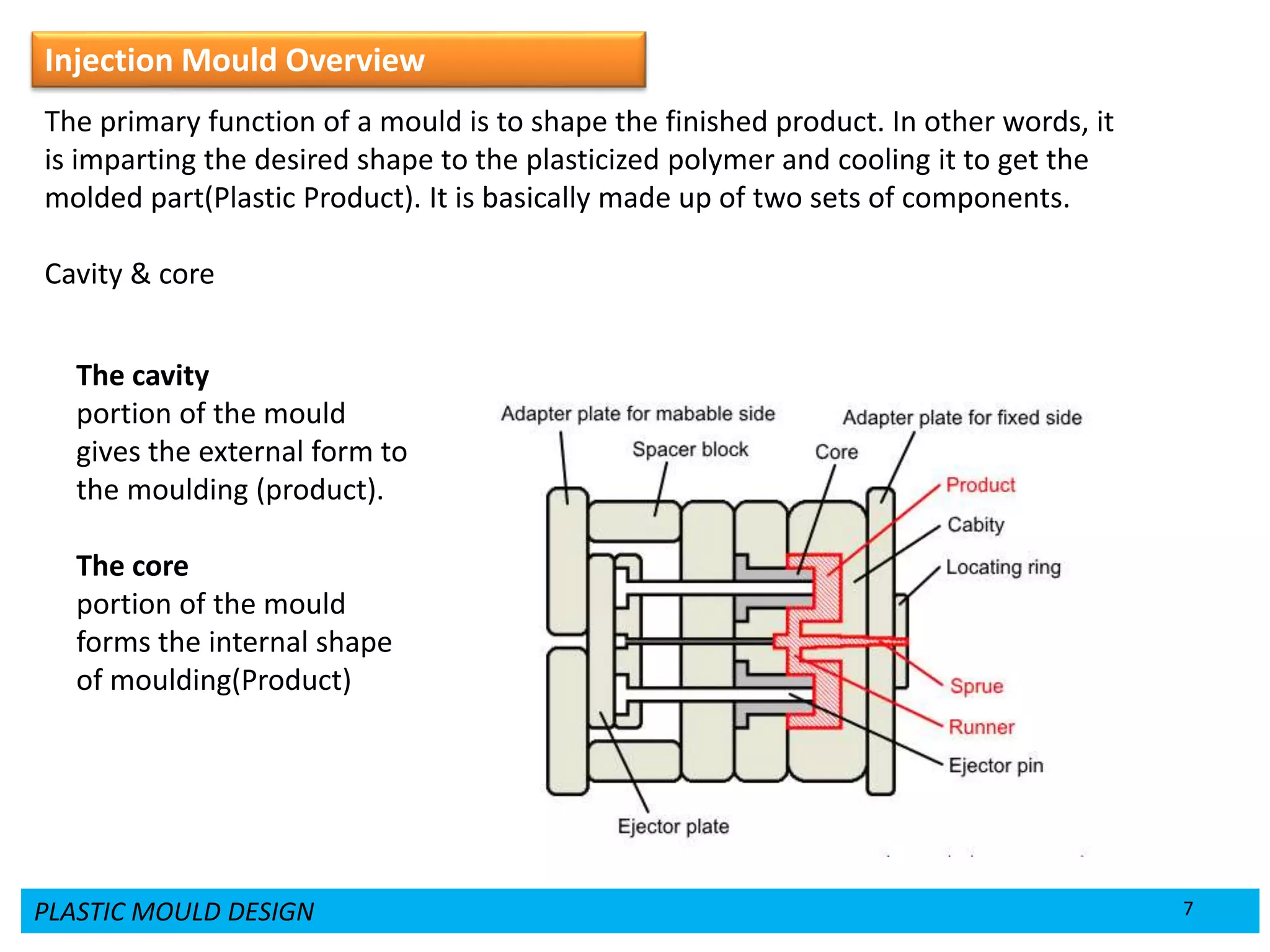
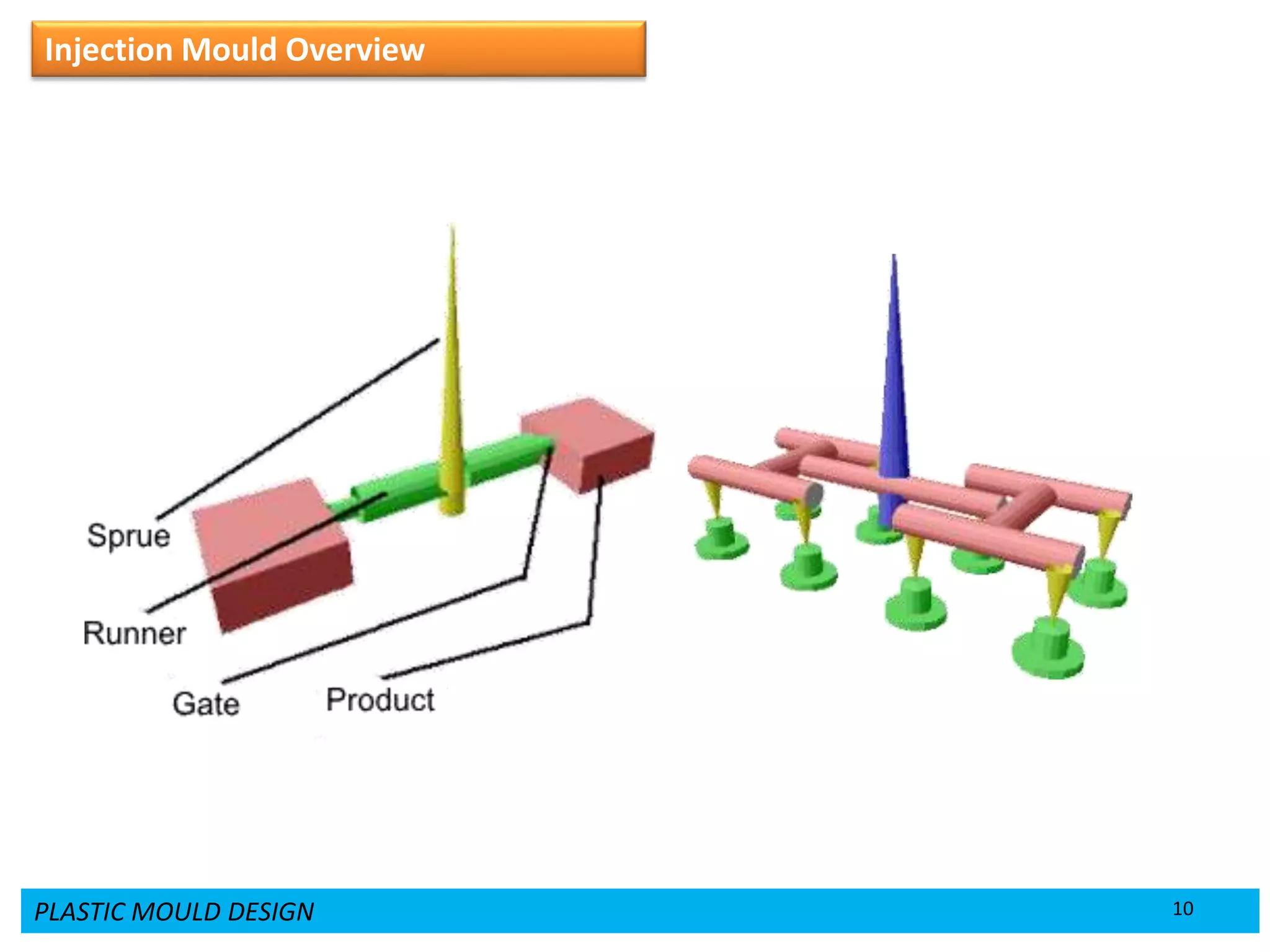
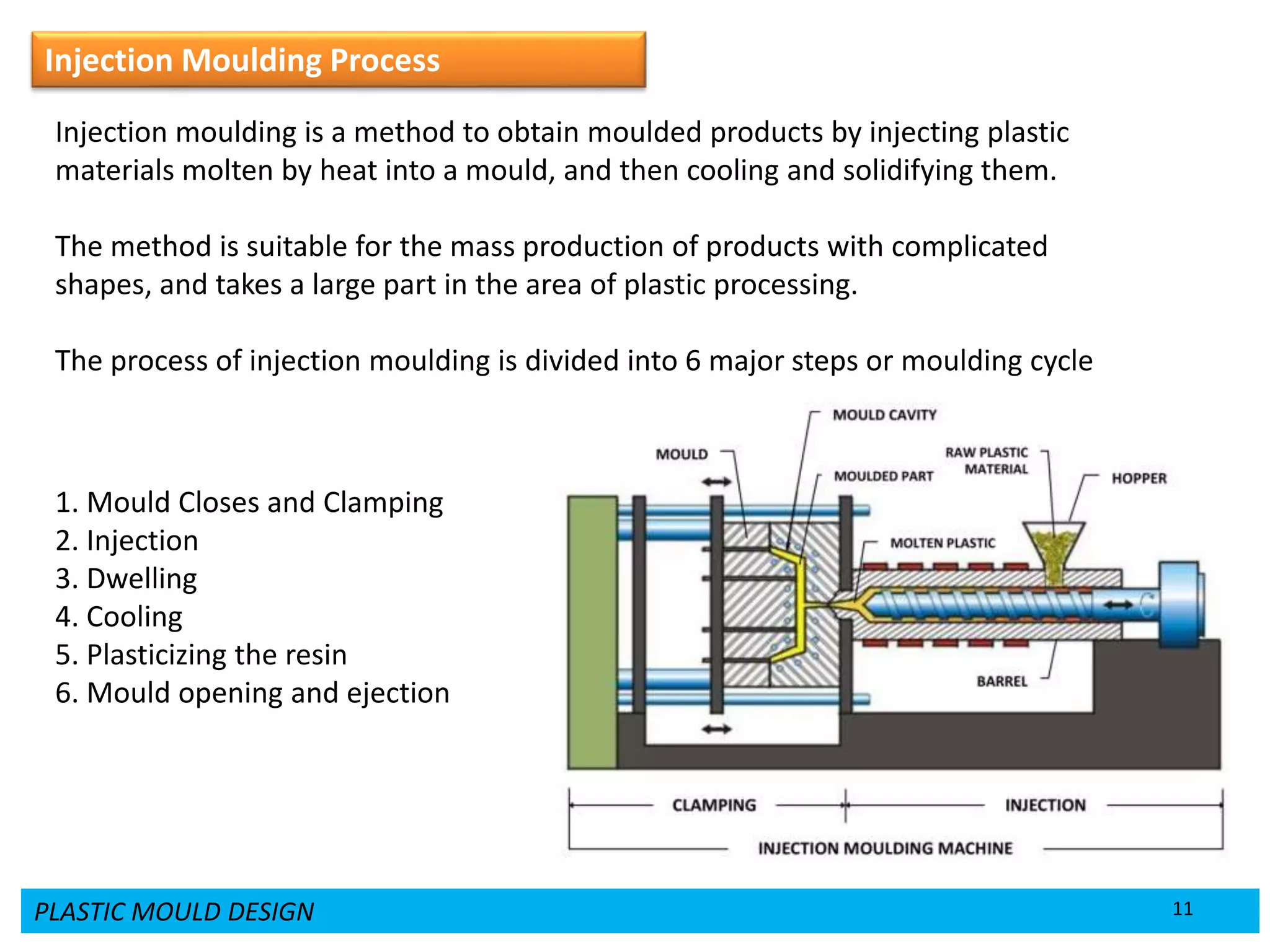
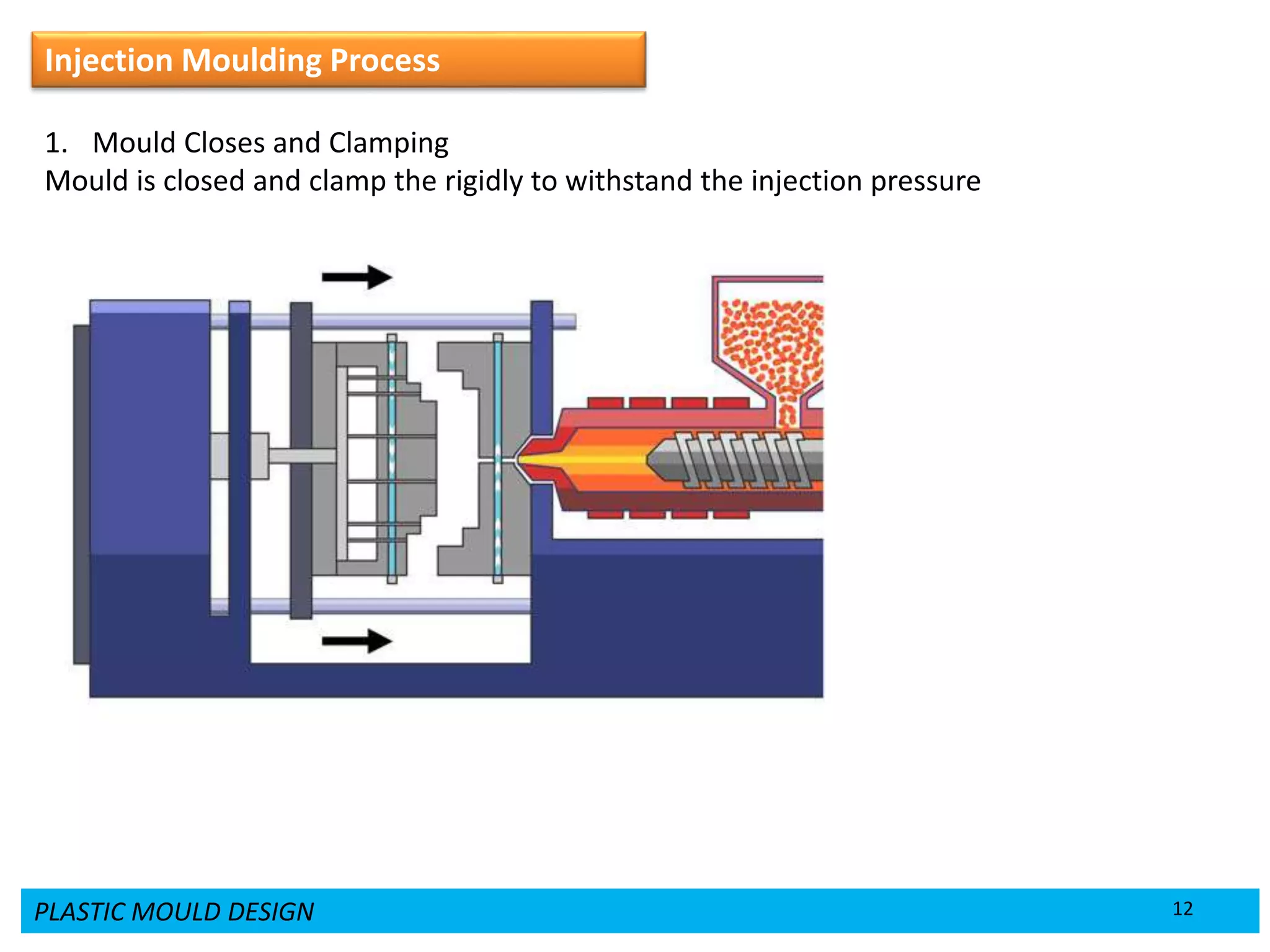
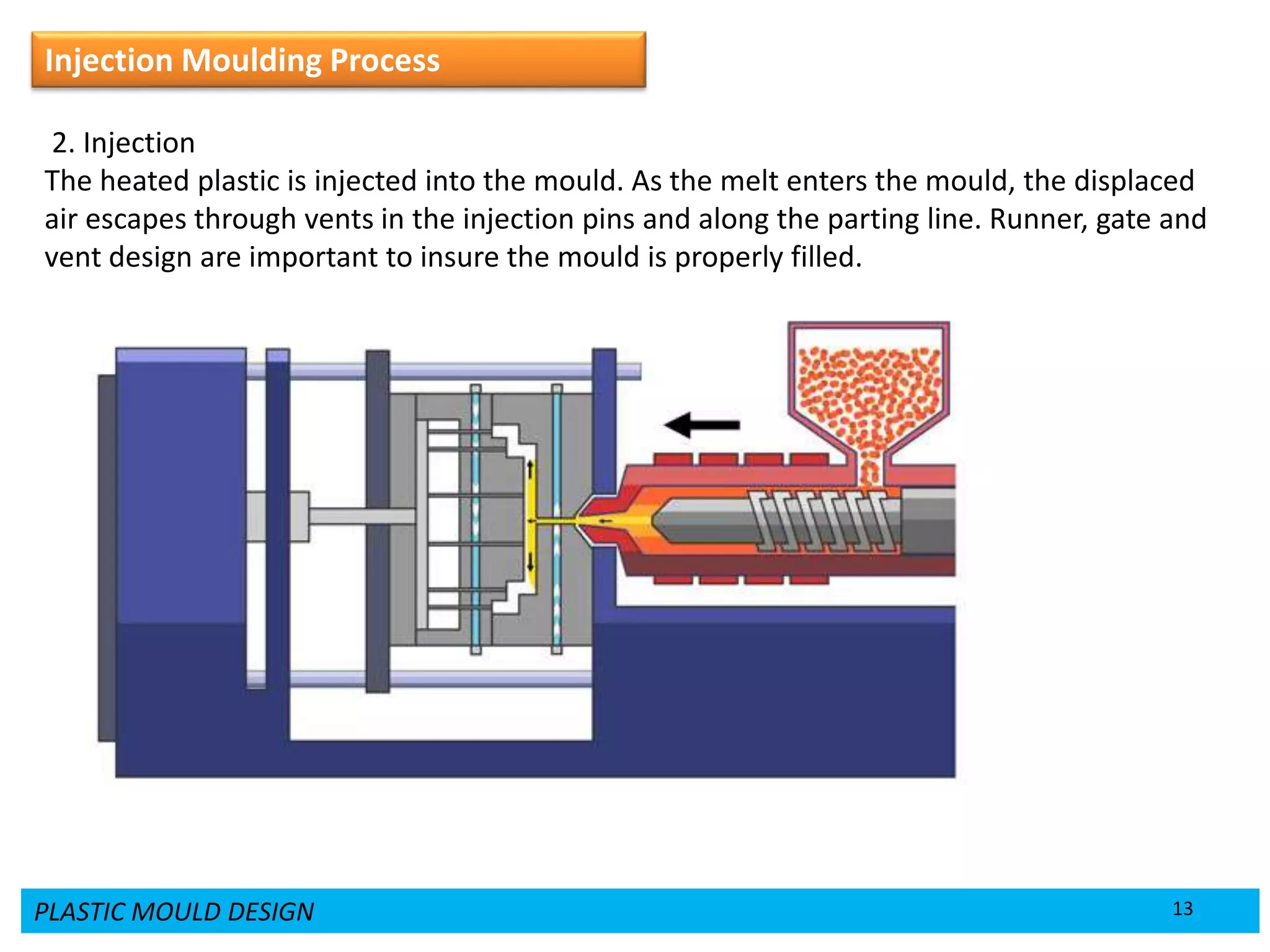
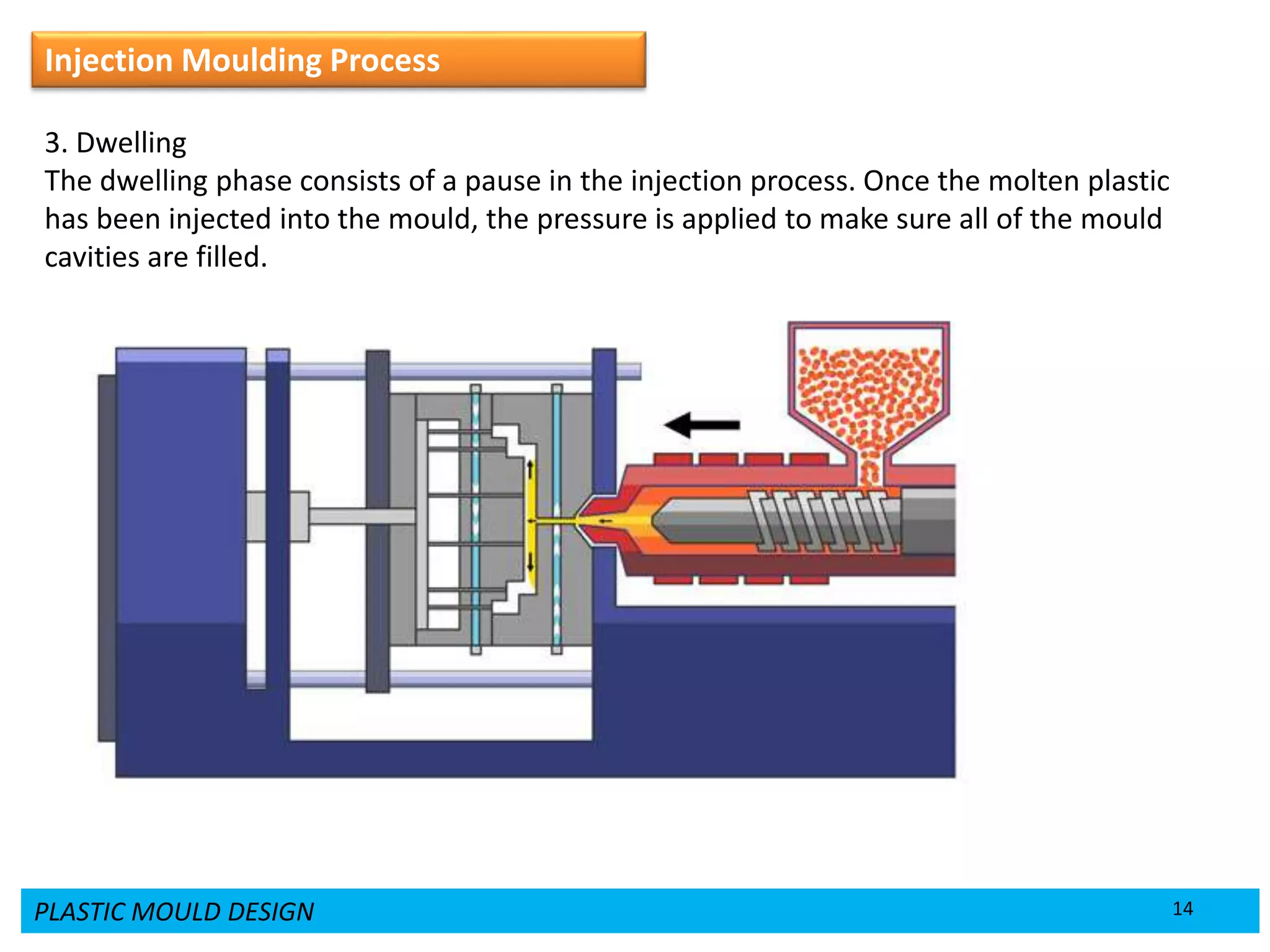
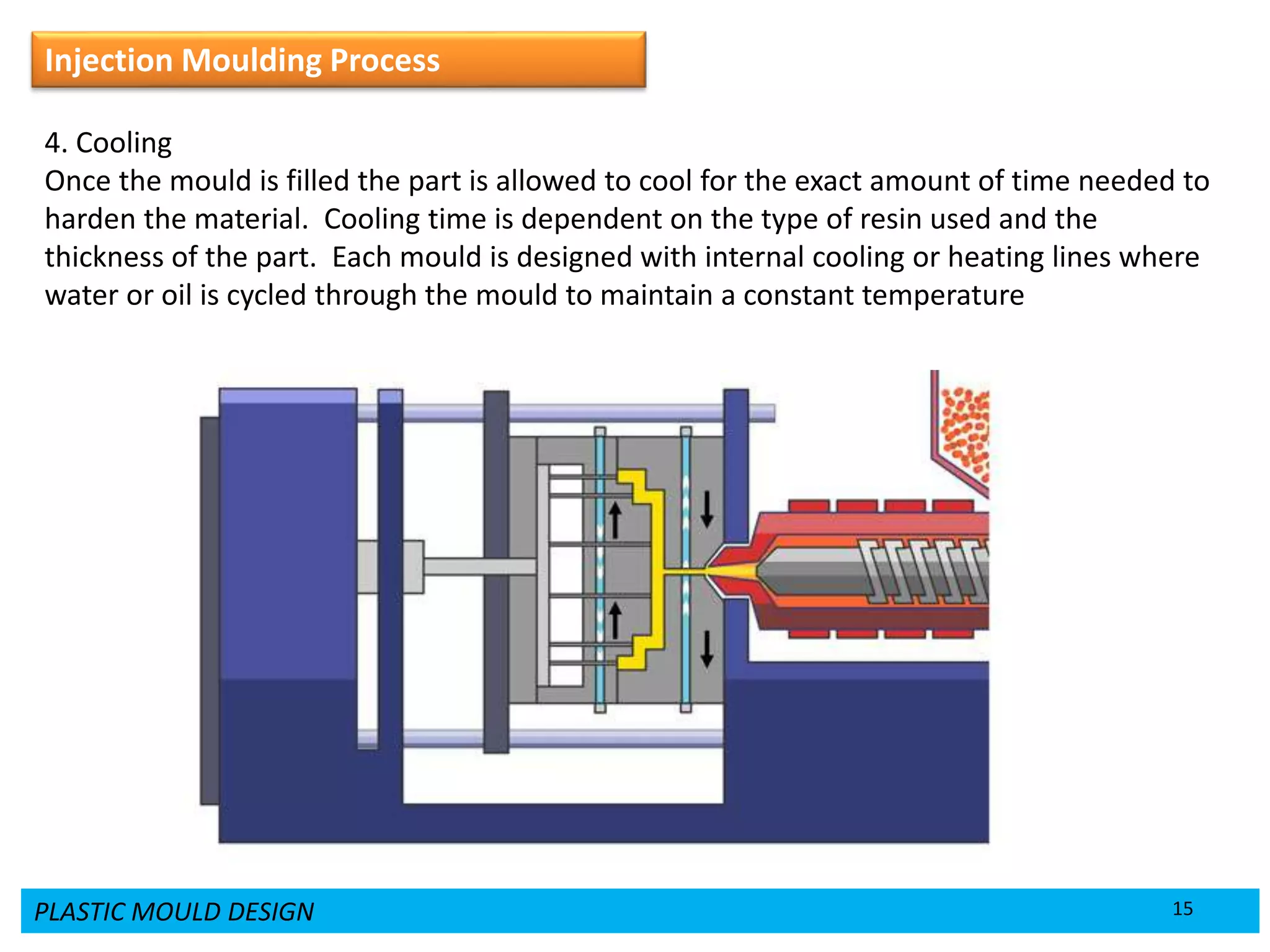
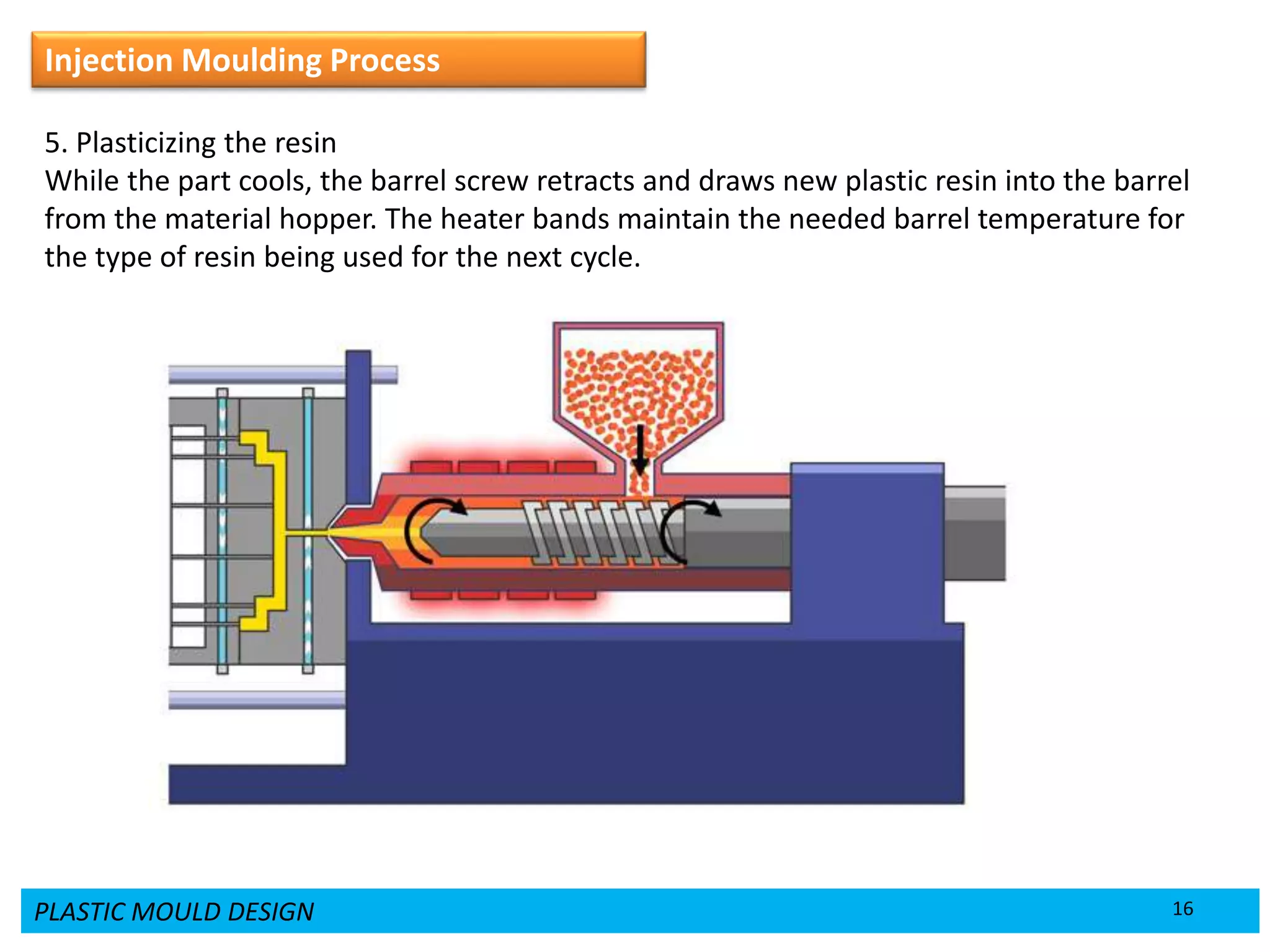
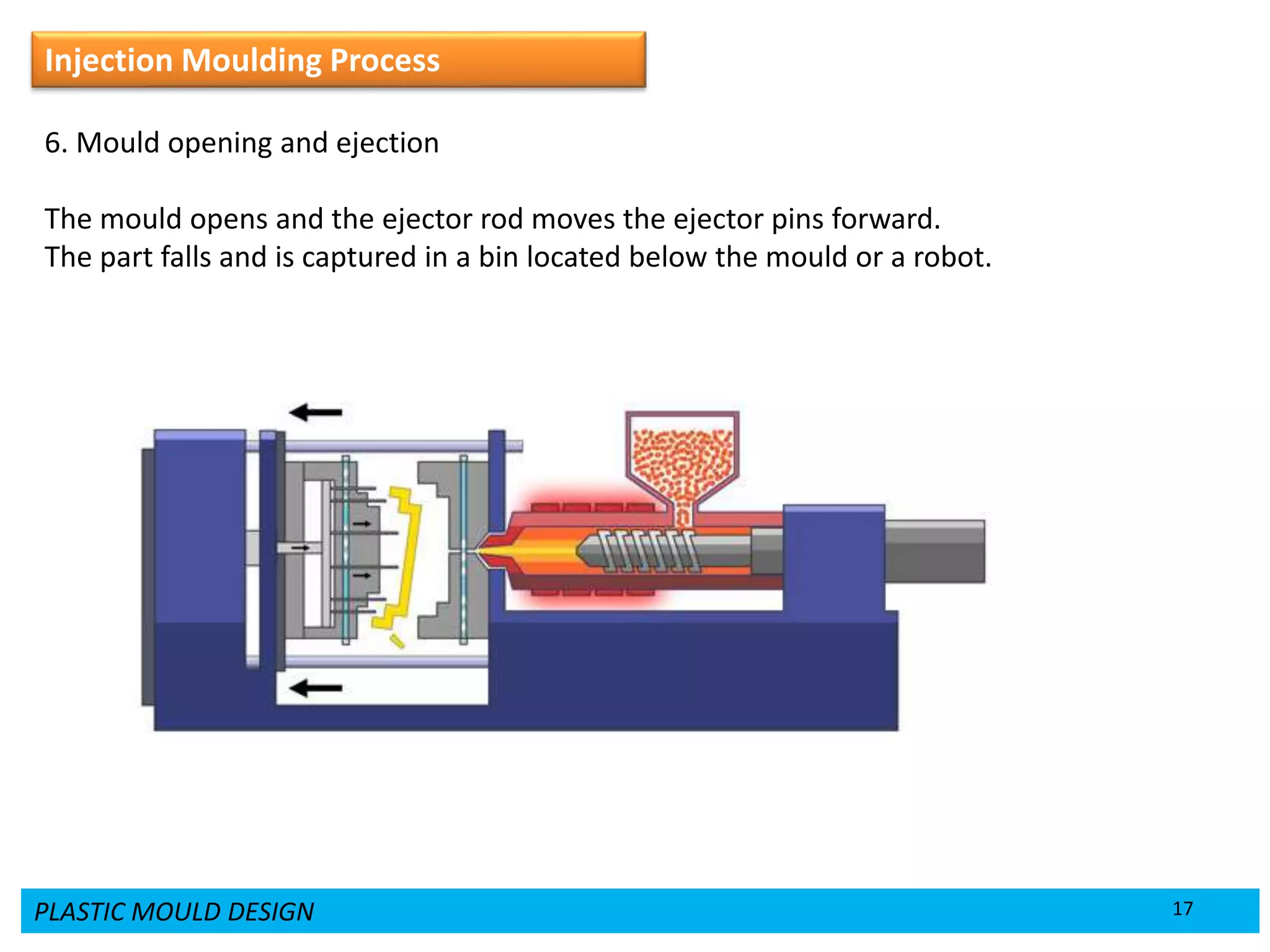
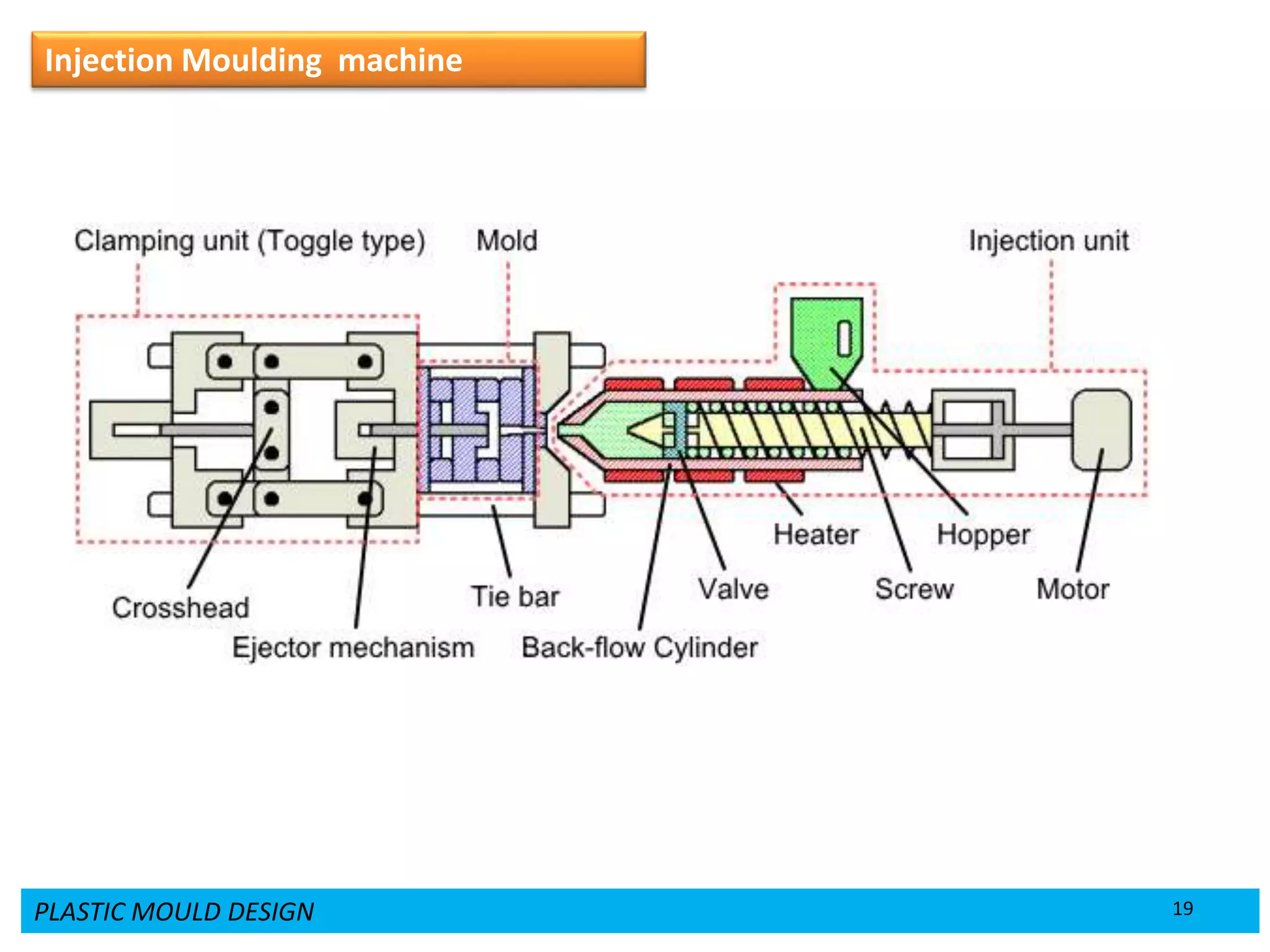
This document provides an overview of plastic mould design and the injection moulding process. It discusses the importance of plastic parts in modern industries and advantages of plastics over metals. Key topics covered include design considerations for plastic parts, common plastic materials, types of moulds, injection mould components like the cavity and core, and the six main steps of the injection moulding process: mould closing and clamping, injection, dwelling, cooling, plasticizing resin, and mould opening and ejection. The document also provides a brief overview of injection moulding machines.