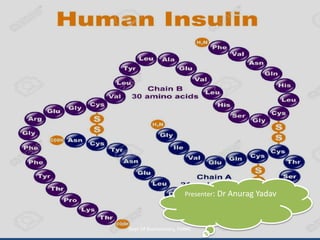
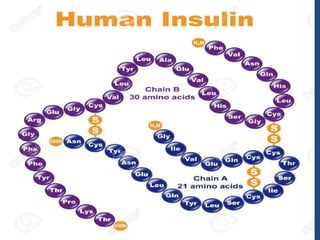
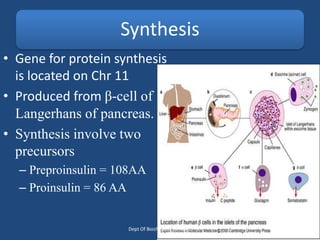
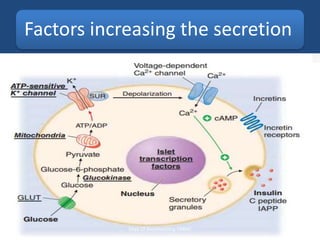
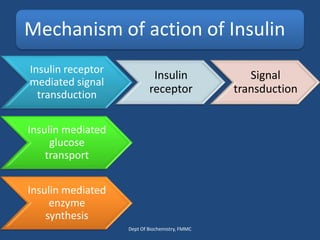
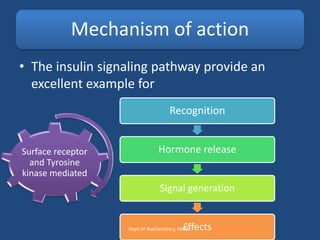
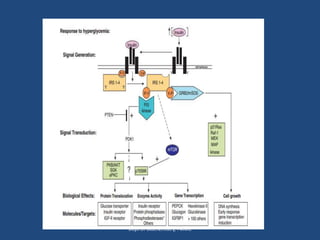
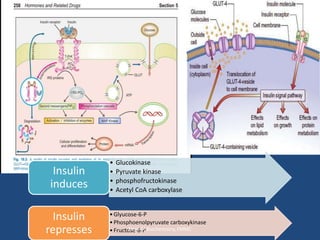
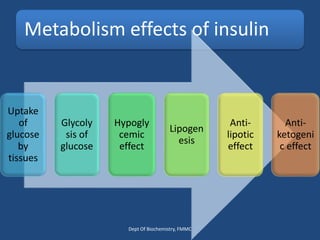
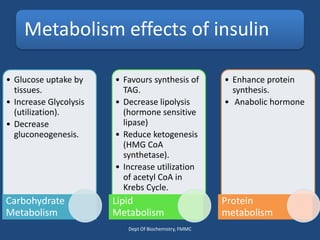
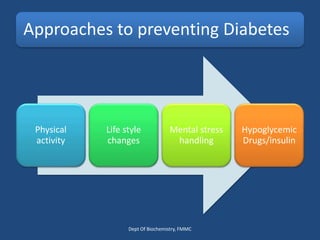
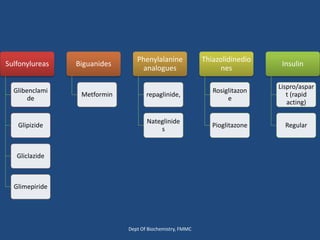
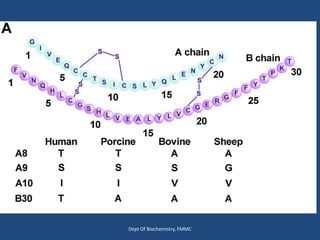
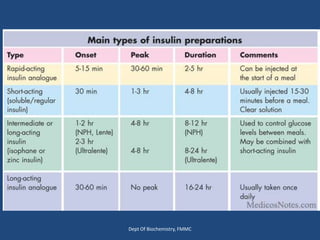
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the β-cells of the pancreas that plays a crucial role in metabolic processes, including the regulation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Its structure consists of 51 amino acids arranged in two chains, and various factors influence its secretion and action, impacting glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism. Disorders related to insulin include different types of diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance, with several diagnostic tests and treatment options available.