This workshop aims to help participants learn how to integrate technology into student-centered learning activities that promote higher-order thinking skills. Participants will explore free web-based tools and learn how to design project-based learning activities that support differentiated instruction. The workshop will cover topics like 21st century skills, essential questions, complex thinking strategies, and authentic assessment and will provide examples of how to enrich lesson plans to engage digital native students.
![Integrating Technology, Higher-Order Thinking, and Student-Centered Learning Doug Adams ALTEC [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hots-rcet-090303120045-phpapp01/75/Integrating-Technology-Higher-Order-Thinking-and-Student-Centered-Learning-1-2048.jpg)












![Visual Ranking and 21 st C Skills Intel’s Education Page http://intel.com/education K-12 Teaching Tools Visual Ranking Tool Click Student Log-In [email_address] Team ID Team Password](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hots-rcet-090303120045-phpapp01/75/Integrating-Technology-Higher-Order-Thinking-and-Student-Centered-Learning-17-2048.jpg)


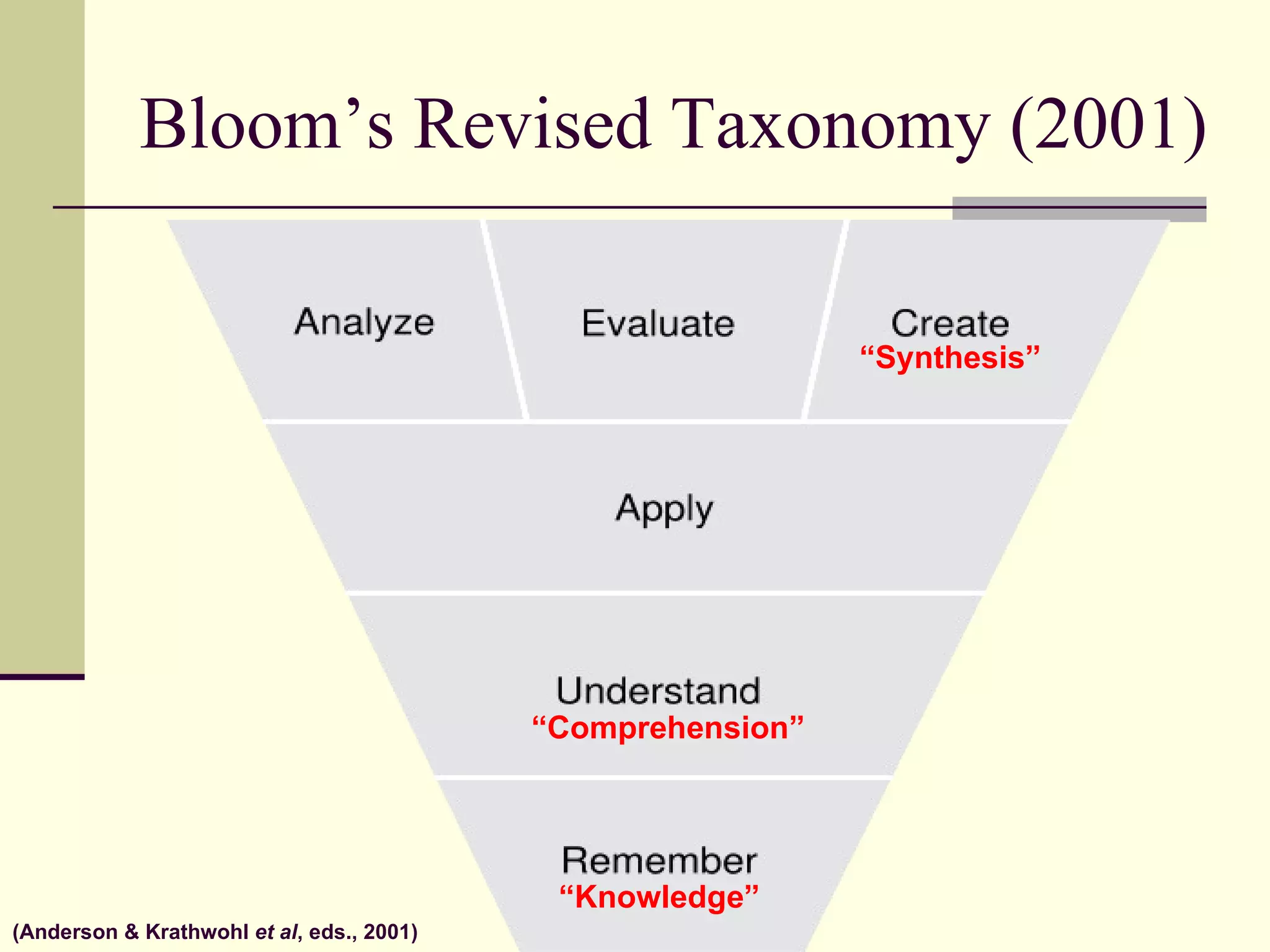


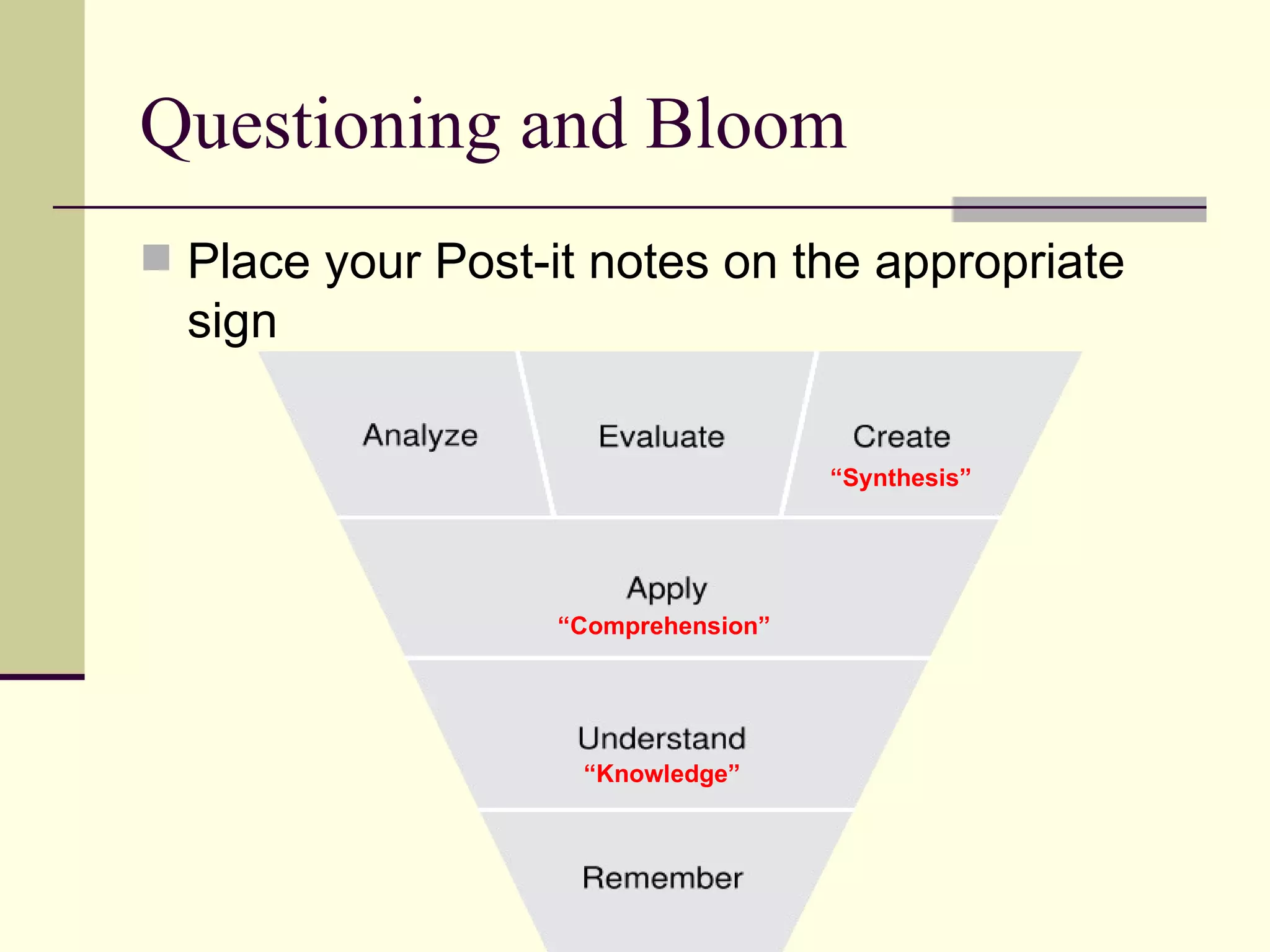









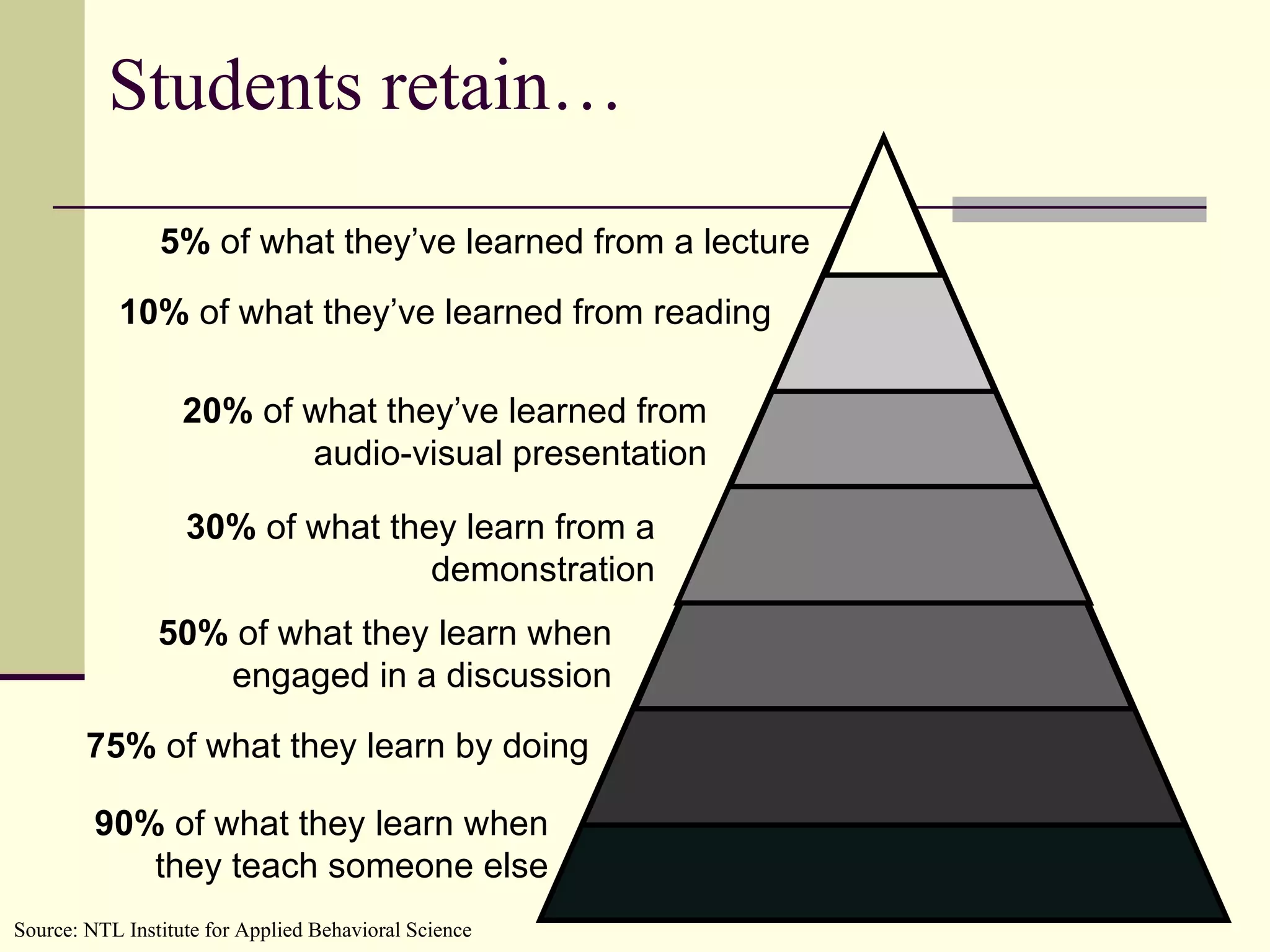









![Resources http://www.slideshare.net/dadams.altec http://dadams-altec.wetpaint.com Doug Adams [email_address] http:// altec.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hots-rcet-090303120045-phpapp01/75/Integrating-Technology-Higher-Order-Thinking-and-Student-Centered-Learning-48-2048.jpg)