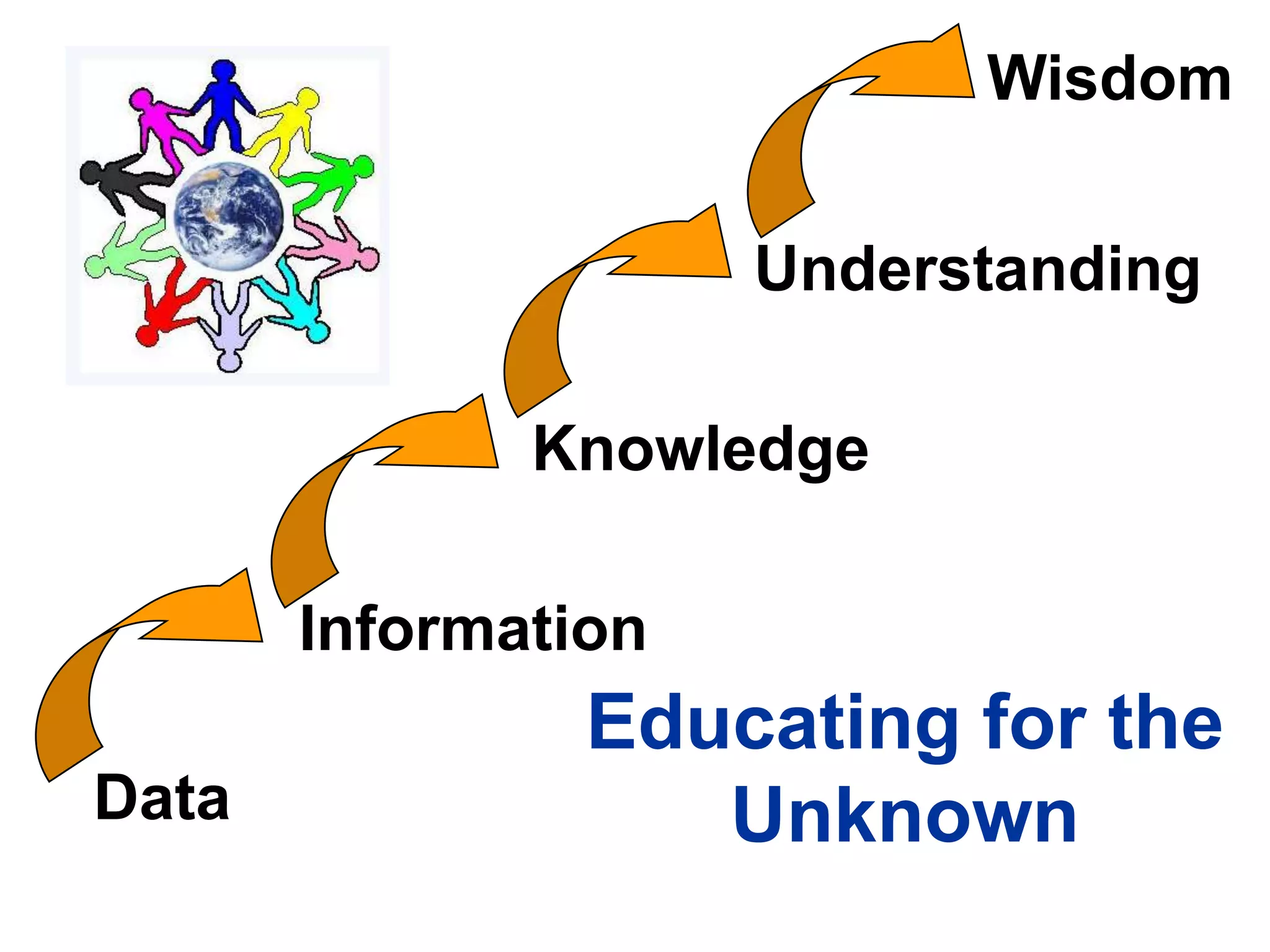
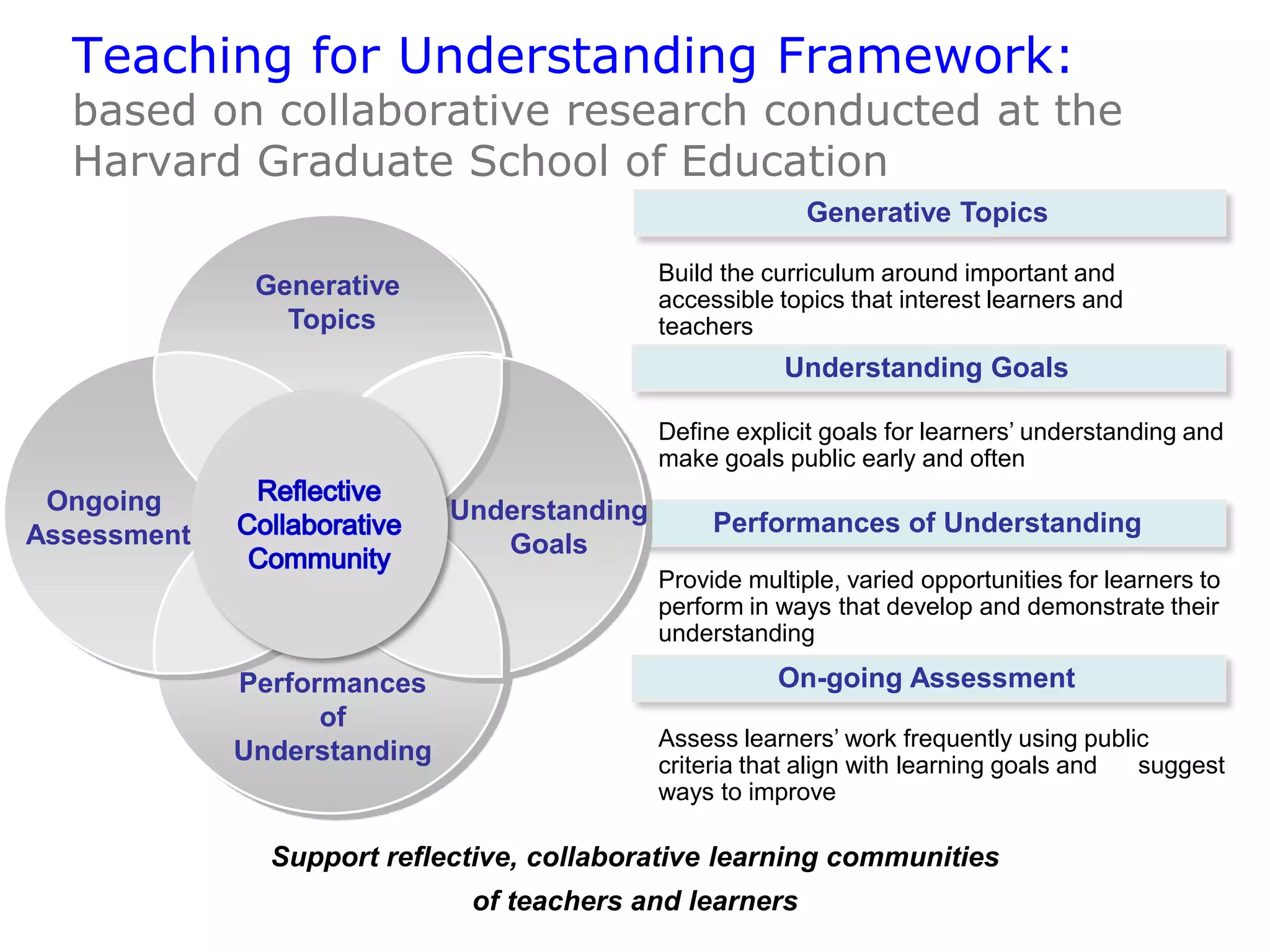
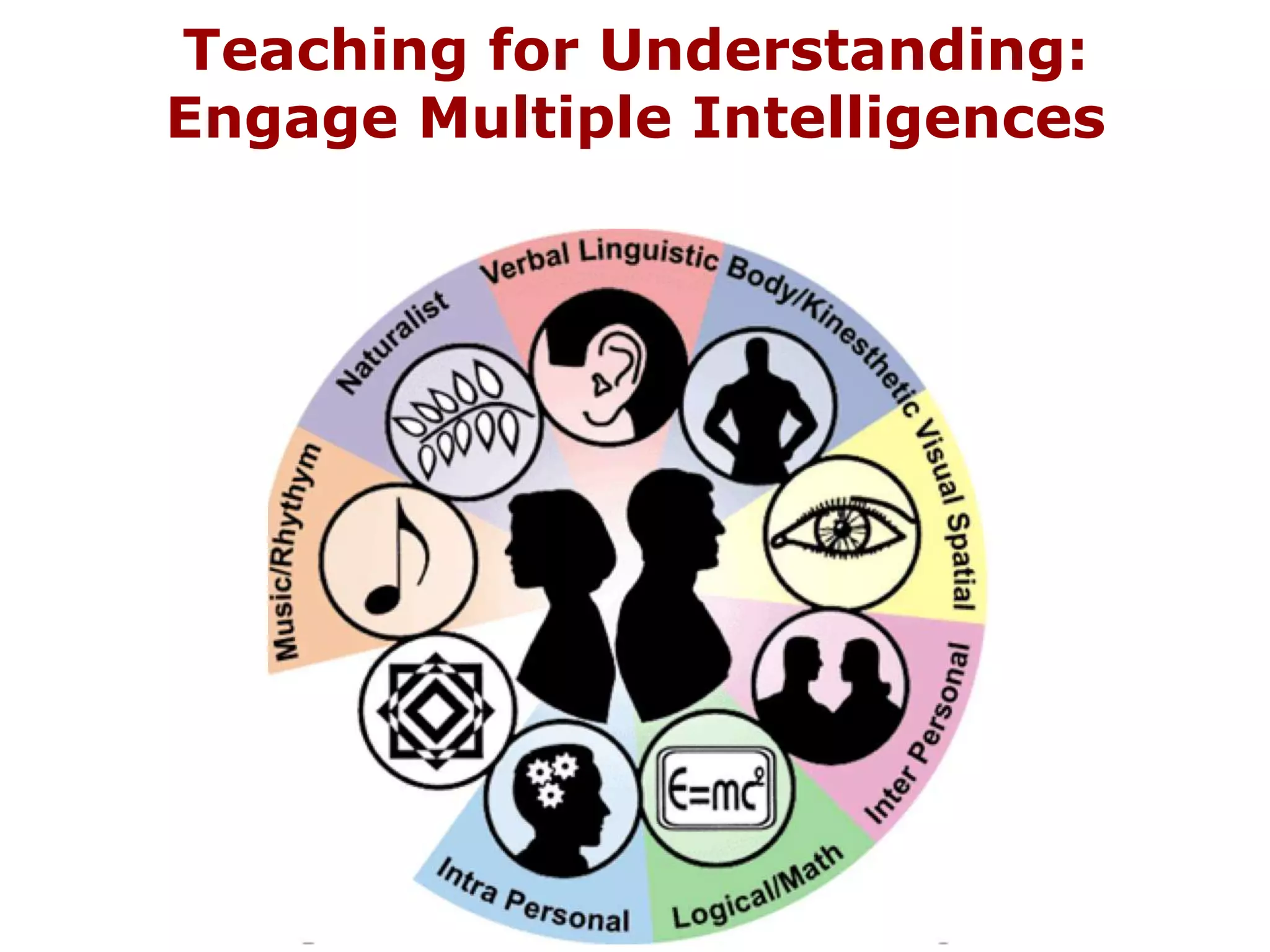
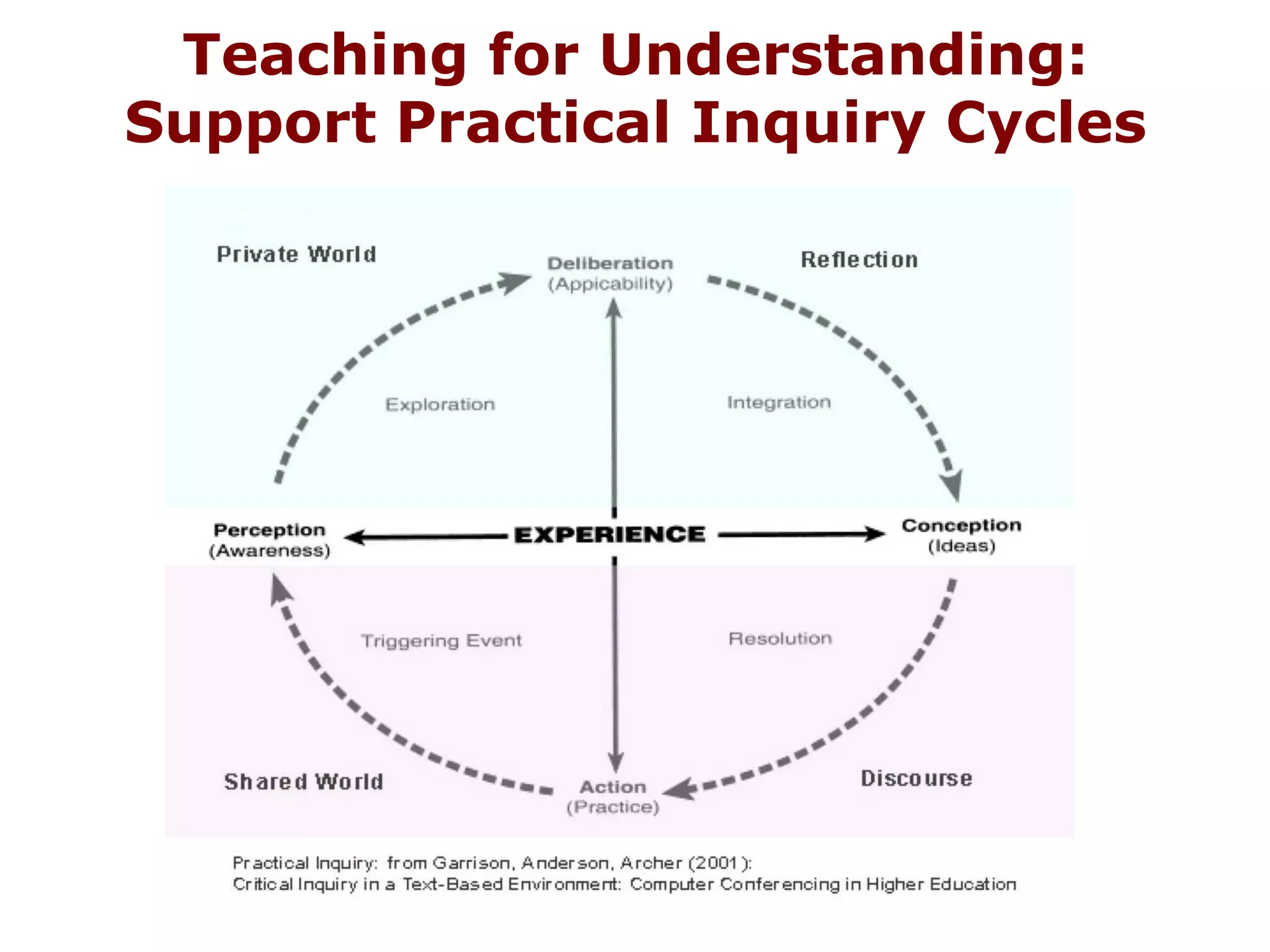
The document discusses the concept of 'teaching for understanding', emphasizing the importance of collaboration, ongoing assessment, and reflective learning communities. It contrasts traditional instruction, which focuses on knowledge transmission, with an approach that promotes understanding as a process of construction and application. Additionally, it outlines how ICT and e-learning can enhance this process by connecting learning to real life, supporting diverse learning pathways, and fostering continuous assessment and inquiry.