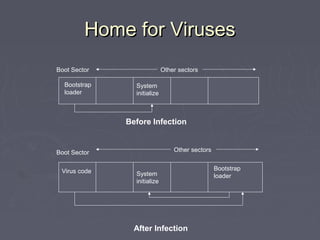
Malicious code, such as viruses and worms, can attach themselves to programs and spread by modifying other programs as they run. They can cause harm by deleting files, displaying messages, or preventing systems from booting properly. Viruses embed themselves in target programs by overwriting code, changing file pointers, or inserting themselves in boot sectors or memory-resident programs. They are able to spread through networks or by infecting files shared between systems. Viruses can be detected by analyzing their code storage and execution patterns, or how they transmit from one system to another.