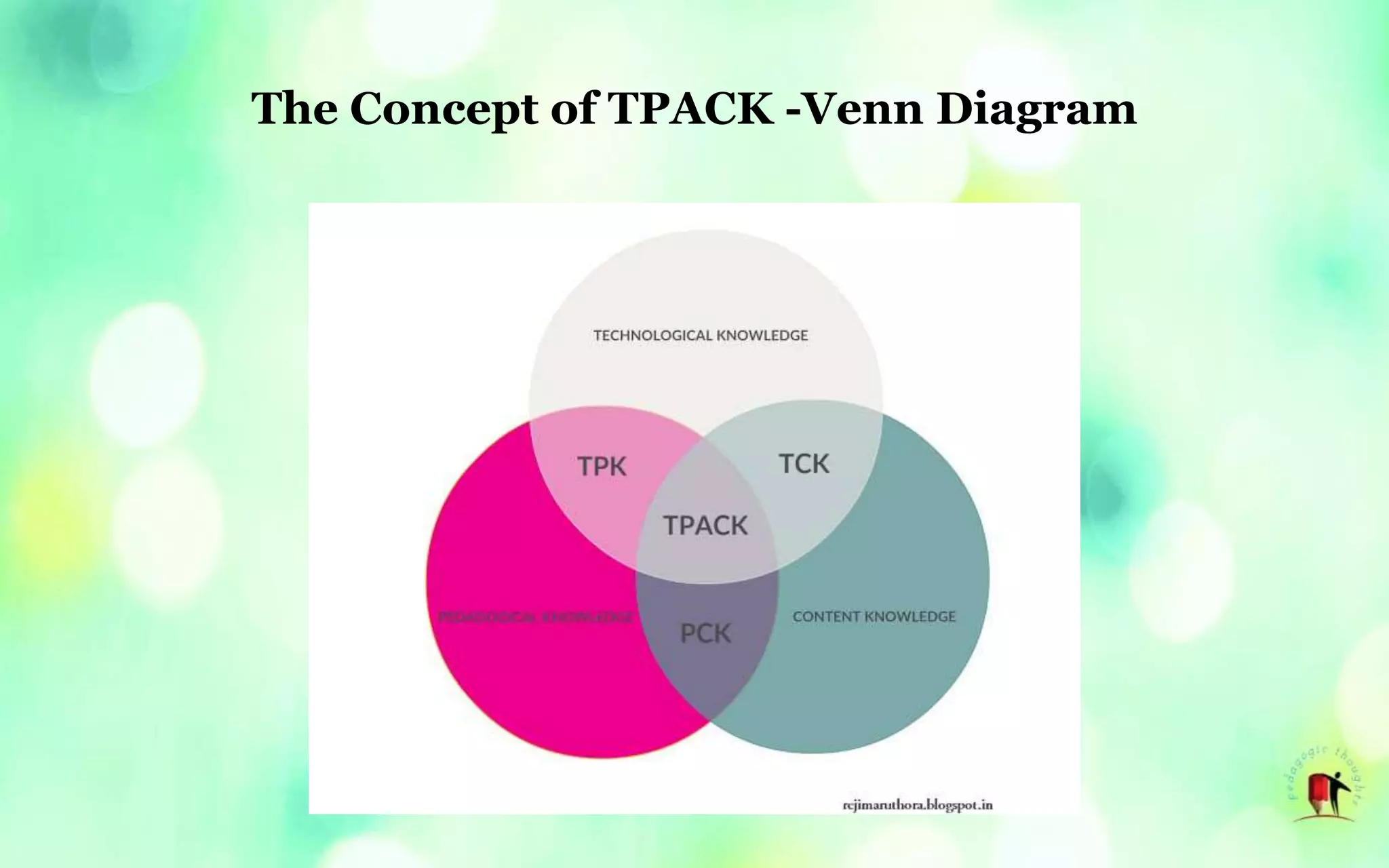
The document discusses the importance of teachers developing techno-pedagogical skills and competencies in the 21st century. It defines key concepts like techno-pedagogy, technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK), and the skills needed by teachers to effectively integrate technology into their teaching practice. TPACK provides a framework to understand the types of knowledge needed for technology-enhanced learning and the interplay between technological knowledge, pedagogical knowledge, and content knowledge.