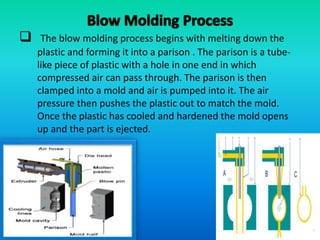
Blow molding is a manufacturing process that uses air pressure to form hollow plastic parts like bottles. There are three main blow molding processes: extrusion blow molding where a tube of molten plastic (parison) is captured in a mold and inflated, injection blow molding where a preform is first injection molded and then blown, and stretch blow molding where preforms are first made via injection molding and then reheated and blown into shape. Blow molding can make parts from various plastics like PET, HDPE, and PP. It is used widely to make containers and bottles for foods, drinks, chemicals and more.