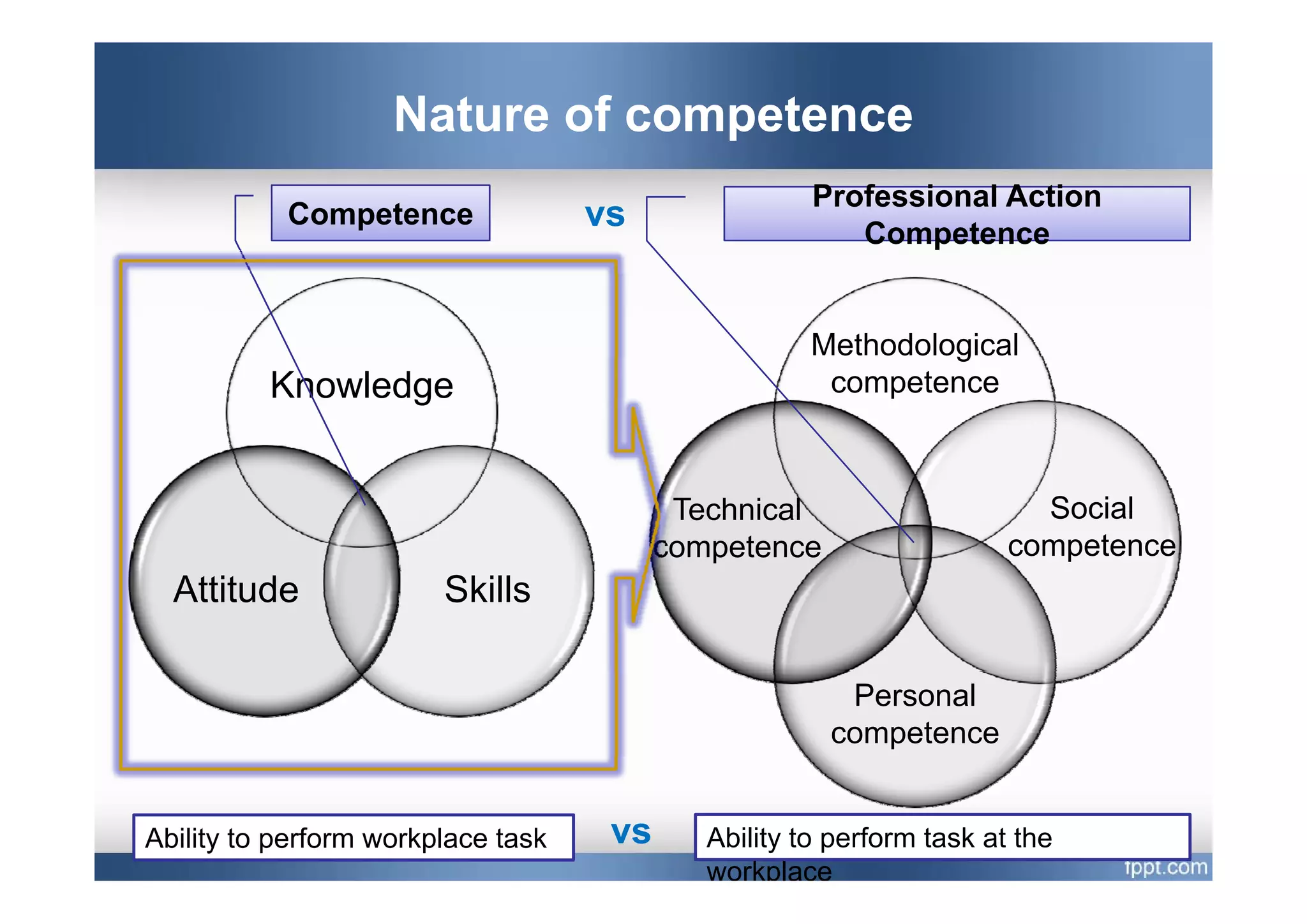
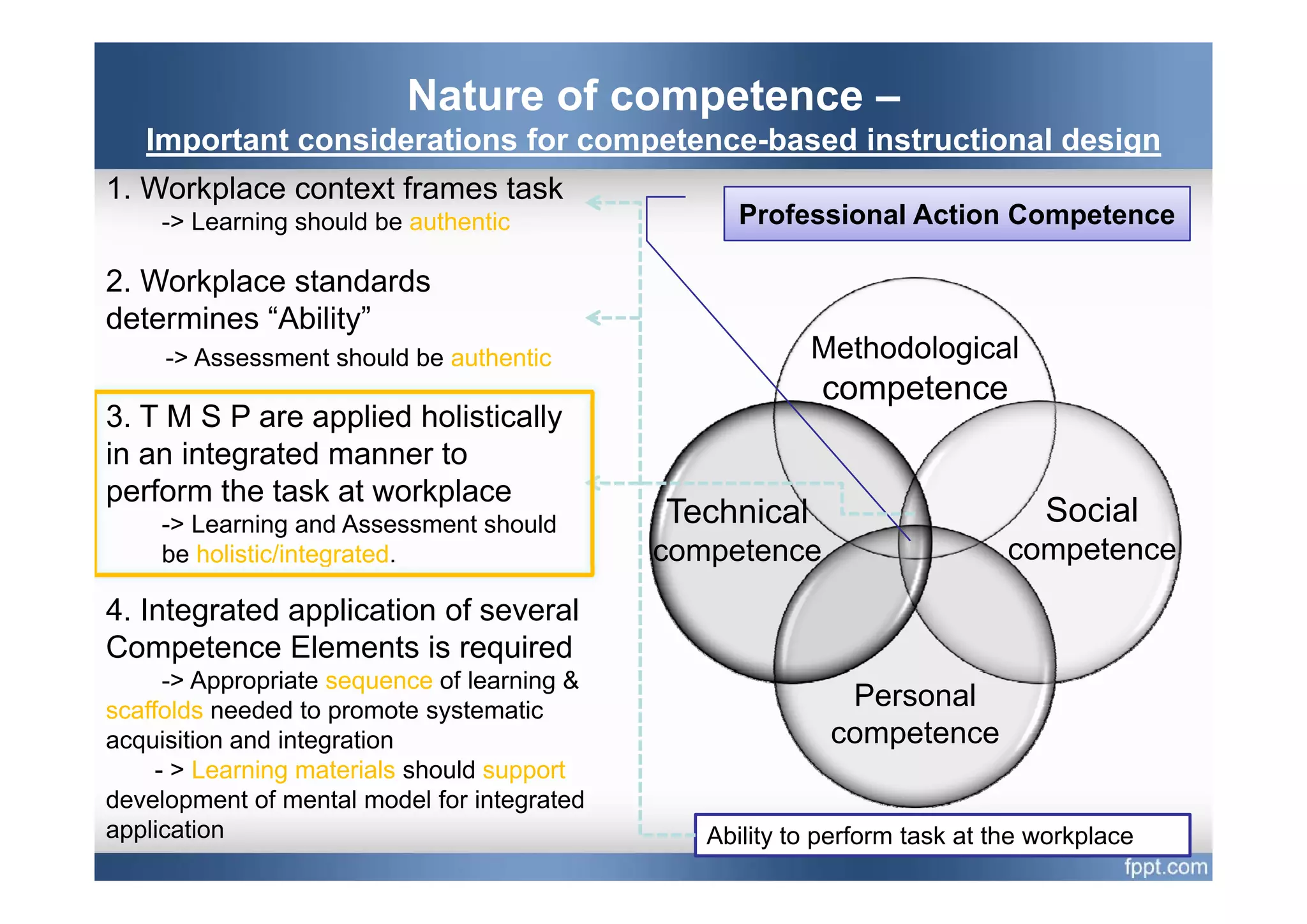
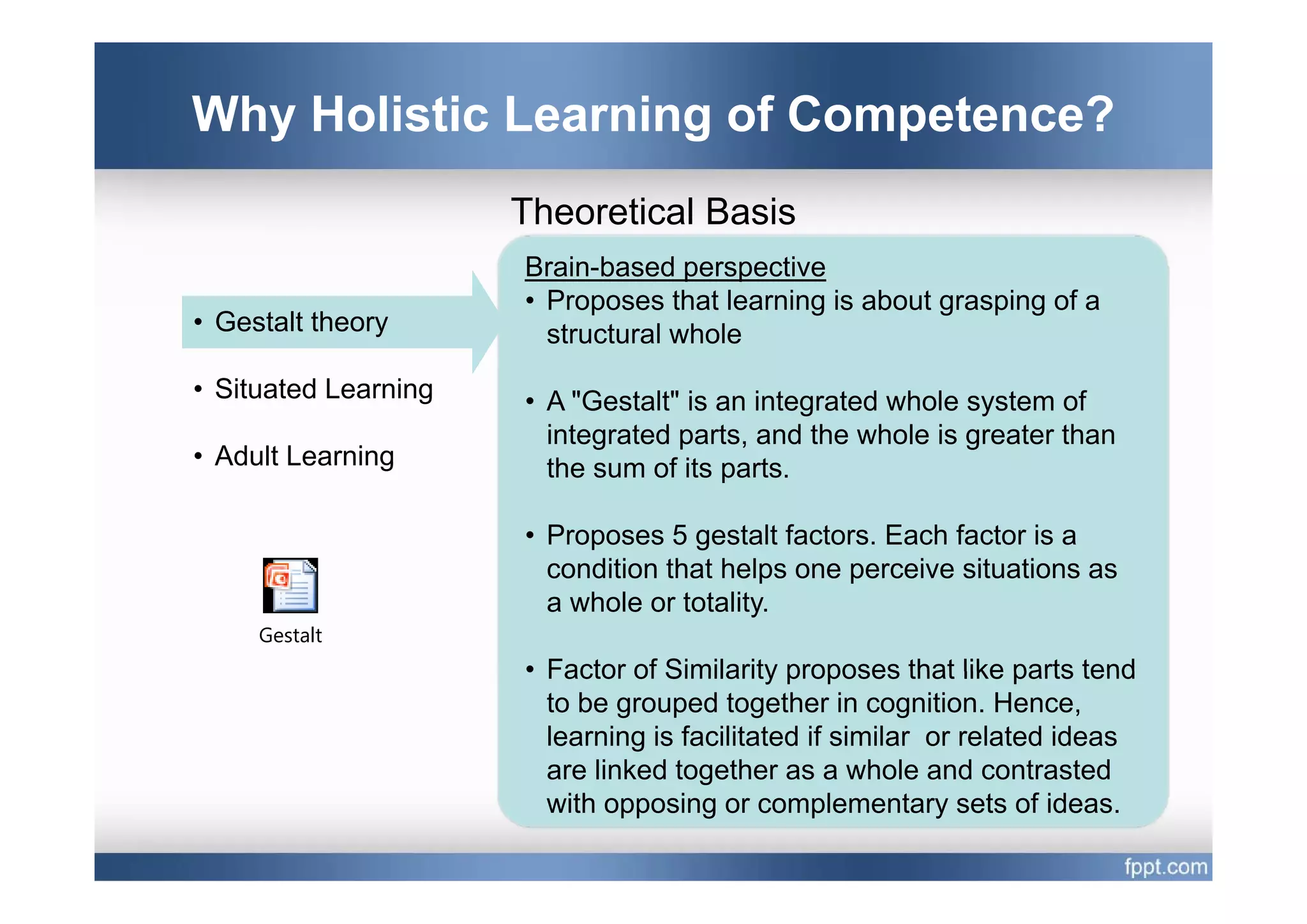
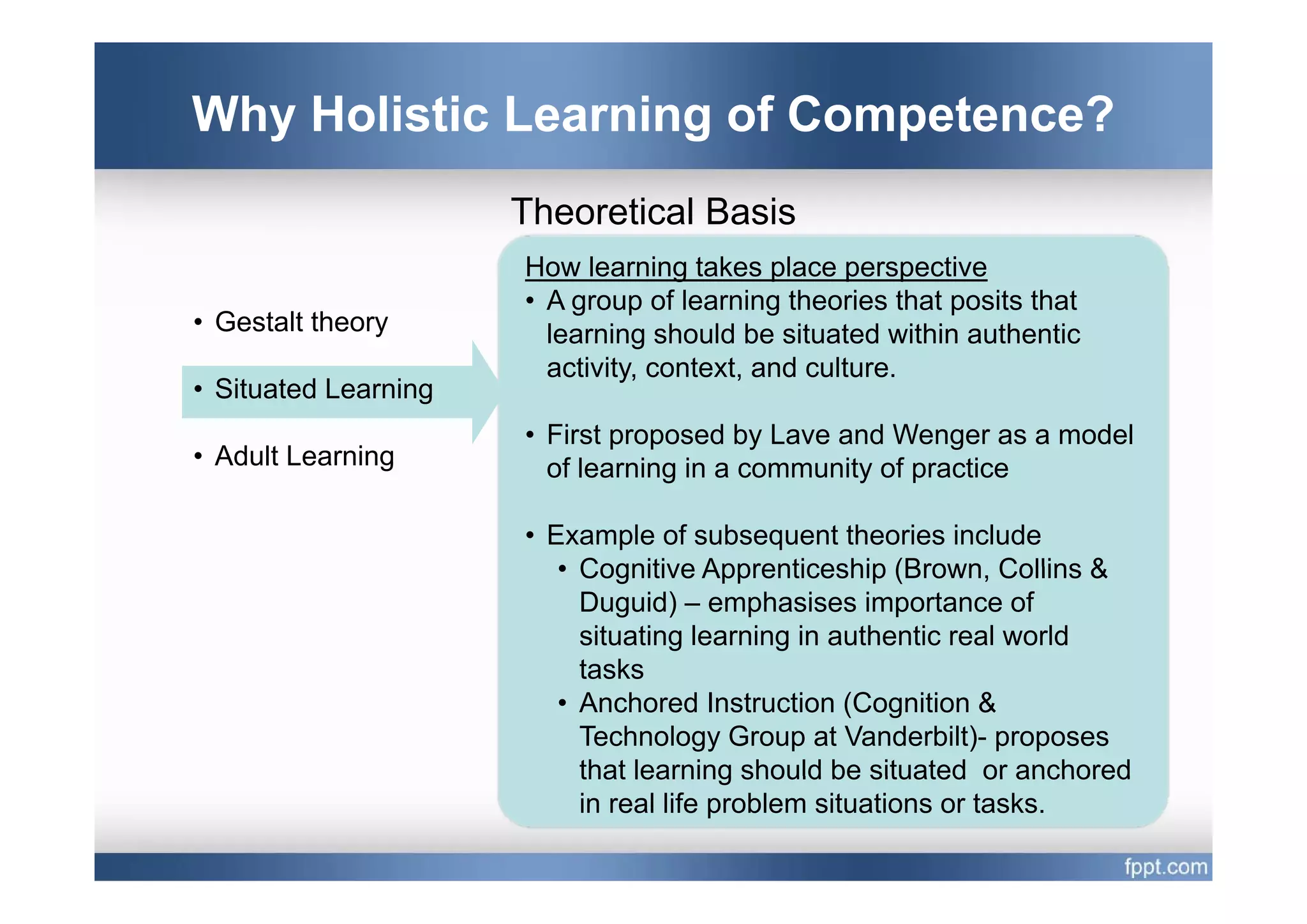
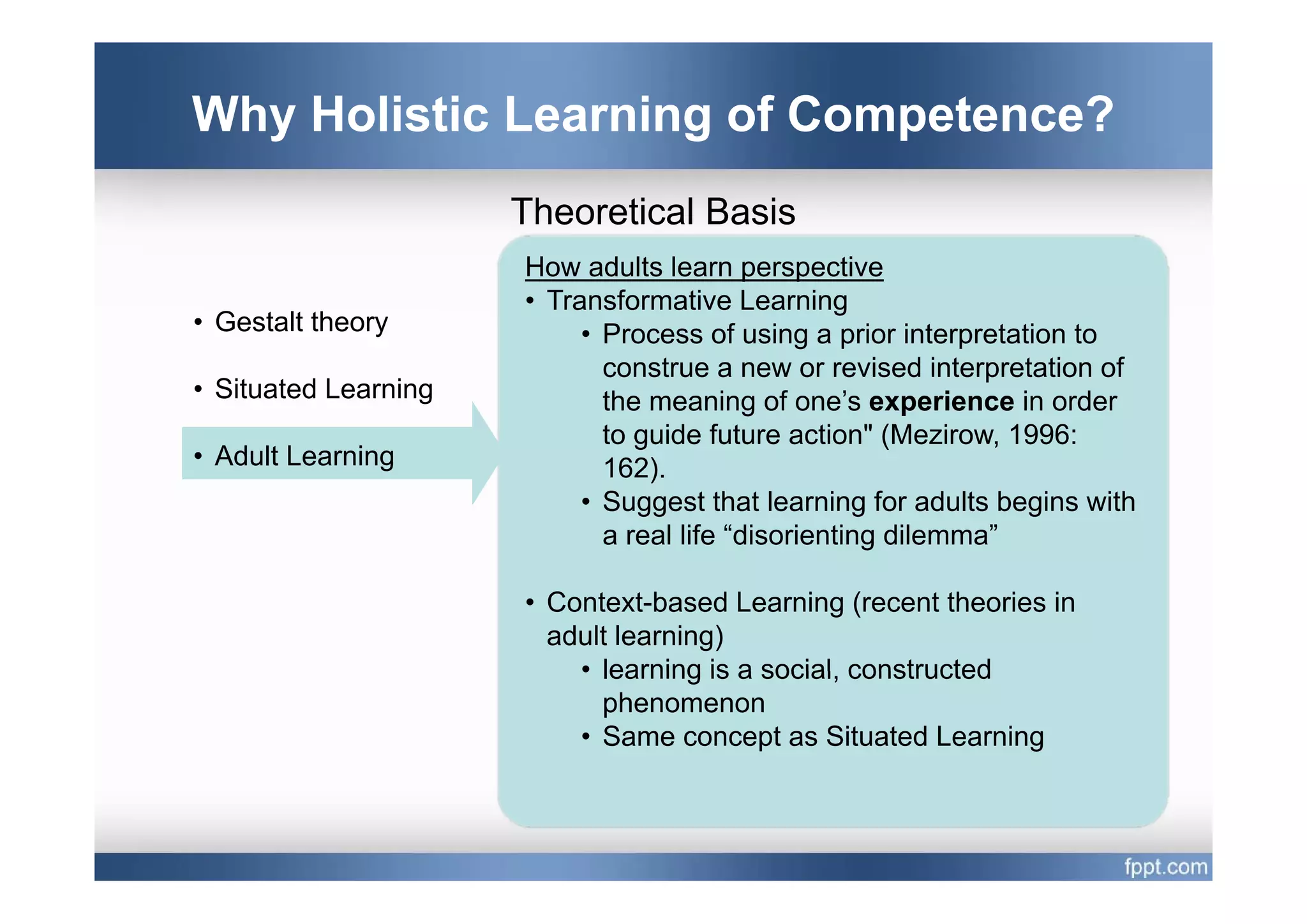
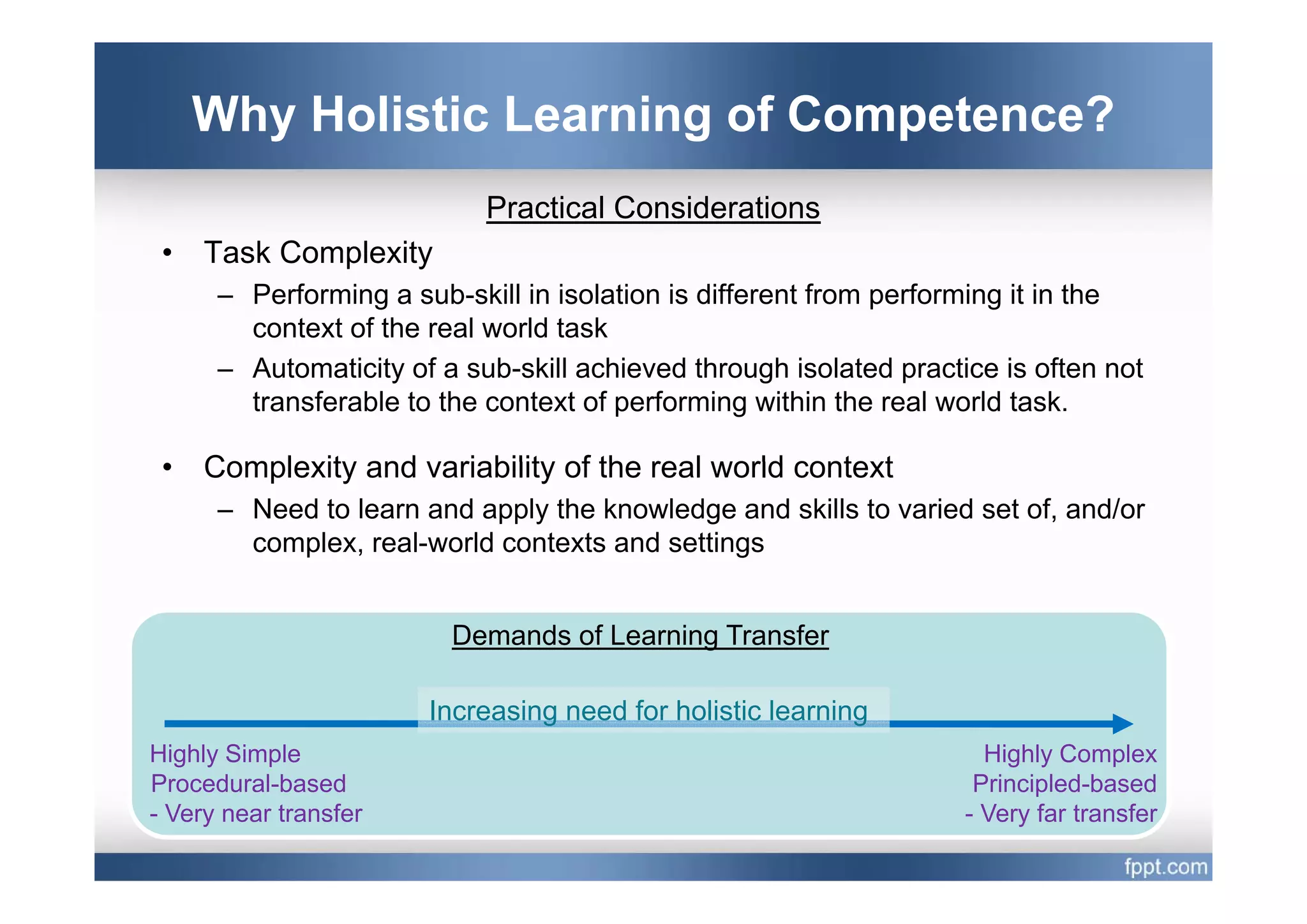
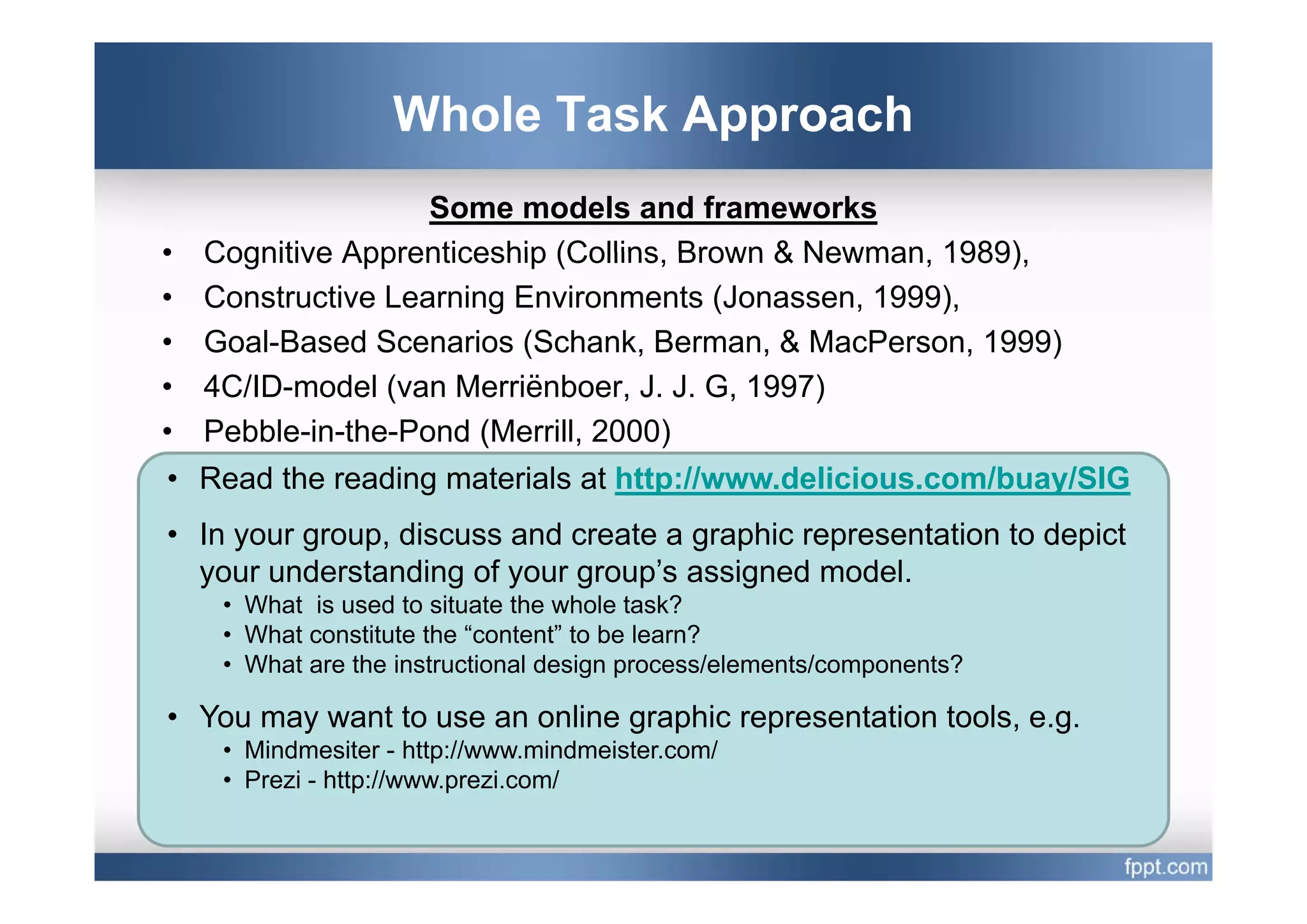
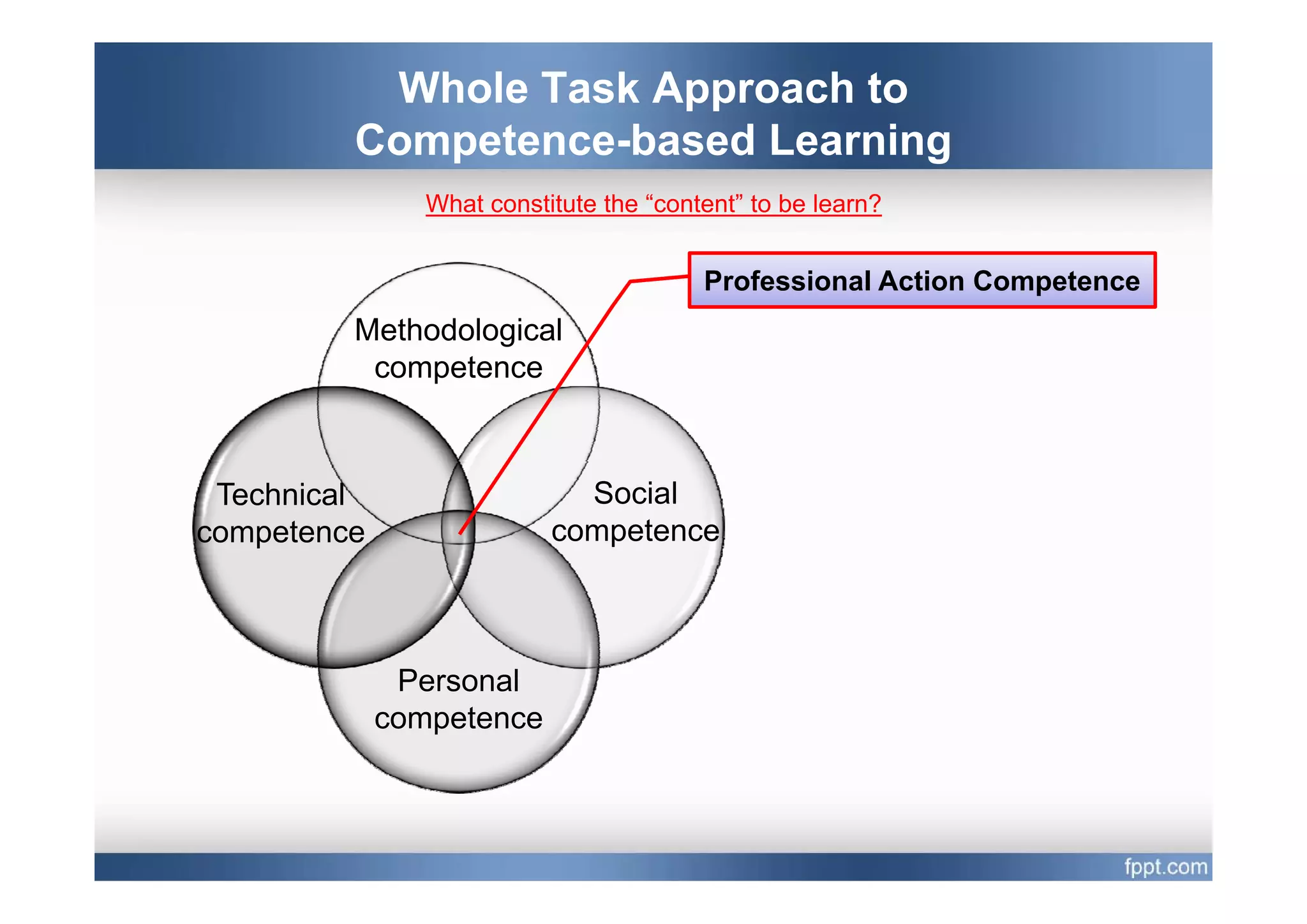
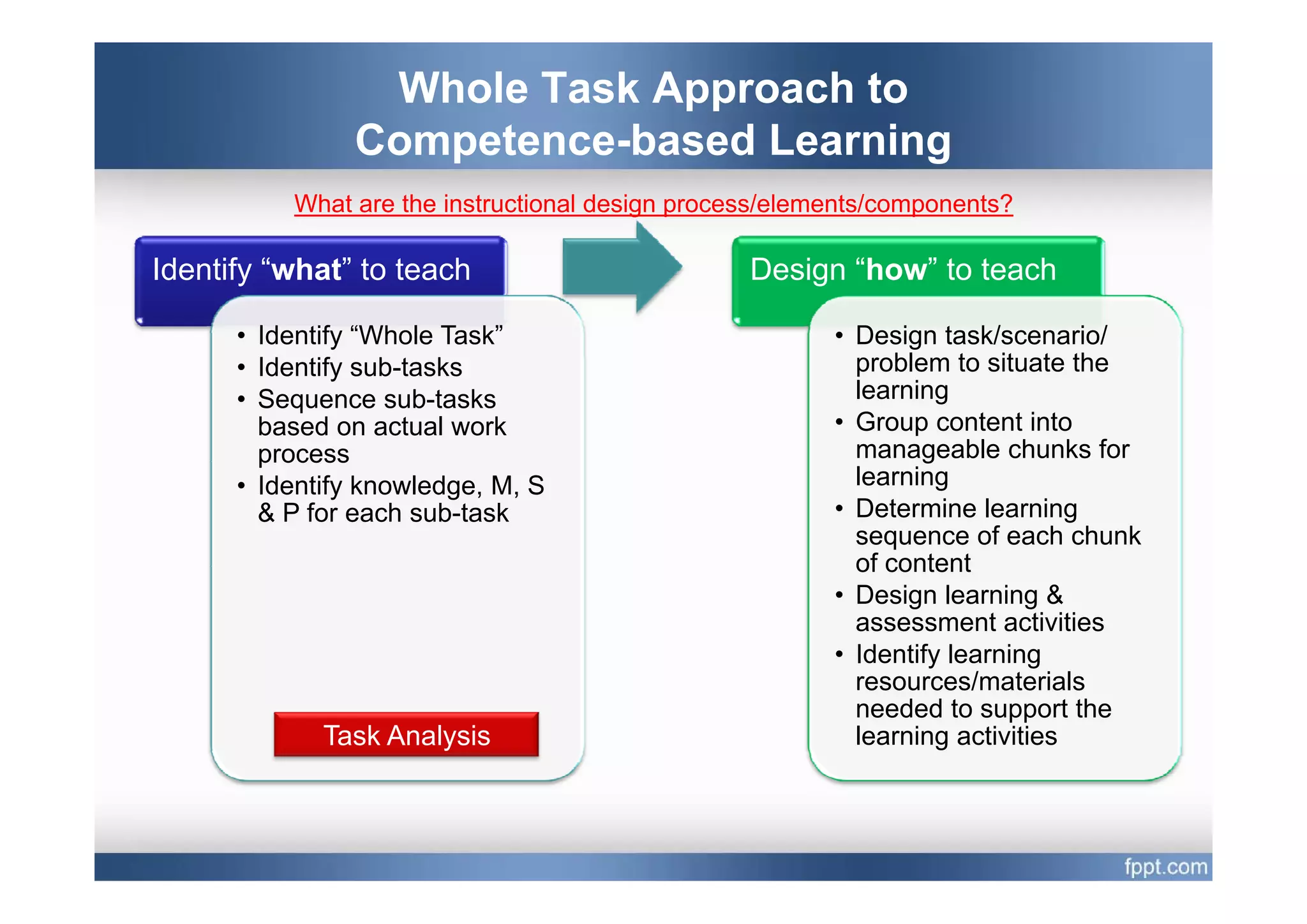
This document provides an overview of a presentation on using a whole task approach to holistic learning of vocational competences. It begins with discussing the differences between holistic education and holistic learning of competence. It then explains why holistic learning of competence is important from theoretical, practical, and brain-based perspectives. The presentation goes on to describe the whole task approach, including using real-world tasks to situate learning, identifying the knowledge, skills, attitudes and personal competence to be learned for each sub-task, and considering instructional design processes like task analysis.