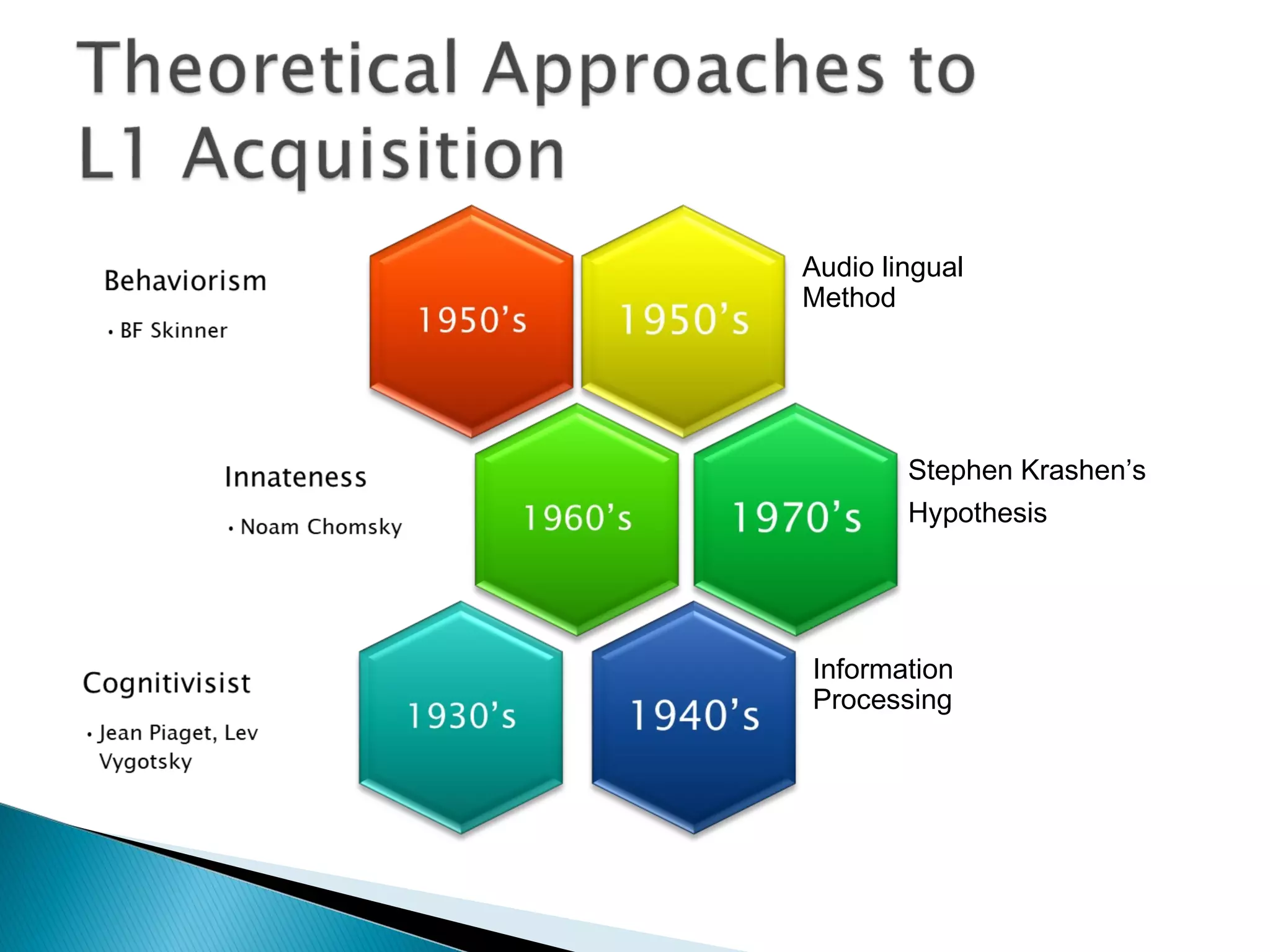
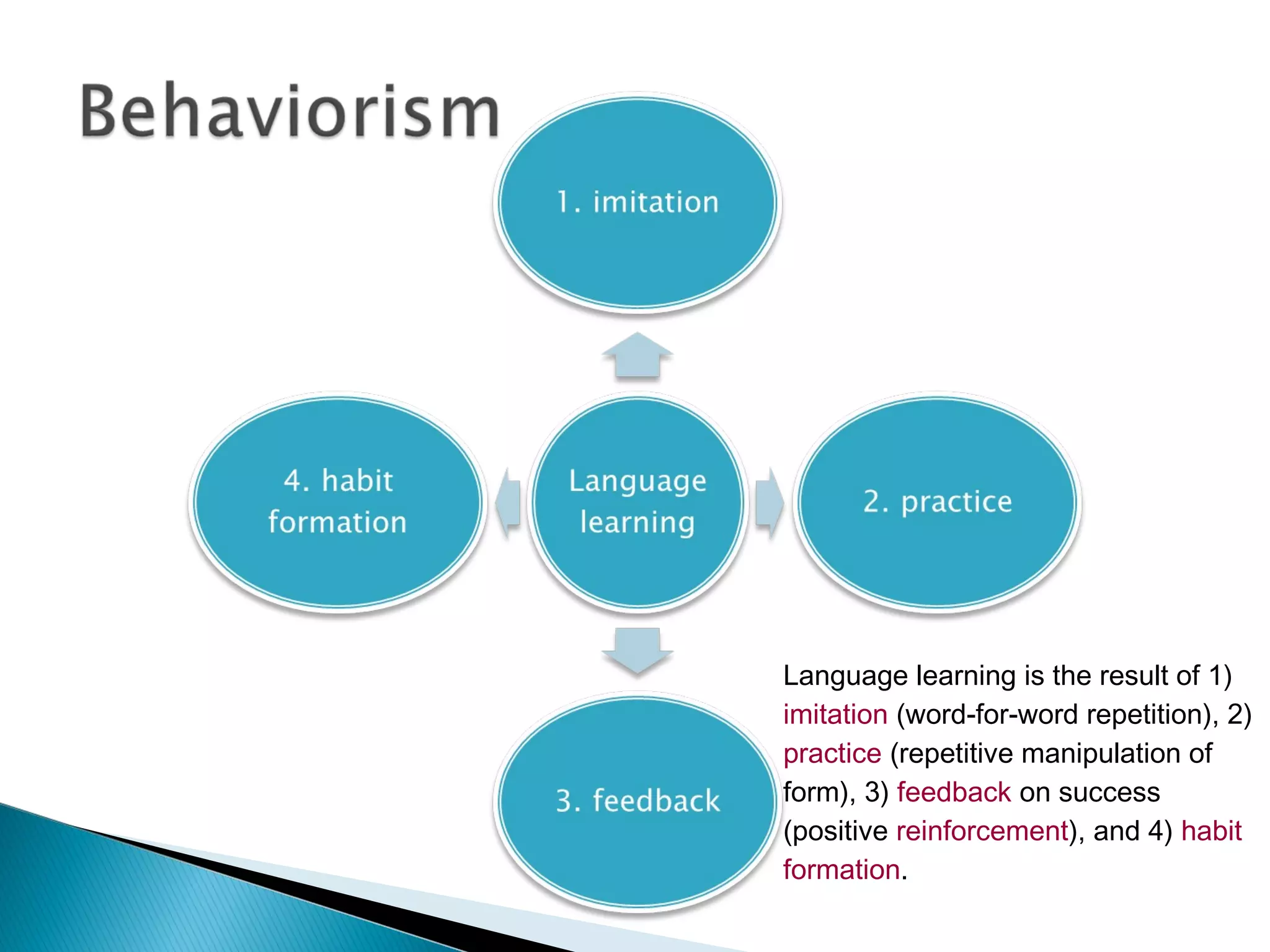
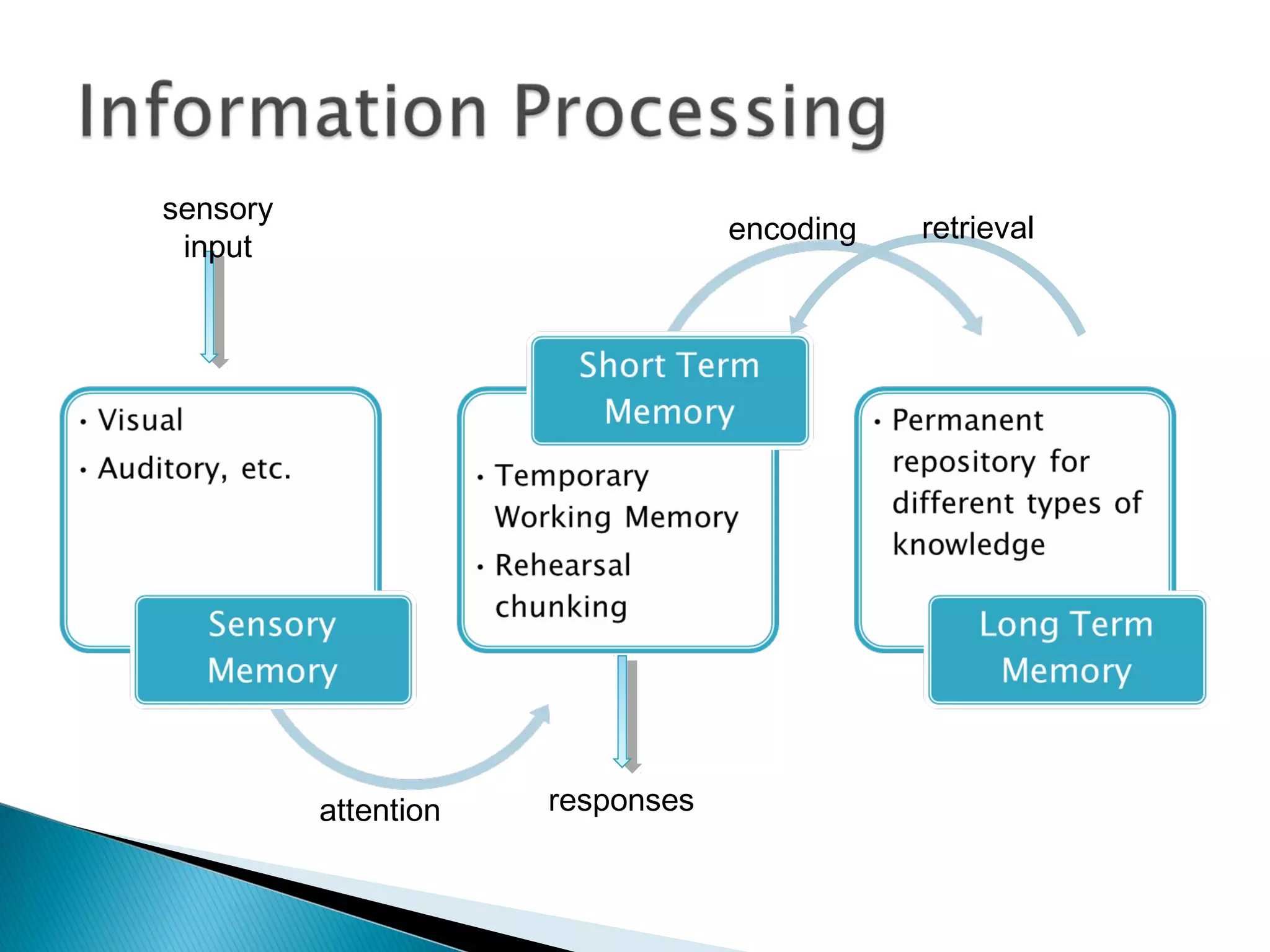
2. It also covers several theories of language learning including the audio-lingual method, information processing theory, Chomsky's theory of Universal Grammar and the Language Acquisition Device, Piaget's theory on cognitive development and language, and Vygotsky's sociocultural theory.
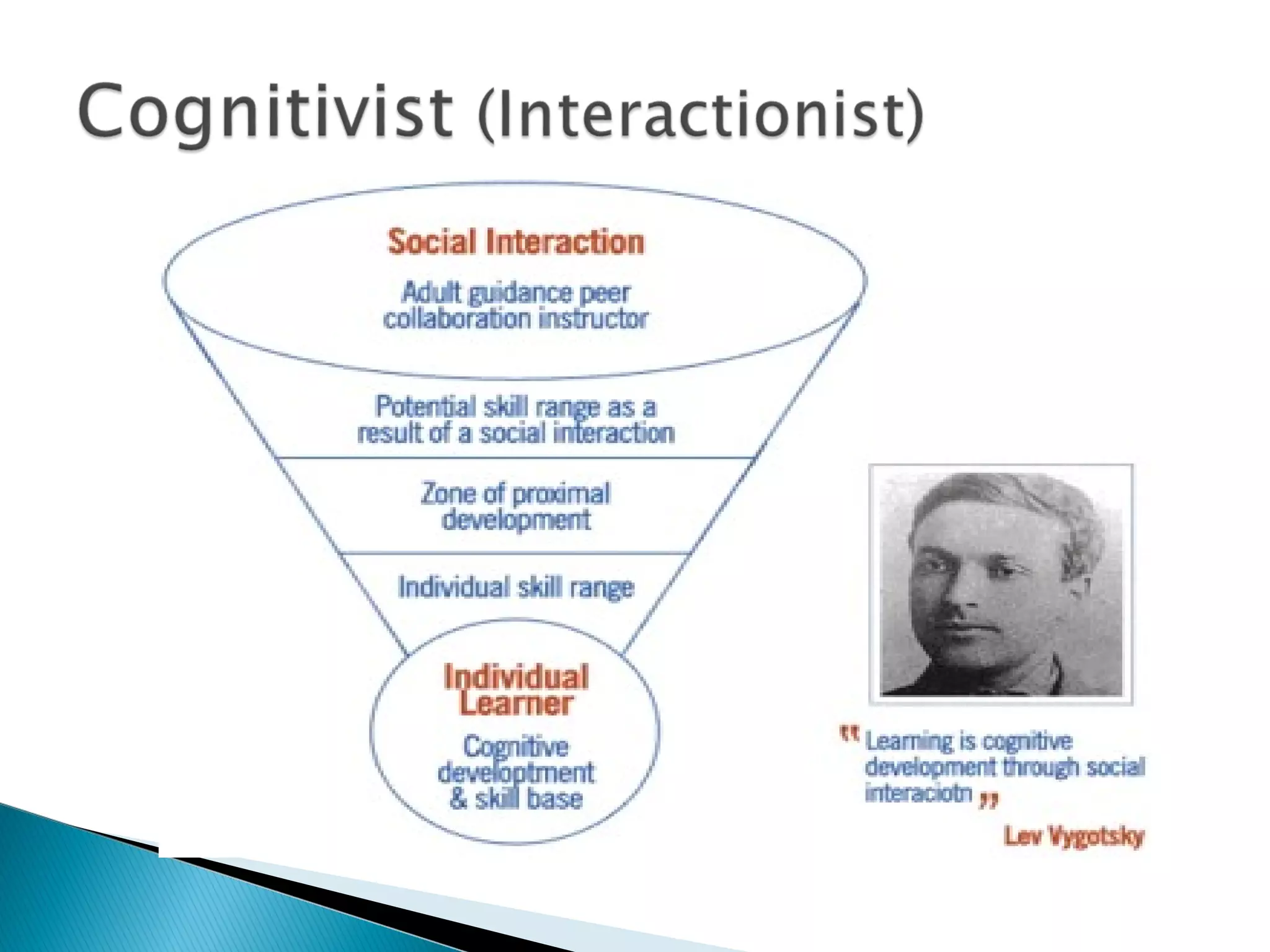
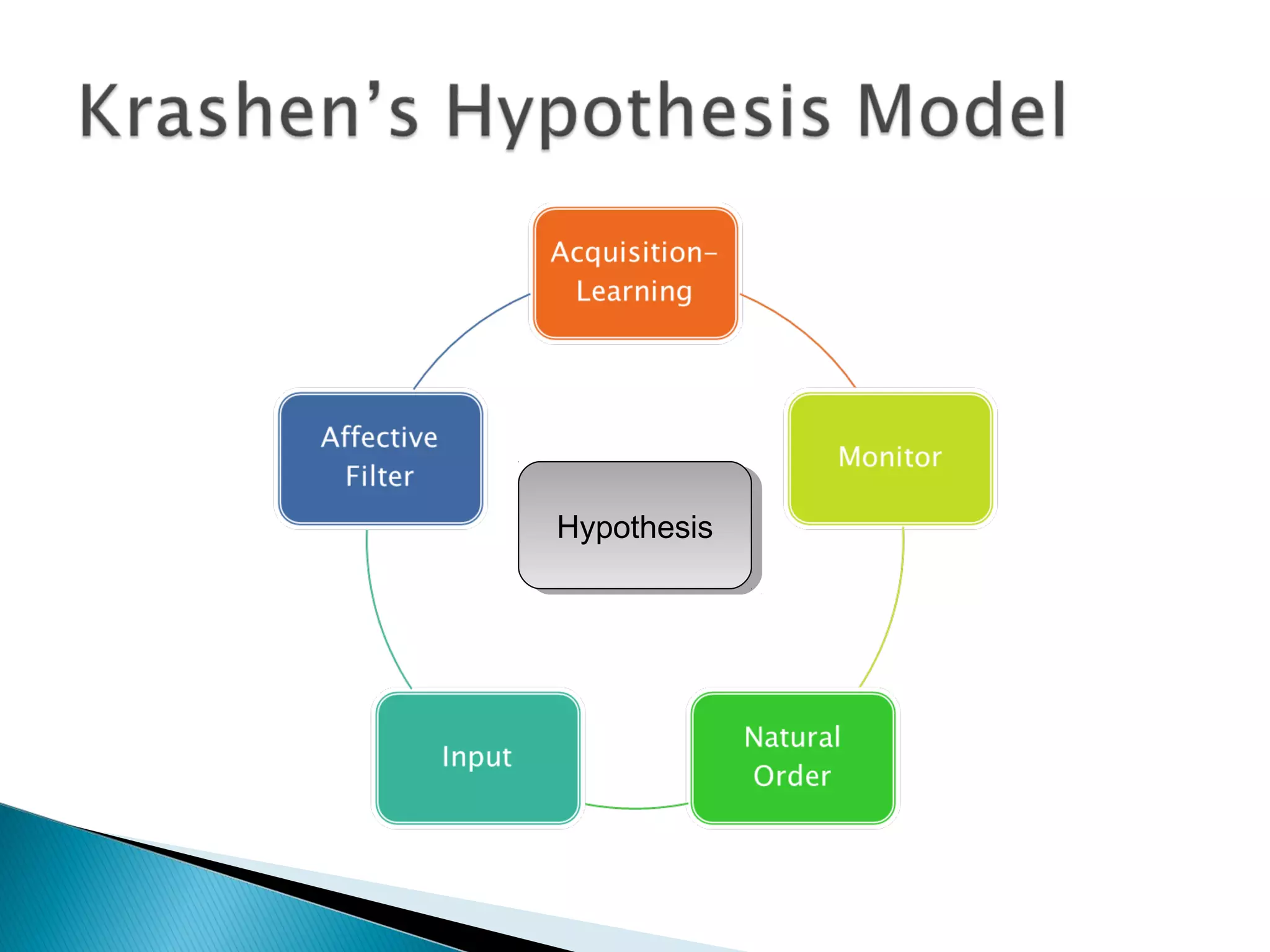
3. Key language learning theories discussed are Krashen's Input Hypothesis, Chomsky's theory of Universal Grammar, Piaget's view of language development depending on cognitive development, and Vygotsky's