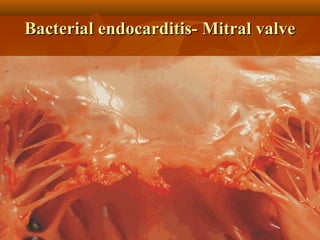
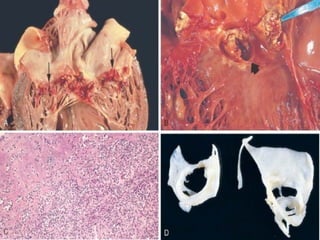
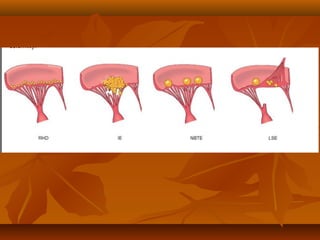
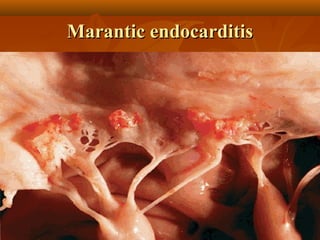
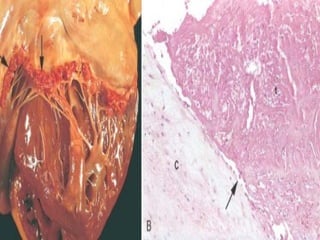
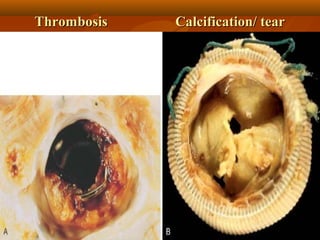
This document describes infective endocarditis, which is the colonization or invasion of heart valves or inner lining of the heart by microbes, leading to the formation of bulky vegetations. It discusses the different types (acute vs subacute), predisposing factors, common causative organisms, pathology, clinical features, diagnosis using the Duke criteria, and noninfected vegetations such as those seen in marantic endocarditis and systemic lupus erythematosus.