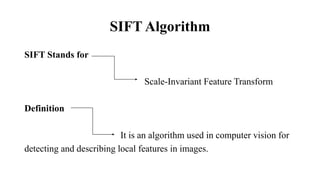
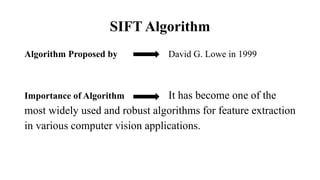
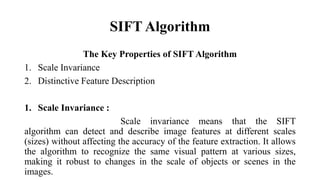
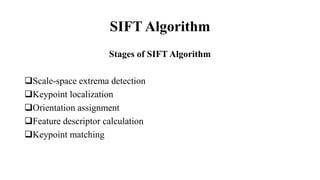
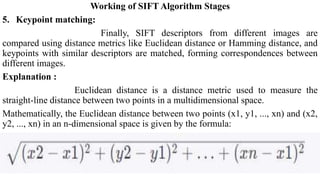
The document discusses the SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) algorithm. SIFT detects and describes local features in images to allow object recognition despite changes in scale, rotation, and illumination. It works by detecting keypoints, assigning orientations based on local image gradients, and generating descriptors of the gradients around each keypoint. Keypoints are matched between images by comparing their descriptors. SIFT has become widely used for tasks like object recognition, image stitching, and 3D reconstruction due to its robustness to transformations.