This document provides an overview of growth hormones including:
- Their structure, synthesis in the pituitary gland, regulation by hypothalamic hormones, and actions in the body.
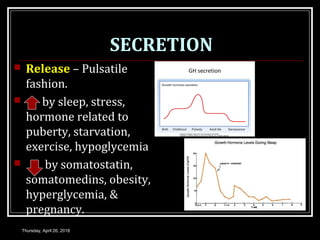
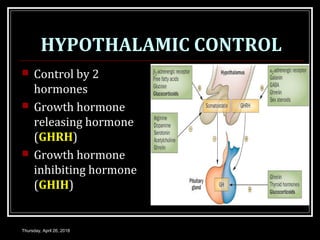
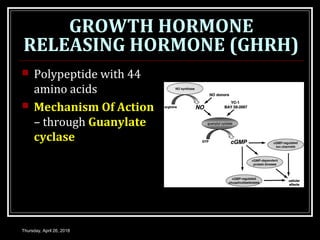
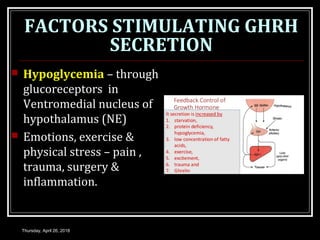
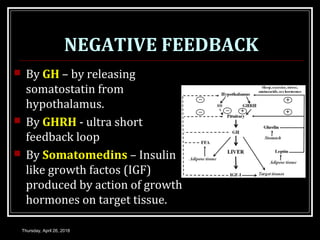
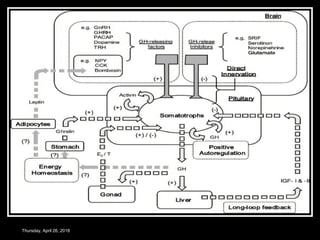
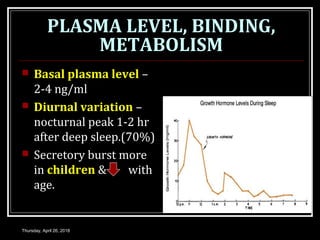
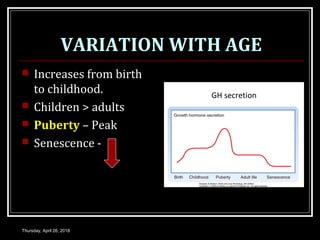
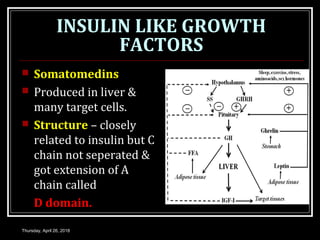
- Growth hormones are released in a pulsatile fashion and stimulate growth and metabolism. Their levels are regulated by hormones like growth hormone releasing hormone and growth hormone inhibiting hormone.
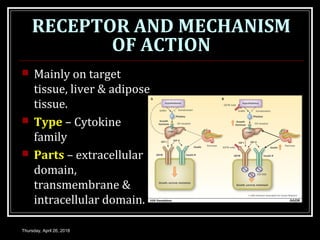
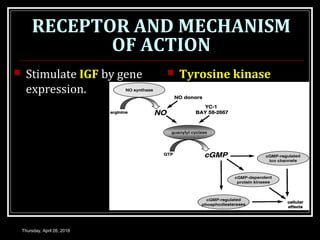
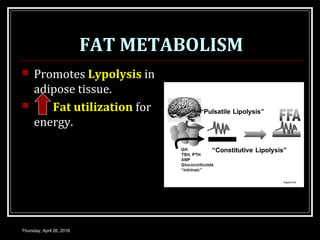
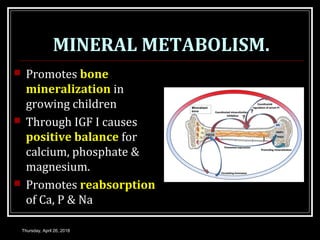
- Growth hormones stimulate the production of insulin-like growth factors and have effects like promoting bone and tissue growth, increasing protein synthesis and fat metabolism, and enhancing milk production.
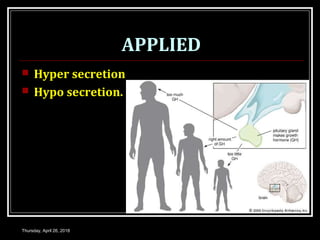
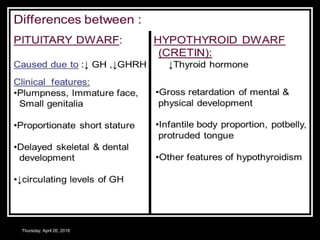
- Abnormalities in growth hormone levels can cause conditions like gigantism, acromegaly, and dwarfism.