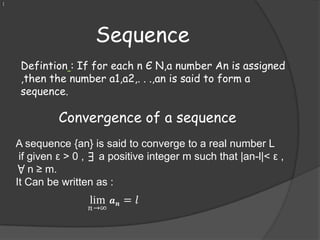
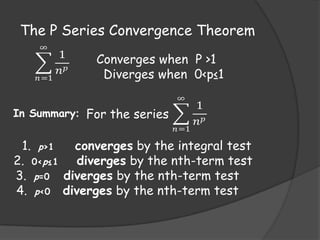
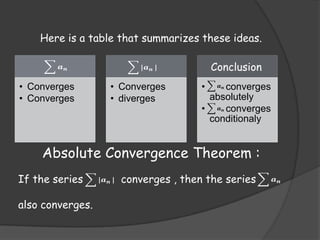
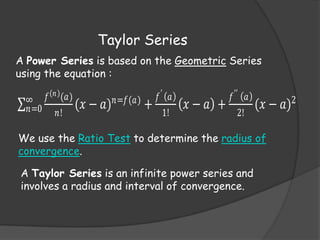
The document provides information on various tests used to determine if an infinite series converges or diverges. It defines absolute convergence, conditional convergence, and discusses tests such as the ratio test, root test, alternating series test, direct comparison test, integral test, and p-series test. It also covers topics like power series, Taylor series, and their intervals and radii of convergence.