SIFT extracts distinctive invariant features from images to enable object recognition despite variations in scale, rotation, and illumination. The algorithm involves:
1) Constructing scale-space images from differences of Gaussians to identify keypoints.
2) Detecting stable local extrema across scales as candidate keypoints.
3) Filtering out low contrast keypoints and those poorly localized along edges.
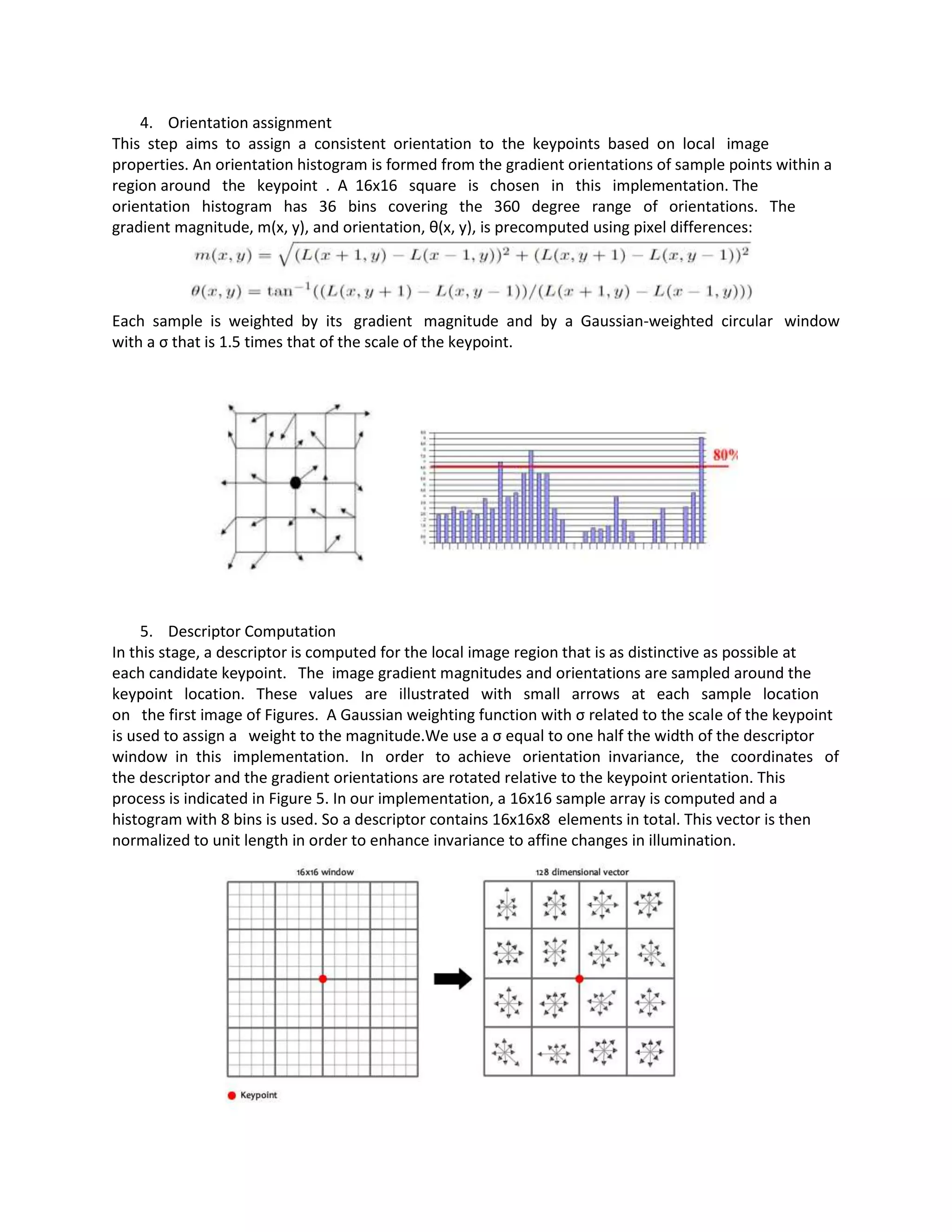
4) Assigning orientations based on local gradient directions.
5) Computing descriptors by sampling gradients around keypoints for matching between images.

![2. Extrema detection
This stage is to find the extrema points in the DOG pyramid. T o detect the local
maxima and minima of D(x, y , σ), each point is compared with the pixels of all its 26
neighbours . If this value is the minimum or maximum this point is an extrema.
3. Noise Elimination
This stage attempts to eliminate some points from the candidate list of keypoints by
finding those that have low contrast or are poorly localised on an edge.[1]. The value of the
keypoint in the DoG pyramid at the extrema is given by:
If the function value at z is below a threshold value this point is excluded.
T o eliminate poorly localized extrema we use the fact that in these cases there is a
large principle curvature across the edge but a small curvature in the perpendicular
direction in the difference of Gaussian function. A 2x2 Hessian matrix, H, computed at the
location and scale of the keypoint is used to find the curvature. With these fomulas,
the ratio of principal curvature can be checked efficiently .
Tr (H) = Dxx + Dyy
Det(H) = DxxDyy - (Dxy )2
R=Tr(H)^2/Det(H)
Where r= ratio between small and large Eigen value.
So if inequality fails, the key point is removed from the candidate list.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intel-131220044044-phpapp01/75/Scale-Invariant-Feature-Tranform-2-2048.jpg)