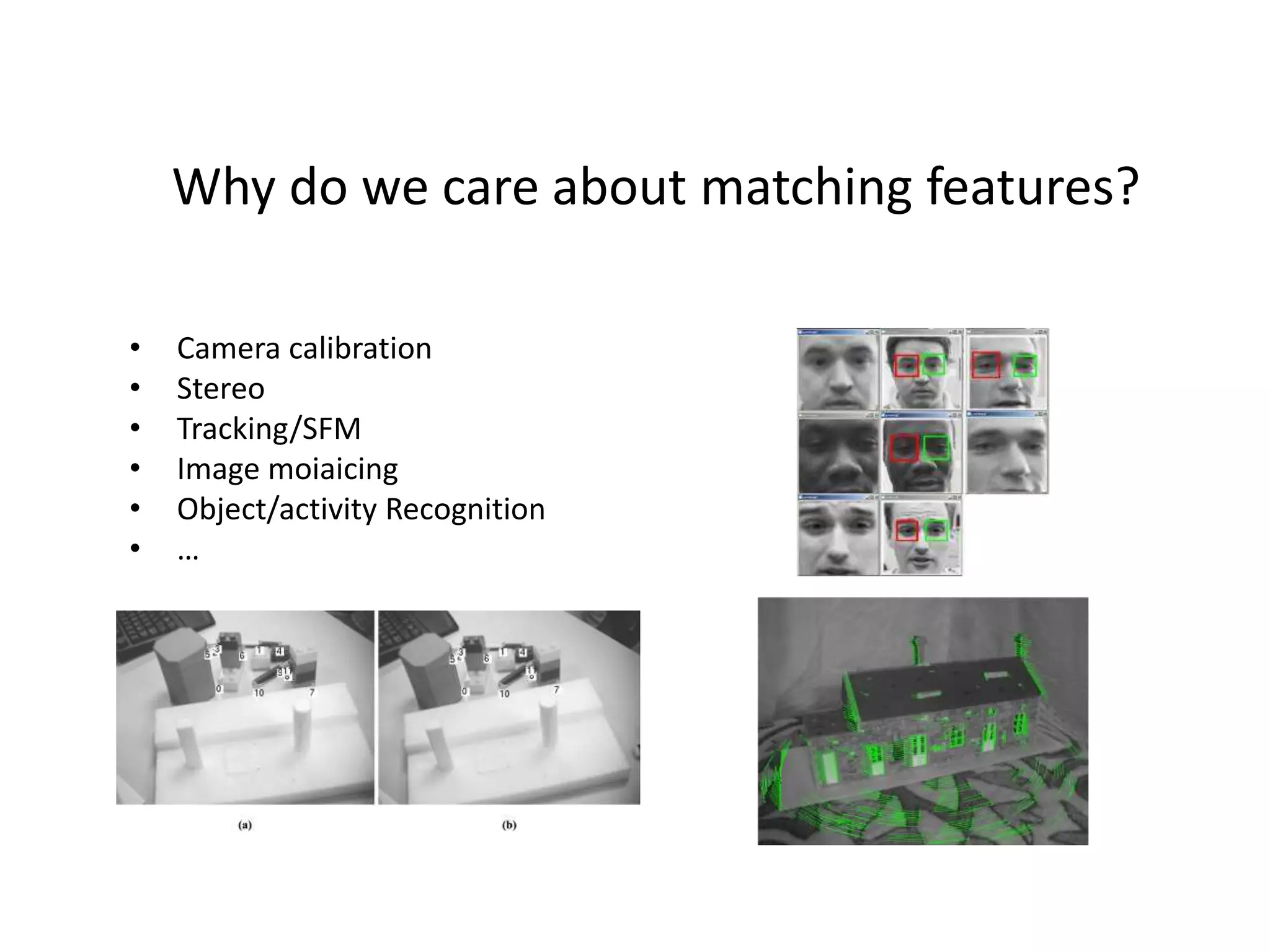
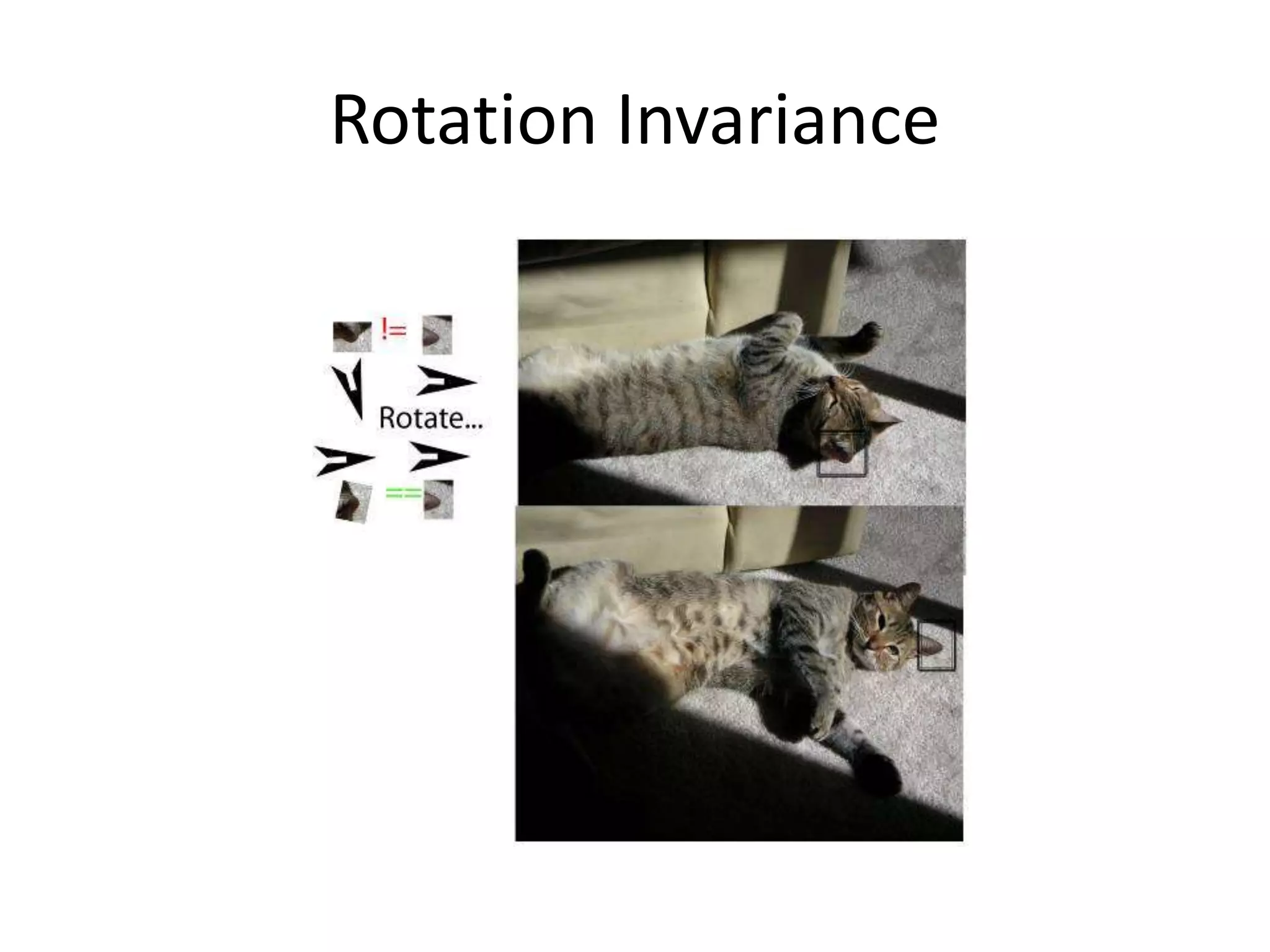
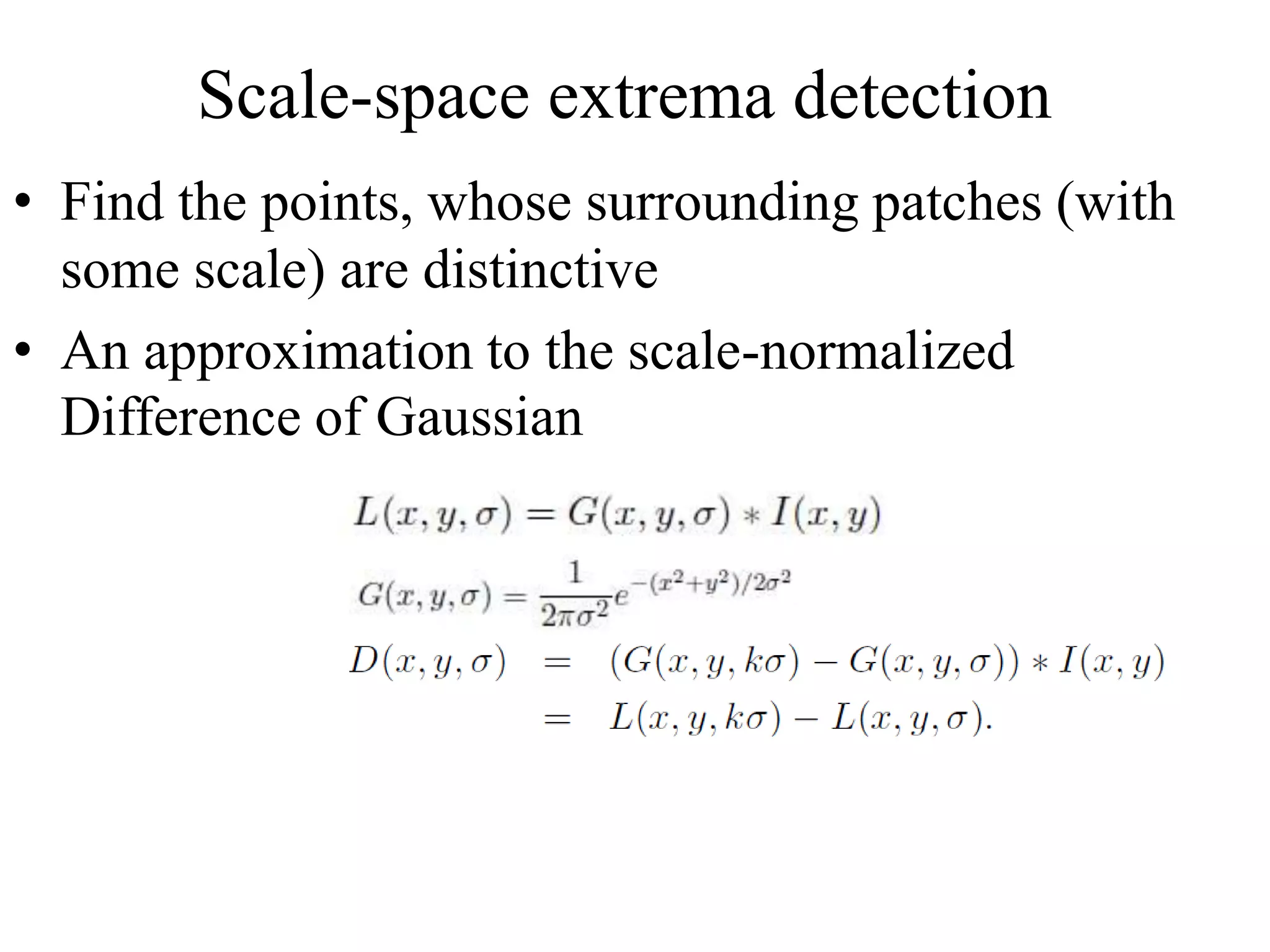
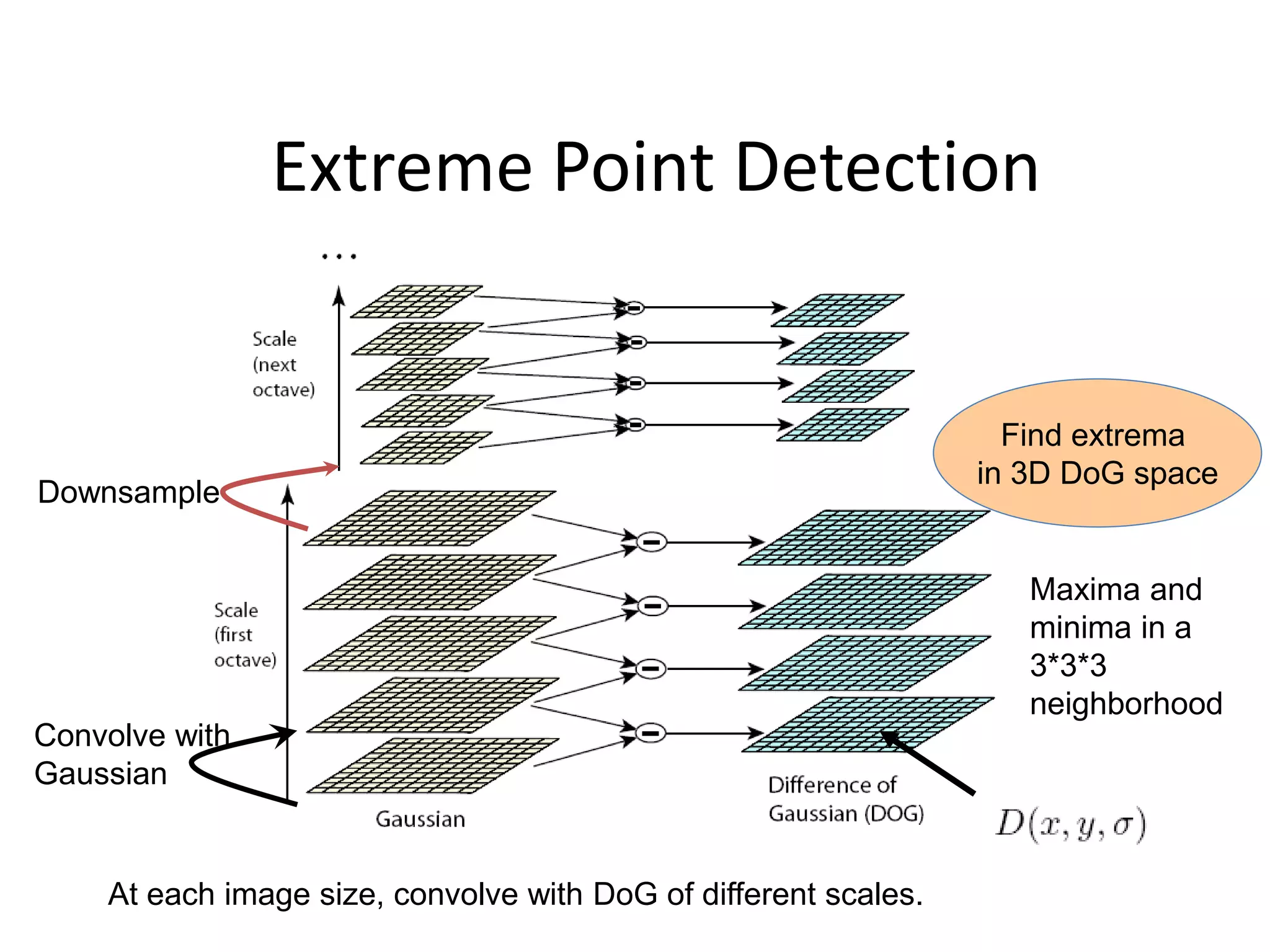
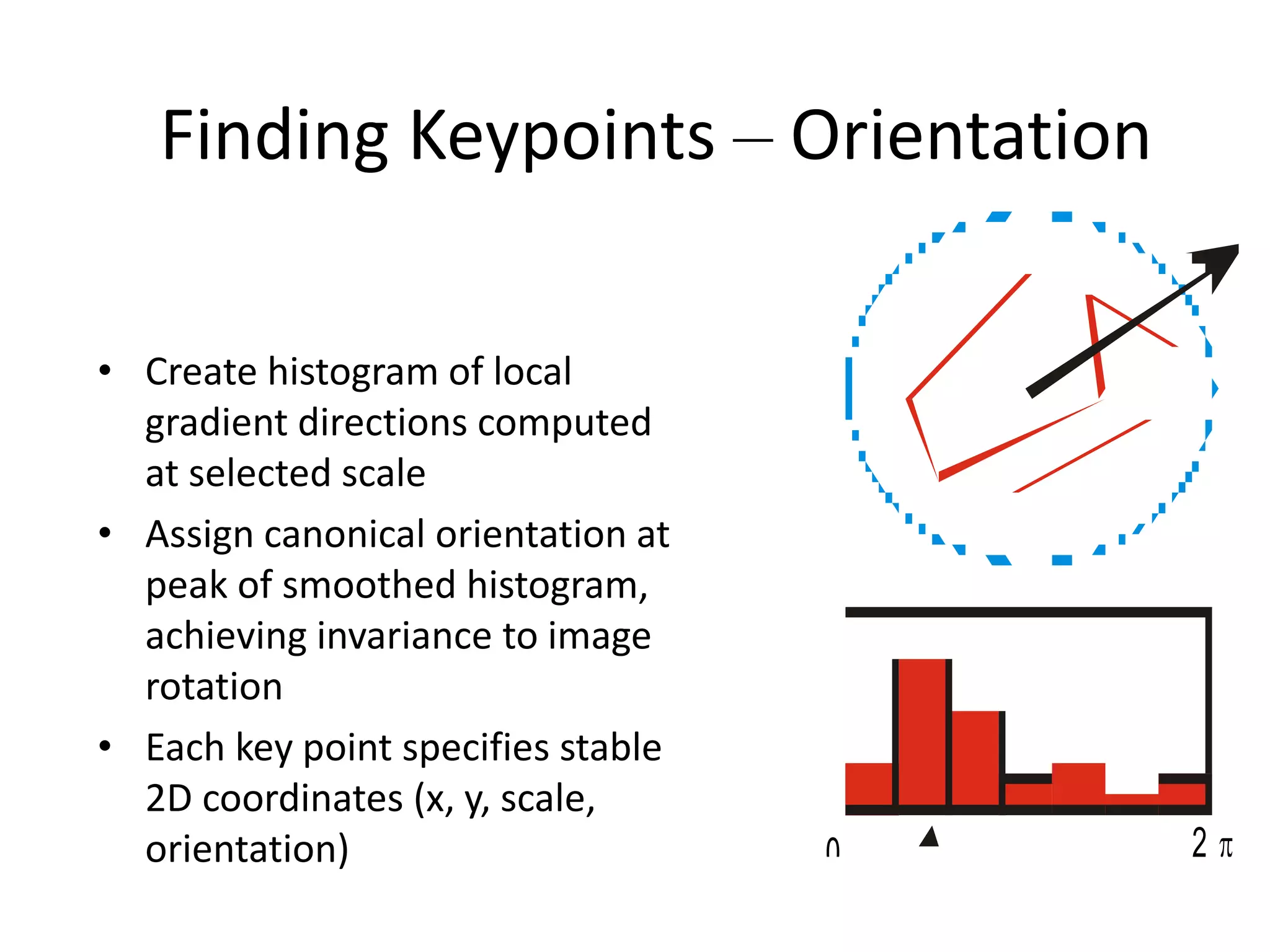
SIFT extracts scale and rotation invariant features from images by using differences of Gaussians to identify keypoints and creating histograms of local gradients to describe keypoints. It achieves scale invariance through scale space analysis using Gaussian pyramids and difference of Gaussians, rotation invariance by assigning a consistent orientation to each keypoint based on local gradient histograms, and other invariances through the gradient-based descriptor. SIFT has been widely used for applications like image matching, object recognition and mosaicing due to its robustness to changes in scale, rotation, illumination and viewpoint.