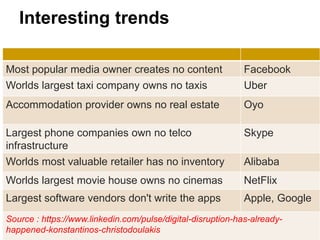
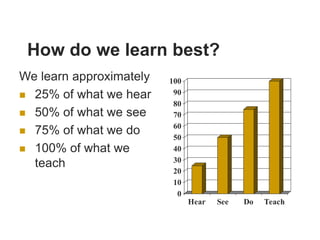
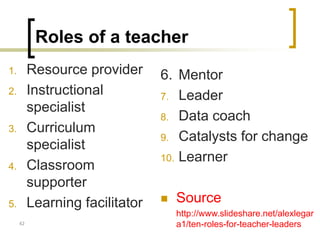
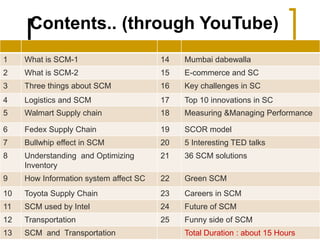
The document discusses pedagogical challenges in the digital environment. It notes that today's students are accustomed to digital devices and have short attention spans. This presents challenges for teachers who must compete with technology for students' attention. The digital environment also allows students more control over their learning in terms of time, place, path, and pace. Teachers now have a role as facilitators helping students convert knowledge into practice. They must use a variety of strategies and be digitally competent to engage Gen Y students. While technology provides opportunities, it also poses challenges as multiple modes of learning are now possible beyond just classroom teaching.












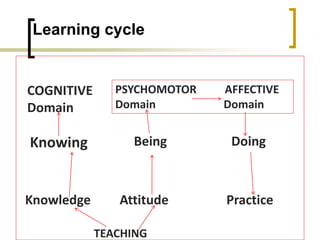
![Types of learning..
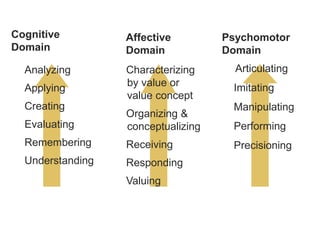
More than one type of learning through three
domains
Cognitive
Psychomotor
Affective
Bloom developed a taxonomy based on the
above..“Allows educators to evaluate learning of
students systematically [Bloom, 1994]”
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pedagogy-challenges-sgd-180311145818/85/Pedagogy-challenges-sgd-14-320.jpg)
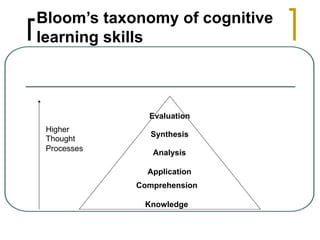


![Application to Engineering
Education
Creativity is very important for the engineering
profession [Goel, 2004]
Creativity requires higher thought processes (Bloom :items 4-
6: Analysis, Synthesis, Evaluation) [Felder et al., 2004]
In many cases lectures and homework assignments focus
exclusively on Bloom item 3: Application [Felder et al., 2004]
“Then, if they put a high-level question on exam and
the students do poorly on it, they blame the students’
lack of ability or poor study habits.”
Need to include high-level tasks in learning (educational)
objectives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pedagogy-challenges-sgd-180311145818/85/Pedagogy-challenges-sgd-21-320.jpg)

![Digital Learning ..1..
…. is "learning facilitated by technology that gives students
some element of control over time, place, path and/or
pace."[1]
[1] : Source : Definition from Digital Learning Now! and the Florida Virtual School.
Time: Learning is no longer restricted to the college day or
academic year. The Internet and a proliferation of Internet
access devices have given students the ability to learn
anytime.
Place: Learning is no longer restricted within the walls of a
classroom. The Internet and a proliferation of Internet
access devices have given students the ability to learn
anywhere and everywhere.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pedagogy-challenges-sgd-180311145818/85/Pedagogy-challenges-sgd-23-320.jpg)