The document discusses several theories of first language acquisition:
1) Behavioral approaches focus on observable responses and reinforcement/punishment, while the nativist approach sees language acquisition as innate with a language acquisition device.
2) The functional approach views language as a tool for interacting with the world and communicating socially.
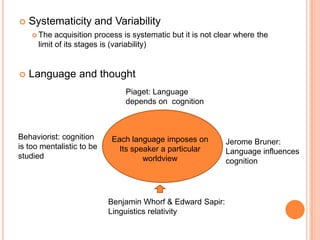
3) Issues in acquisition include the interplay between nature and nurture, universals versus variability across languages, and the influence of language on thought and cognition.