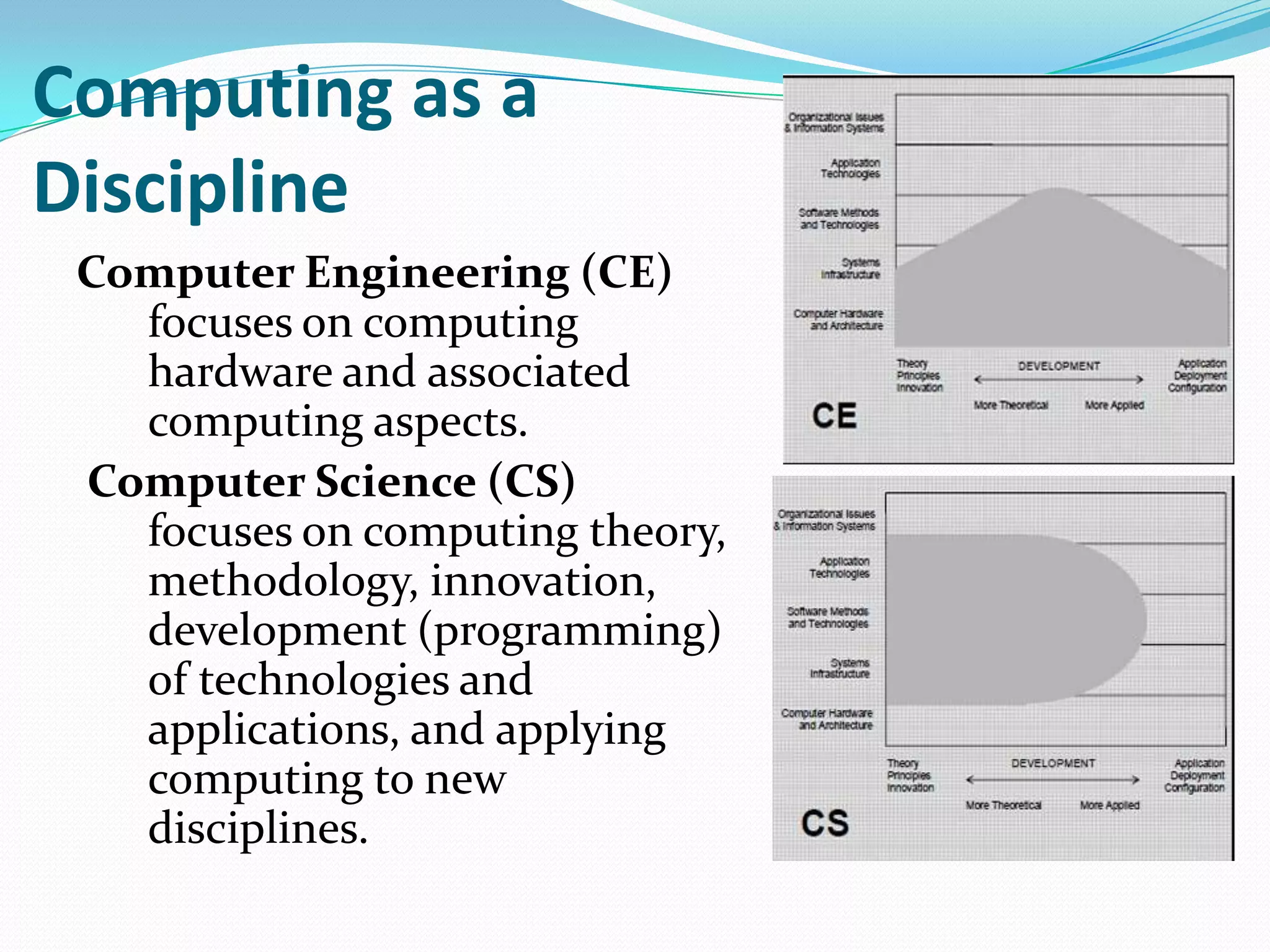
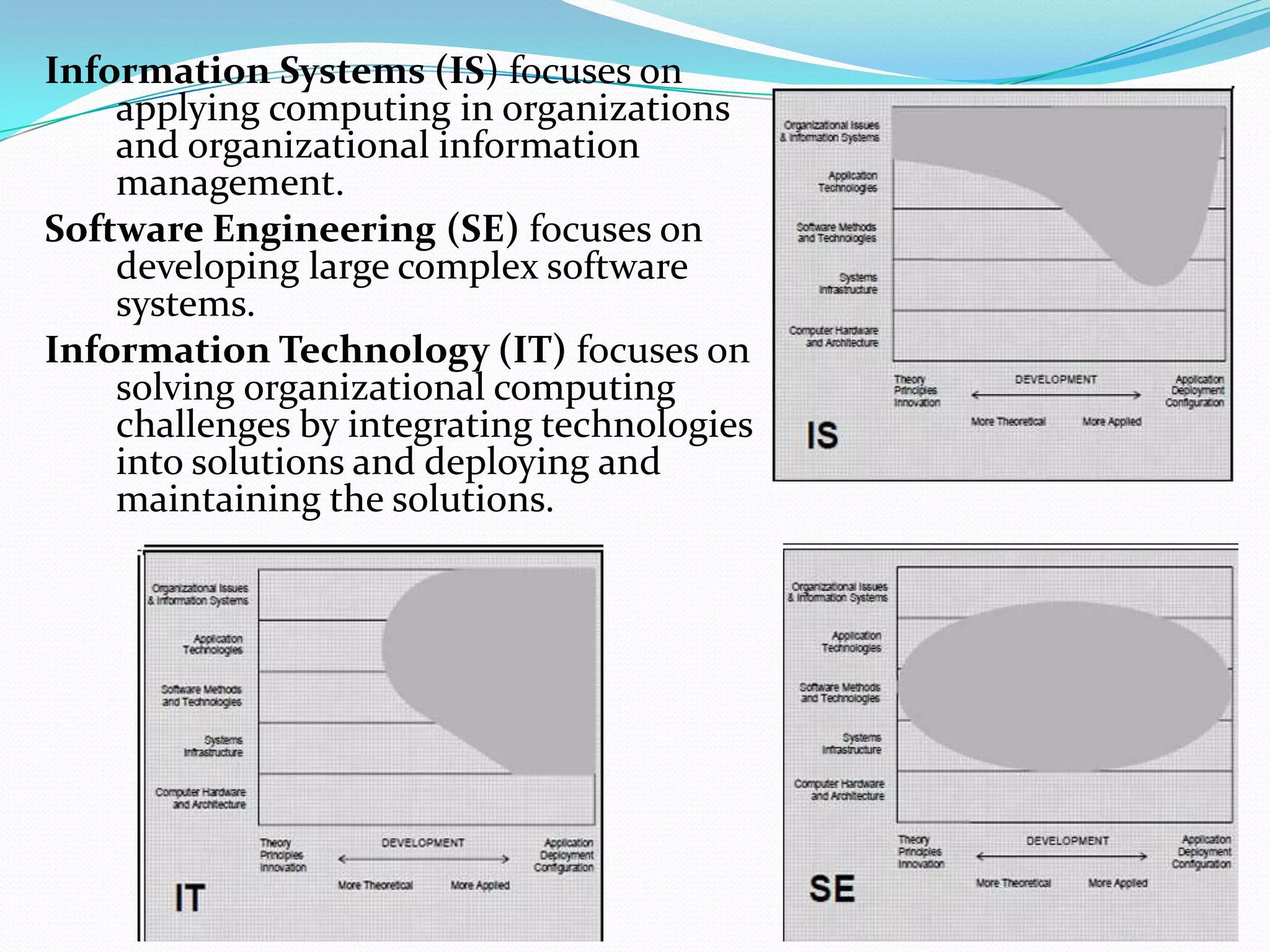
The document outlines the importance of computer science education and its various sub-disciplines, including computer engineering, software engineering, and information technology. It highlights five critical reasons for learning computer science, emphasizing algorithmic thinking, creativity, empowerment, preparation for the future, and collaboration. Additionally, it provides pedagogical guidelines for teaching computer science effectively, addressing the knowledge, skills, and strategies required for educators in this field.