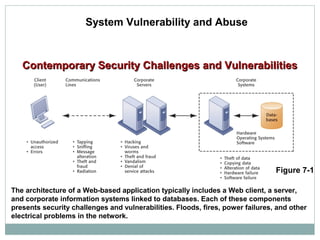
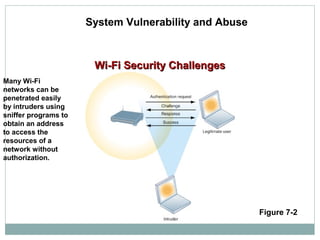
This document discusses system vulnerabilities and security challenges. It describes how hardware, software, and disaster-related problems can make systems vulnerable. It then discusses specific vulnerabilities like those in internet networks, email, wireless networks, and malicious software. The document also covers computer crimes like hacking, spoofing, and types of identity theft. It provides examples of vulnerabilities across technical systems, networks, and user behaviors.