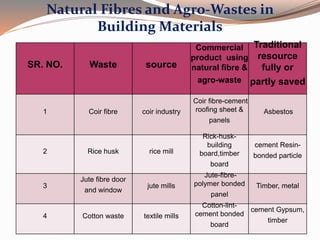
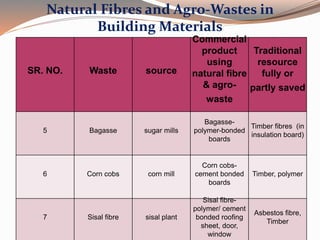
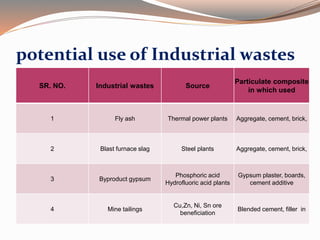
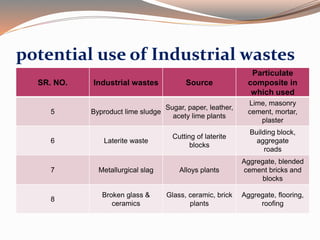
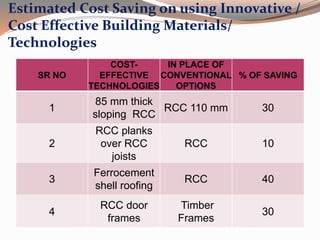
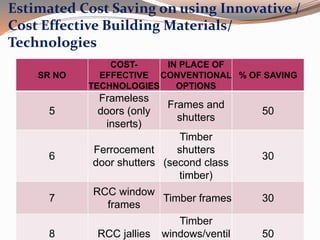
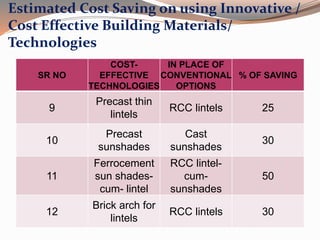
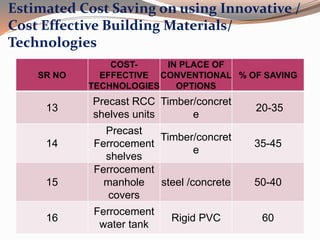
Low cost housing aims to reduce construction costs while maintaining safety and quality. Building material costs typically account for 65-70% of total costs, while labor accounts for 30-35%. Costs can be reduced by using locally available, low-cost materials and improving construction scheduling. Demonstration houses in various cities used materials like concrete blocks, filler slab roofs, and ferrocement doors to achieve costs of Rs.40,000-60,000 per unit. Waste materials and industrial byproducts can also be utilized in building materials to further reduce expenses.