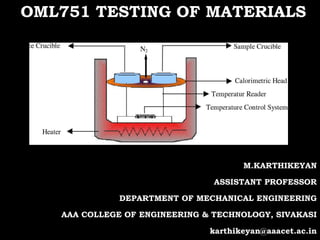
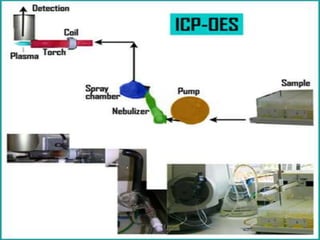
This document discusses inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES), a technique used to detect chemical elements. ICP-OES uses inductively coupled plasma to produce excited atoms and ions that emit electromagnetic radiation at wavelengths specific to each element. The plasma is generated by inductive coupling from cooled electrical coils operating at megahertz frequencies, reaching temperatures of 6000-10,000 K. Sample solutions are nebulized and injected into the argon plasma, where atoms are excited and emit light proportional to their concentration, which is measured by a spectrometer. Typical applications include environmental testing, food and drinks analysis, materials testing, and healthcare.