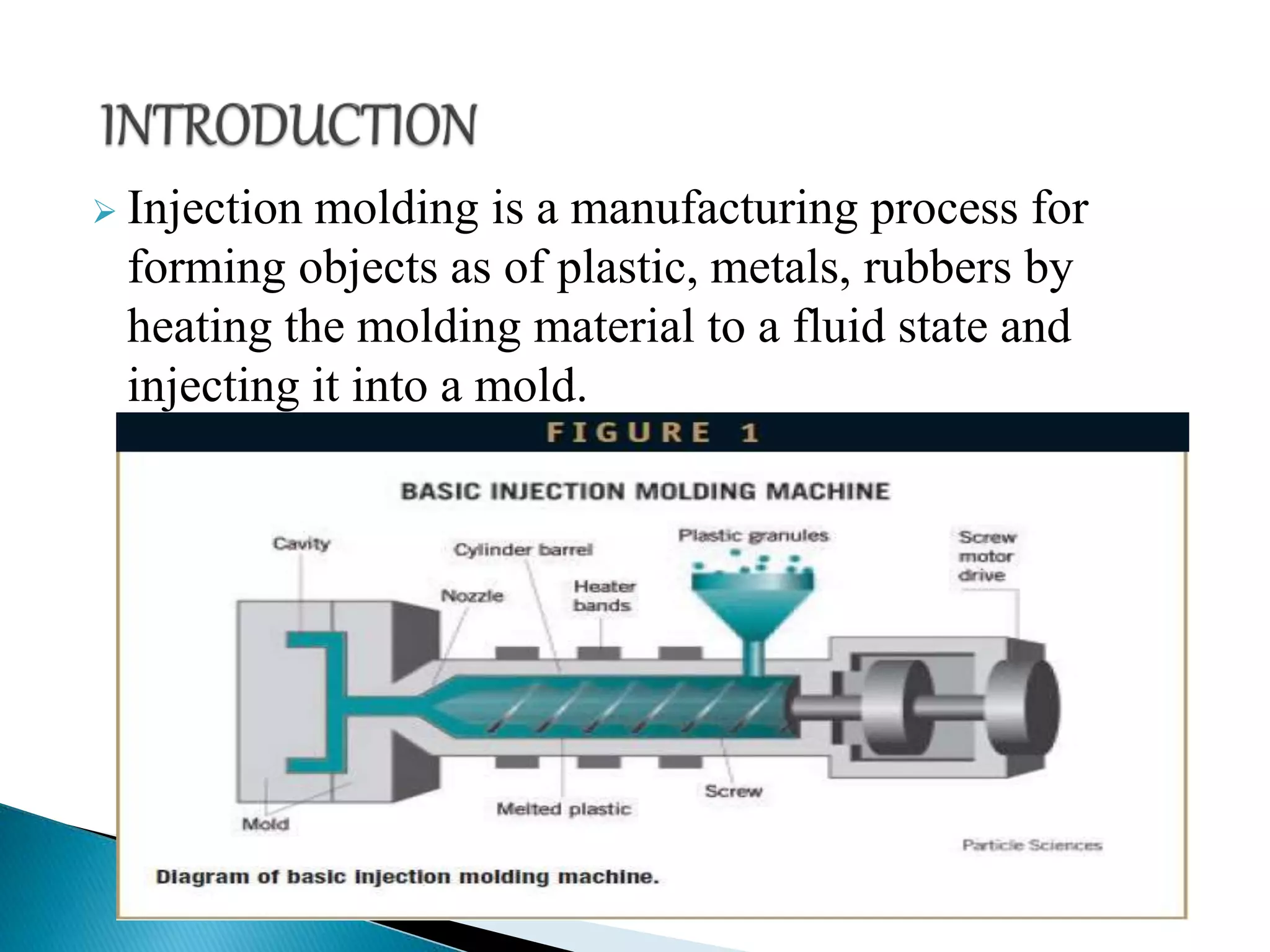
This document provides an overview of injection molding. It discusses the injection molding process, materials used, system components including the injection unit, clamp unit and mold. It describes the working of injection molding including the molding cycle of injection, cooling and ejection. It outlines the advantages of high production rates and dimensional tolerances but also limitations of high equipment costs. It concludes with references for further reading on injection molding technology fundamentals and plastics processing.