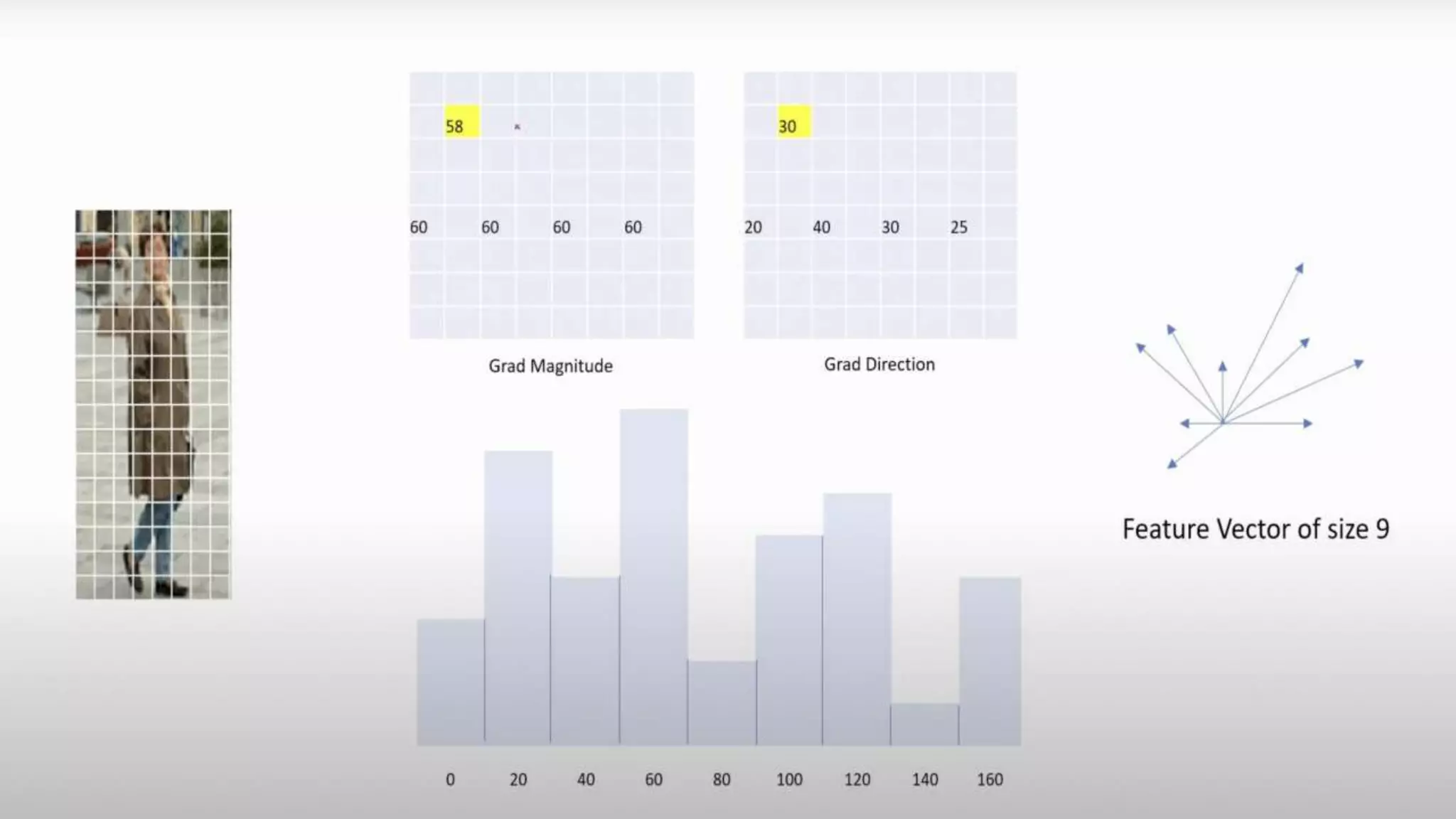
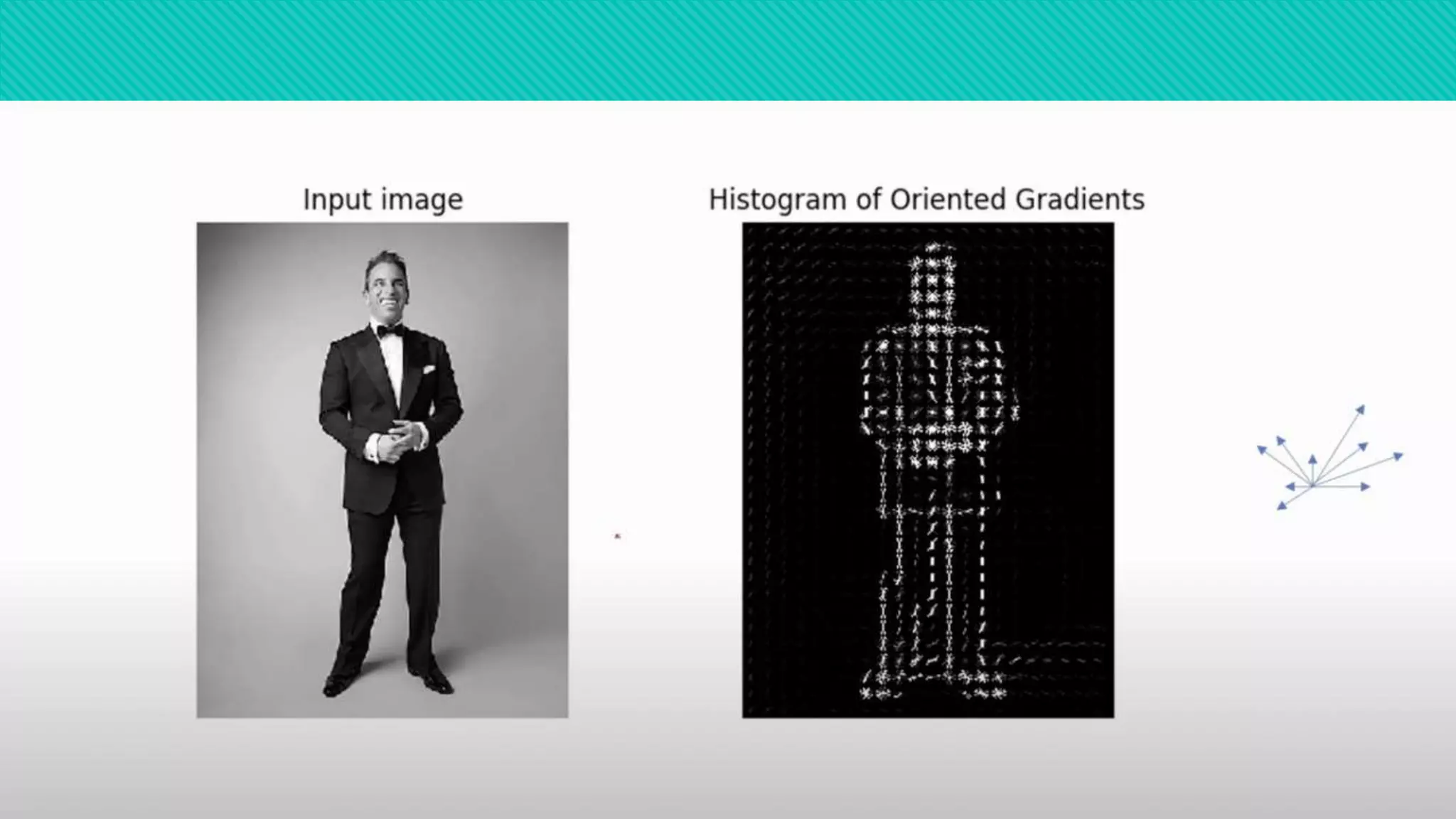
The document discusses two algorithms for object detection: HOG and SIFT.
HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients) focuses on the shape of an object by using the magnitude and direction of gradients to generate histograms and compute features. SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) describes local image areas by extracting invariant features to generate a set of key points for matching objects across different scales and rotations. Both algorithms can be used to detect objects by matching image features to trained models.