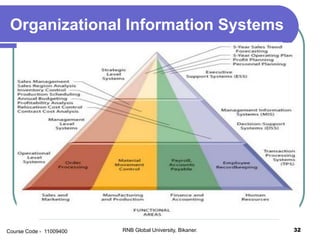
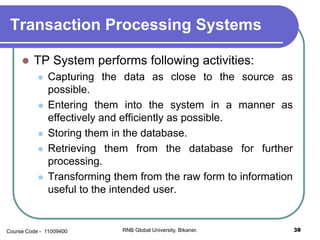
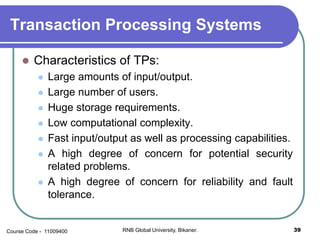
This document provides an introduction to information systems and their types. It defines an information system as a set of components that collect, manipulate, store, and disseminate data to provide information to users. Management information systems (MIS) are discussed as evaluating and processing organizational data to produce useful information for management decision making. Different types of information like strategic, tactical, and operational are classified based on their characteristics and applications.