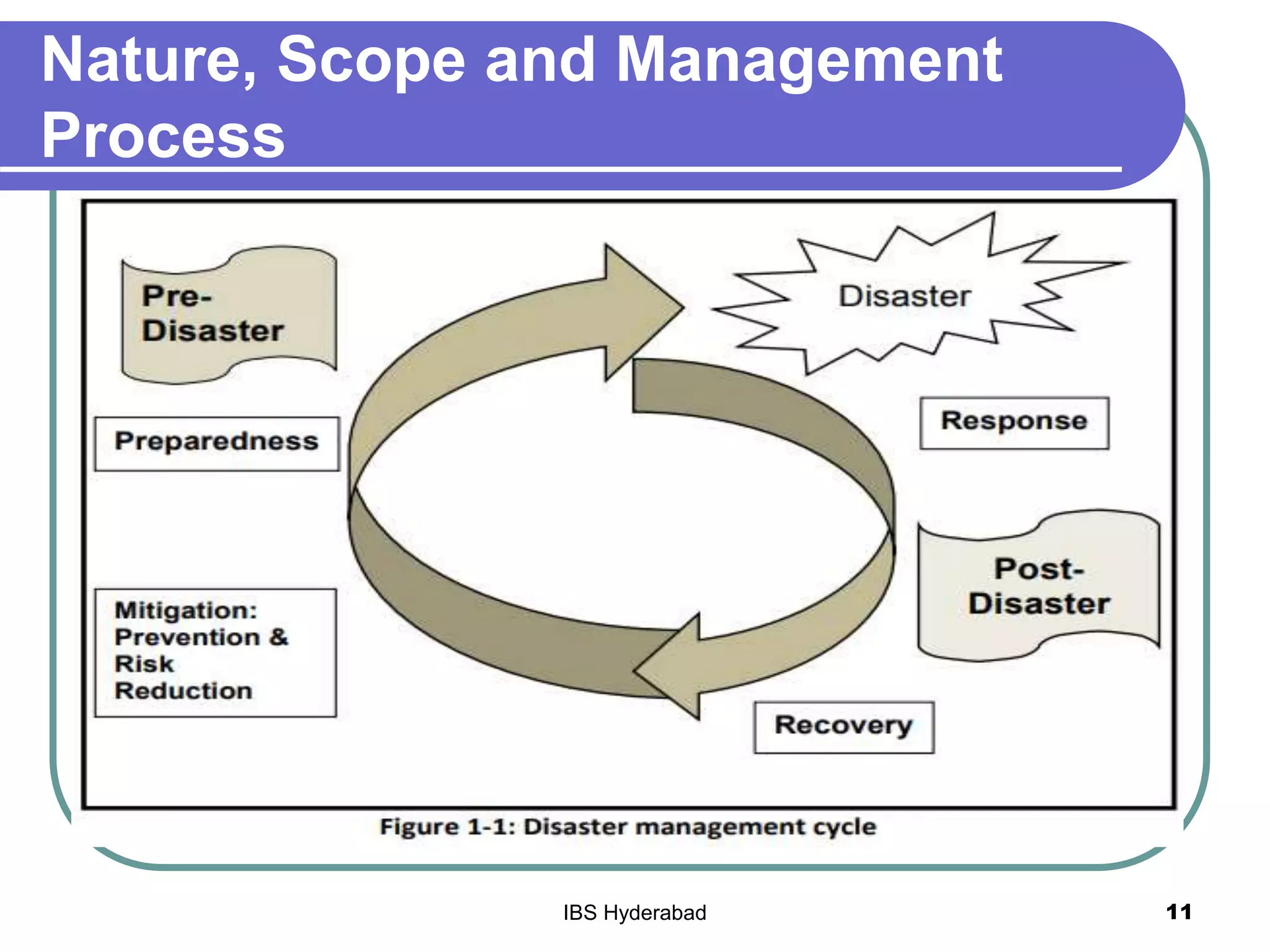
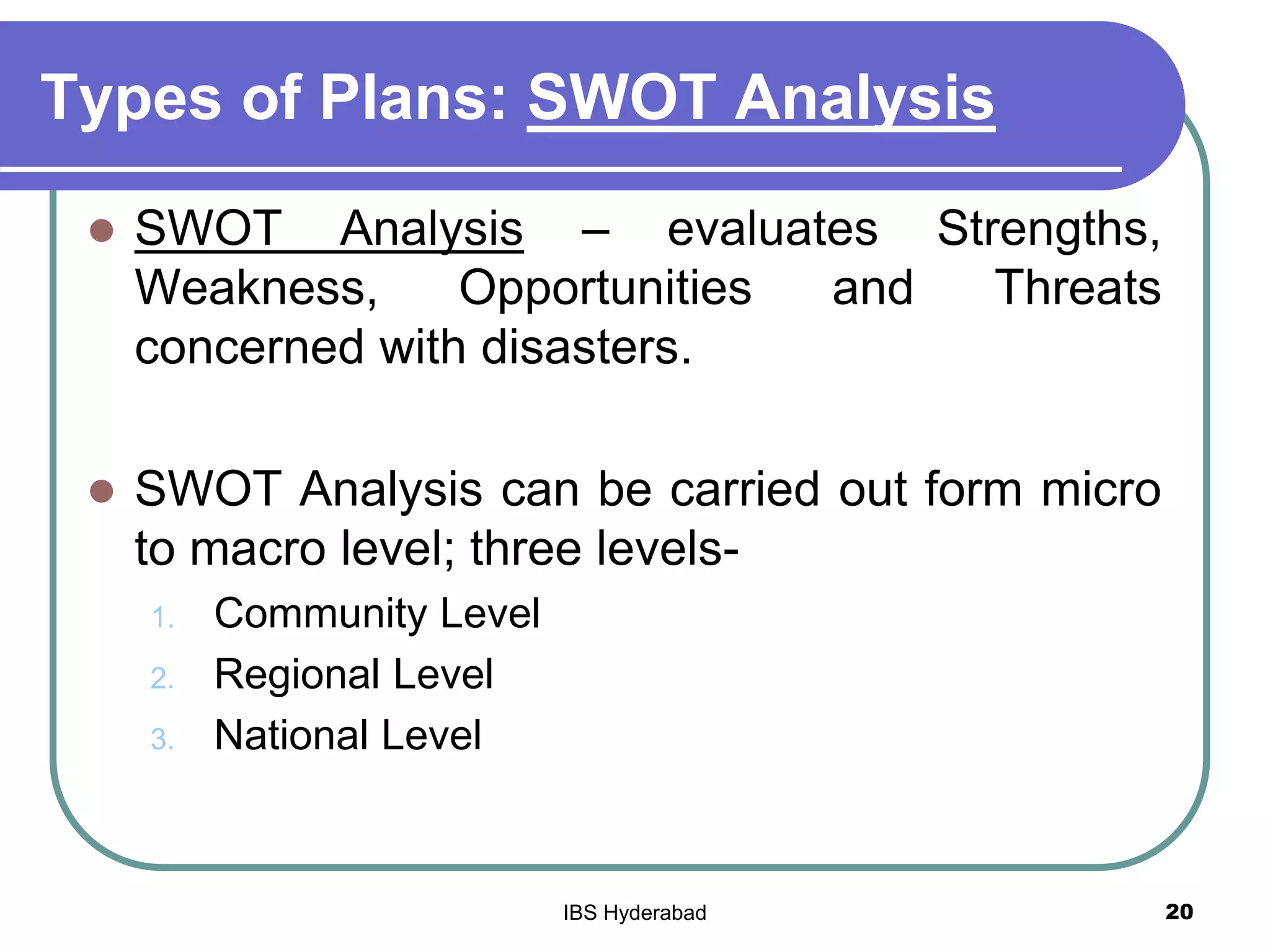
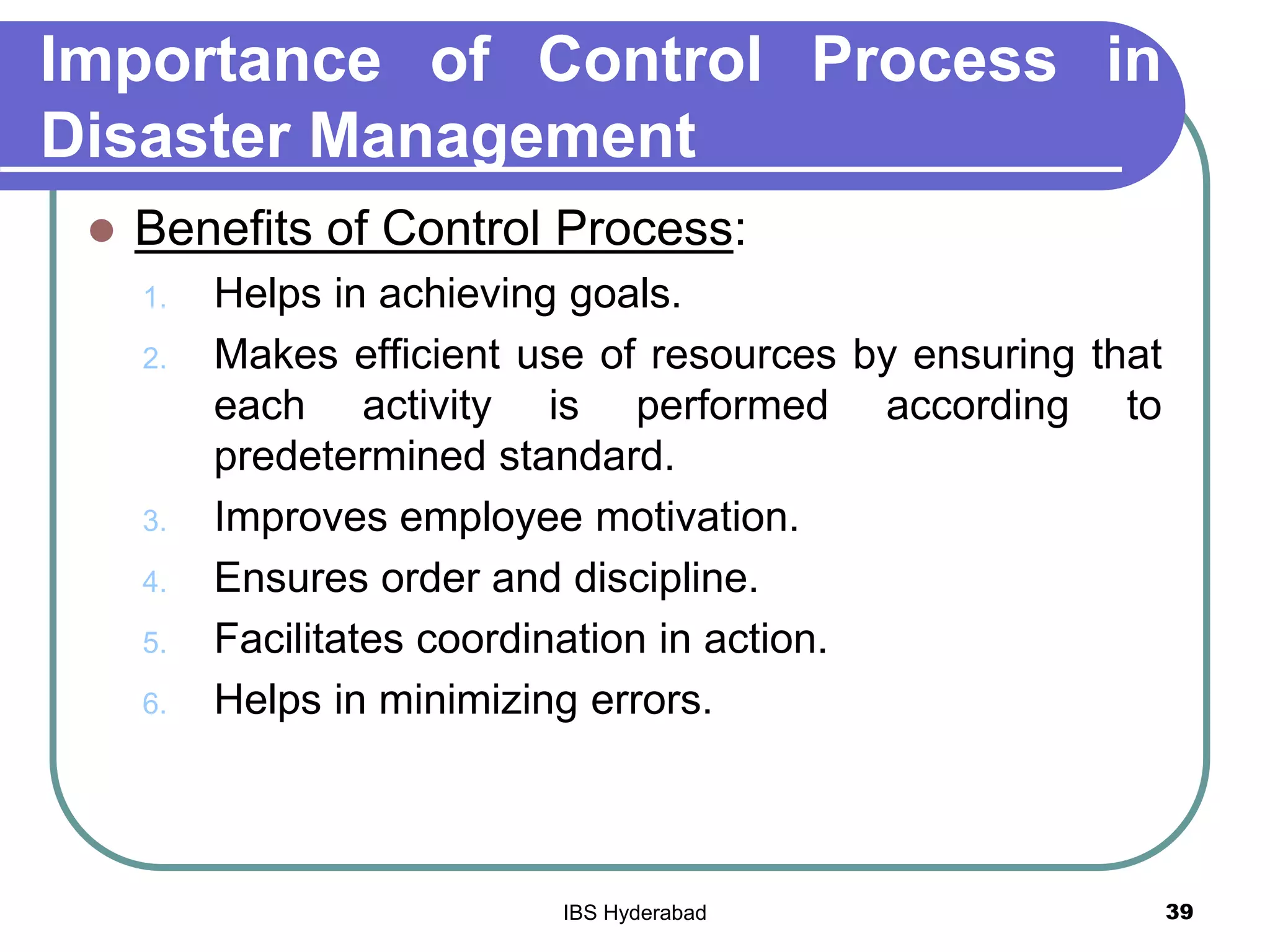
This document discusses disaster management and planning. It covers the nature and scope of disaster management, including policy and types of plans. Some key points discussed include:
- Disaster management aims to reduce losses from disasters through optimal resource utilization and preparation.
- Plans like hazard and vulnerability analysis and SWOT analysis assess risks at the community, regional, and national levels.
- The disaster management policy provides guidance to promote community-based management and capacity building at all levels.
- Identification, prevention and preparation are important pre-crisis phases of crisis management.