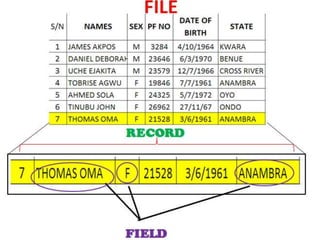
This document defines key concepts related to computer files. It discusses:
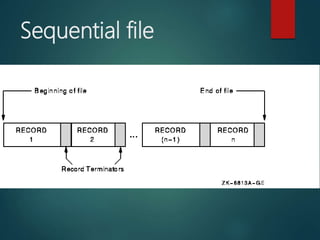
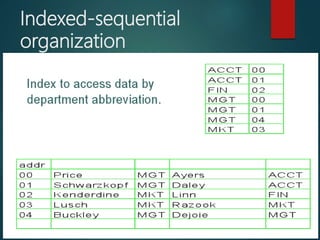
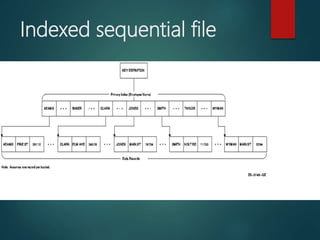
1. File organization types including serial, sequential, direct access, and indexed sequential. Sequential files store records in key sequence while direct access allows direct retrieval by calculating a record's address.
2. Methods of accessing files which can be serial, sequential, or direct/random.
3. Criteria for classifying files as master, transactional, or reference files based on their content, organization, and storage medium.
4. An assignment to research operating procedures for computer data processing.






























![Assignment
1. Read up the topic: “handling
computer files”.
2. Outline the operating procedure for
computer data processing [see pages 86
& 87 of your ICT textbook]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conceptofcomputerfiles-161018104950/85/Concept-of-computer-files-36-320.jpg)
