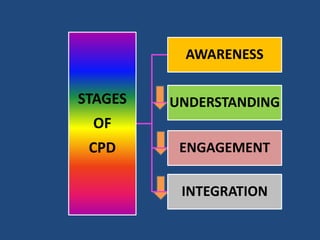
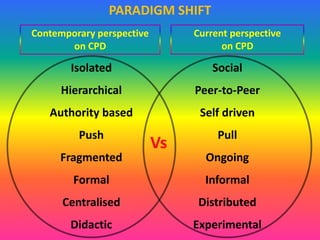
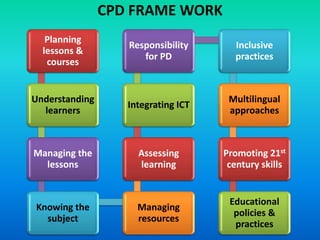
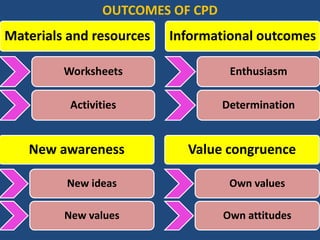
The document discusses the significance and practices of Continuing Professional Development (CPD) for teachers, highlighting its role in enhancing educational quality. It outlines various methods of CPD, including self-study, peer observation, and professional learning communities, emphasizing the importance of collaborative and informal learning. Ultimately, the document argues that effective CPD leads to improved teacher quality, which positively impacts student learning outcomes.