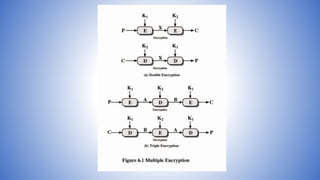
The document discusses the security vulnerabilities of DES and the emergence of Triple DES (3DES) as a more secure alternative, particularly in response to theoretical attacks and brute-force vulnerabilities. It explains the mechanics of multiple encryption methods, including Double DES and Triple DES, detailing the use of one or more keys for encryption and the implications for security. The document highlights that 3DES, despite being slower, is widely adopted in key management standards and has no practical attacks known against it, though potential concerns exist with two-key 3DES compared to the preferred three-key version.





![Why Triple-DES?
• why not Double-DES?
• NOT same as some other single-DES use, but have
• meet-in-the-middle attack
• works whenever use a cipher twice
• since X = EK1[P] = DK2[C]
• attack by encrypting P with all keys and store
• then decrypt C with keys and match X value
• can show takes O(256) steps](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationandnetworksecurity27tripledes-210723160919/85/Information-and-network-security-27-triple-des-8-320.jpg)





