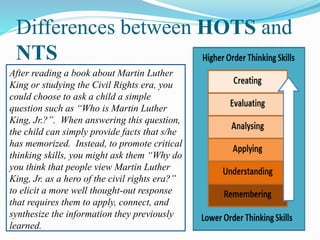
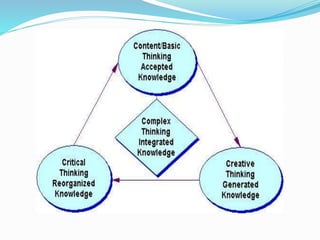
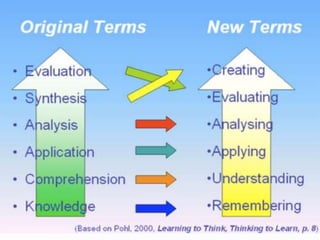
The document discusses higher order thinking skills (HOTS) such as critical thinking, problem solving, and creative thinking. It provides background on HOTS and strategies to develop them, including George Polya's problem solving process and Bloom's Taxonomy of learning domains. The document also discusses encouraging HOTS through questioning techniques, mind mapping, project-based learning, and the need to develop these skills for students to succeed in school and career.