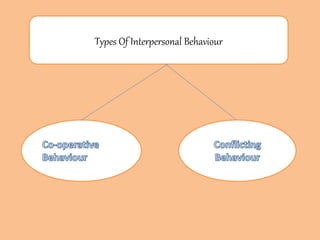
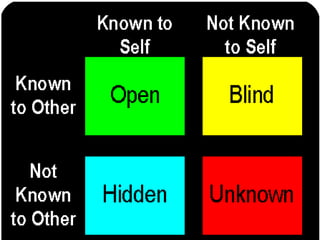
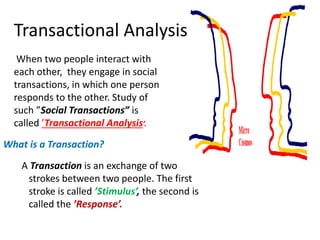
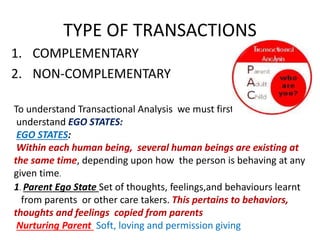
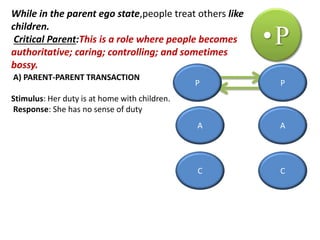
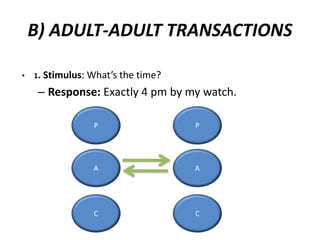
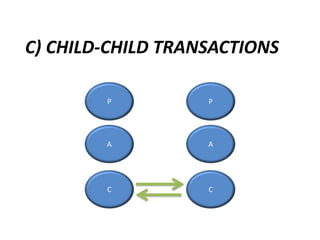
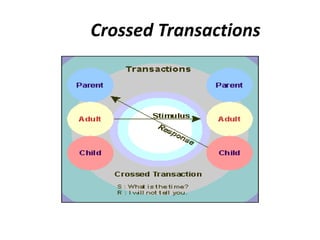
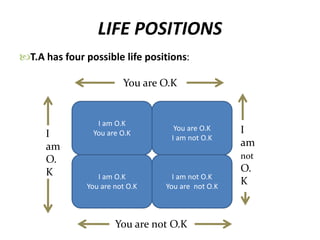
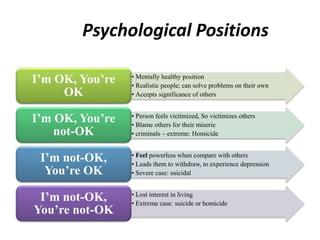
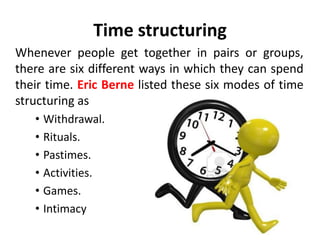
This document provides an overview of interpersonal behavior and transactional analysis. It discusses that interpersonal behavior is shaped by communication skills, emotional intelligence, and social skills. It then explains the Johari window model and how it can help people understand their interpersonal relationships and communication. Transactional analysis is introduced as the study of social transactions between people in terms of stimulus and response. The concepts of ego states, life positions, strokes, script analysis, and time structuring are defined in transactional analysis. Advantages of using transactional analysis to improve interpersonal communication are also highlighted.