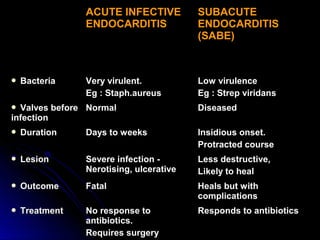
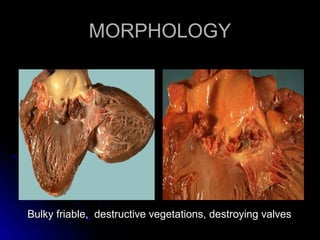
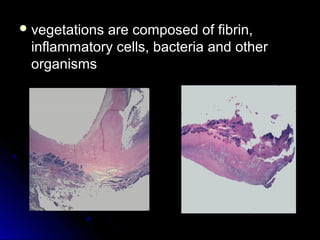
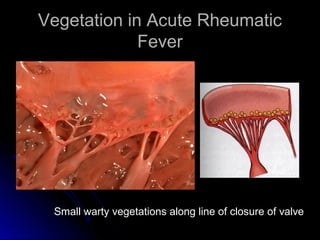
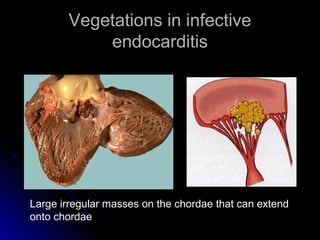
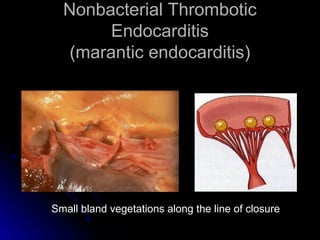
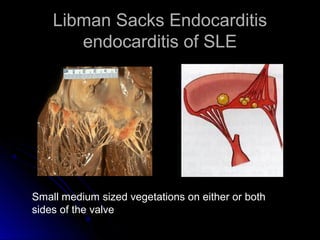
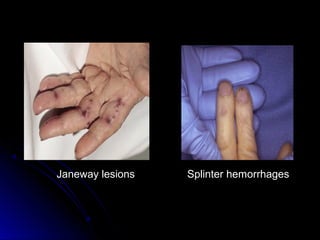
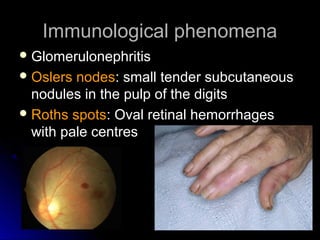
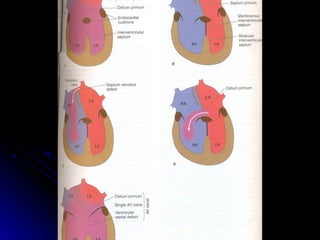
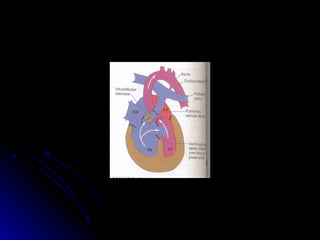
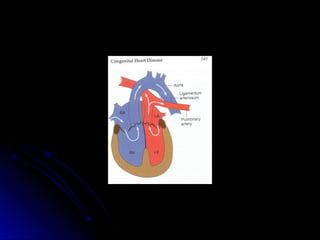
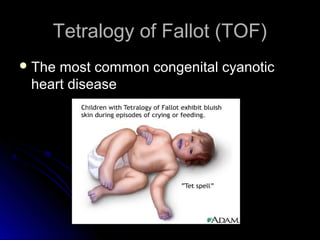
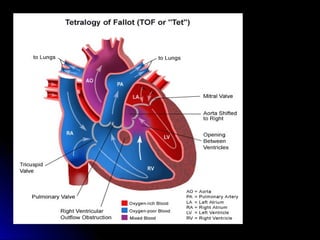
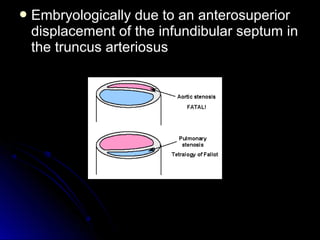
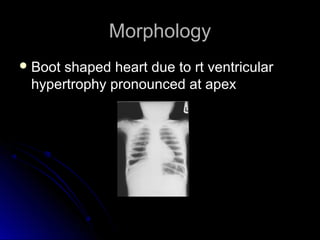
Infective endocarditis is a colonization or invasion of the heart valves or endocardium by microbes, leading to the formation of bulky, friable vegetations composed of thrombotic debris and microorganisms. It is usually caused by bacteria and may present as either acute or subacute forms. Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common congenital cyanotic heart disease, characterized by a ventricular septal defect, obstruction of the right ventricular outflow tract, overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy.