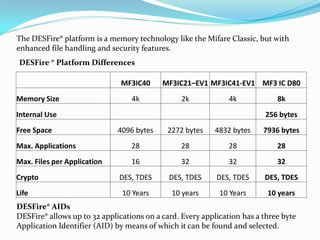
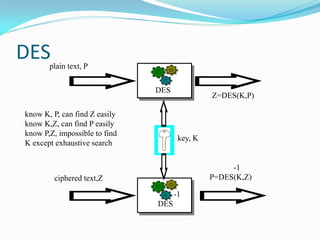
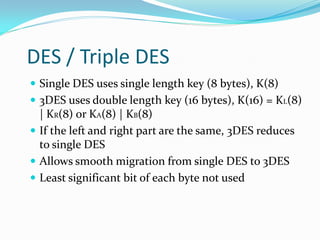
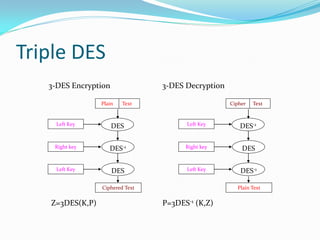
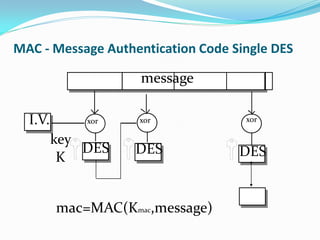
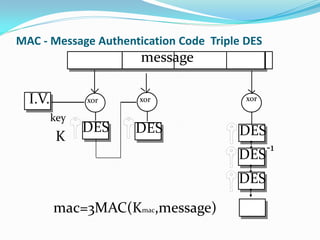
Mifare cards come in two technologies: Classic Mifare with sector/block structure, and Desfire with a file system and greater security features like DES encryption. Desfire has enhanced memory sizes up to 8k, more files and applications per card, and supports DES and triple DES encryption. It allows up to 32 applications identified by Application IDs. DESfire implements cryptographic security through challenge-response authentication, data encryption for confidentiality, message signatures for integrity and non-repudiation. DES is a symmetric key algorithm that encrypts data in 64-bit blocks, with security increased using triple DES. DESfire supports public key algorithms for encryption/decryption and signing with hash functions like MD5 and SHA providing message