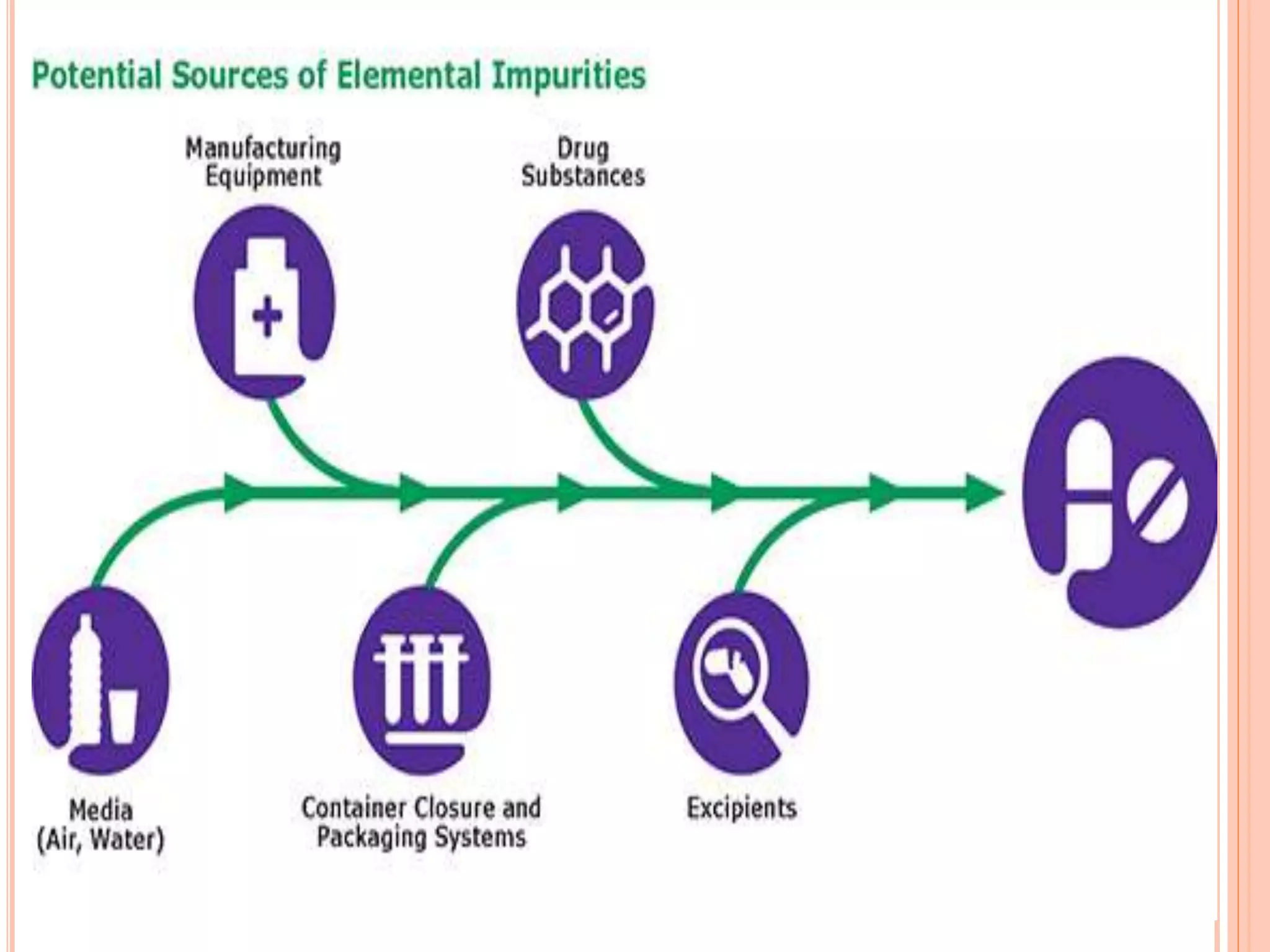
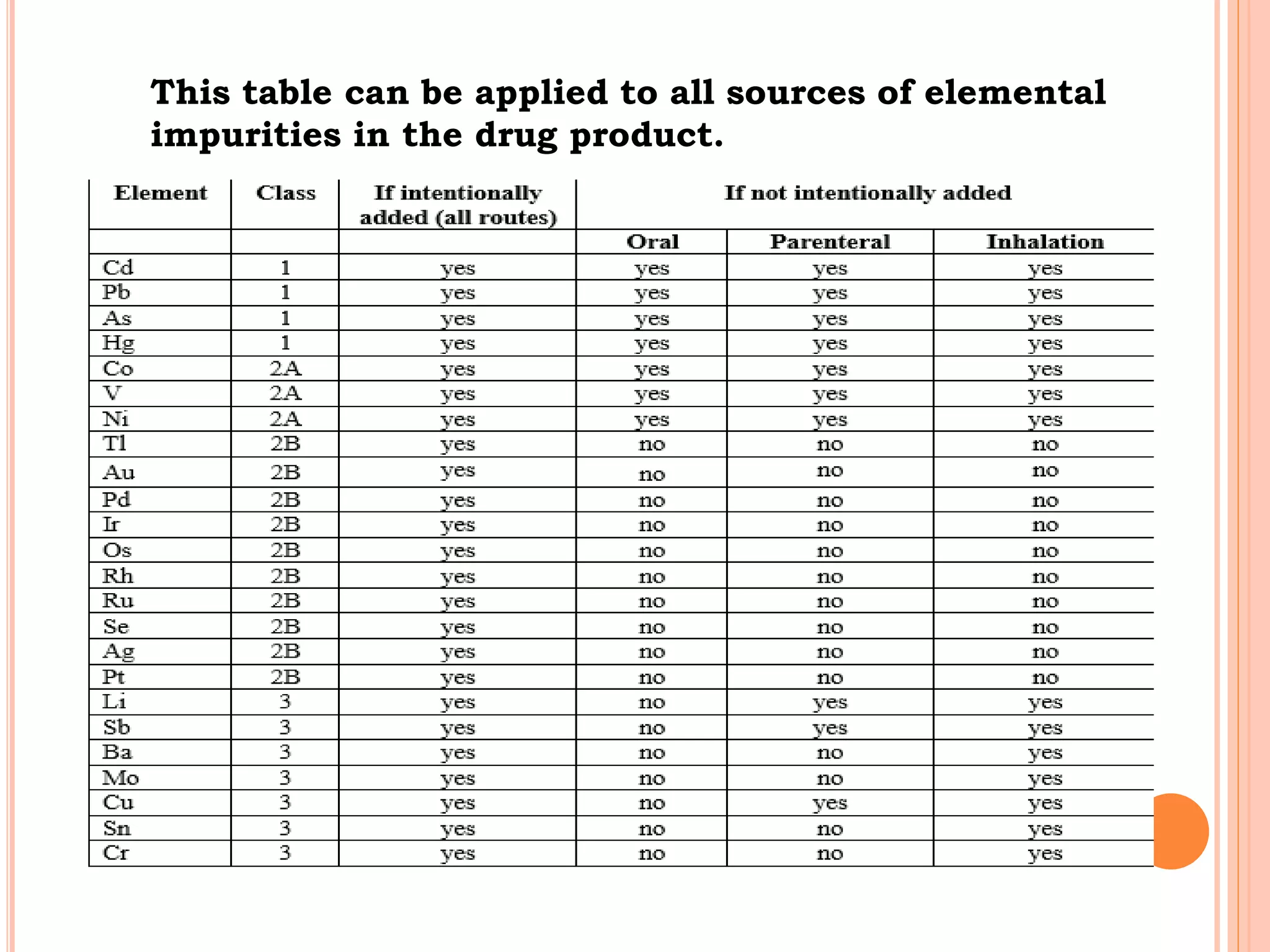
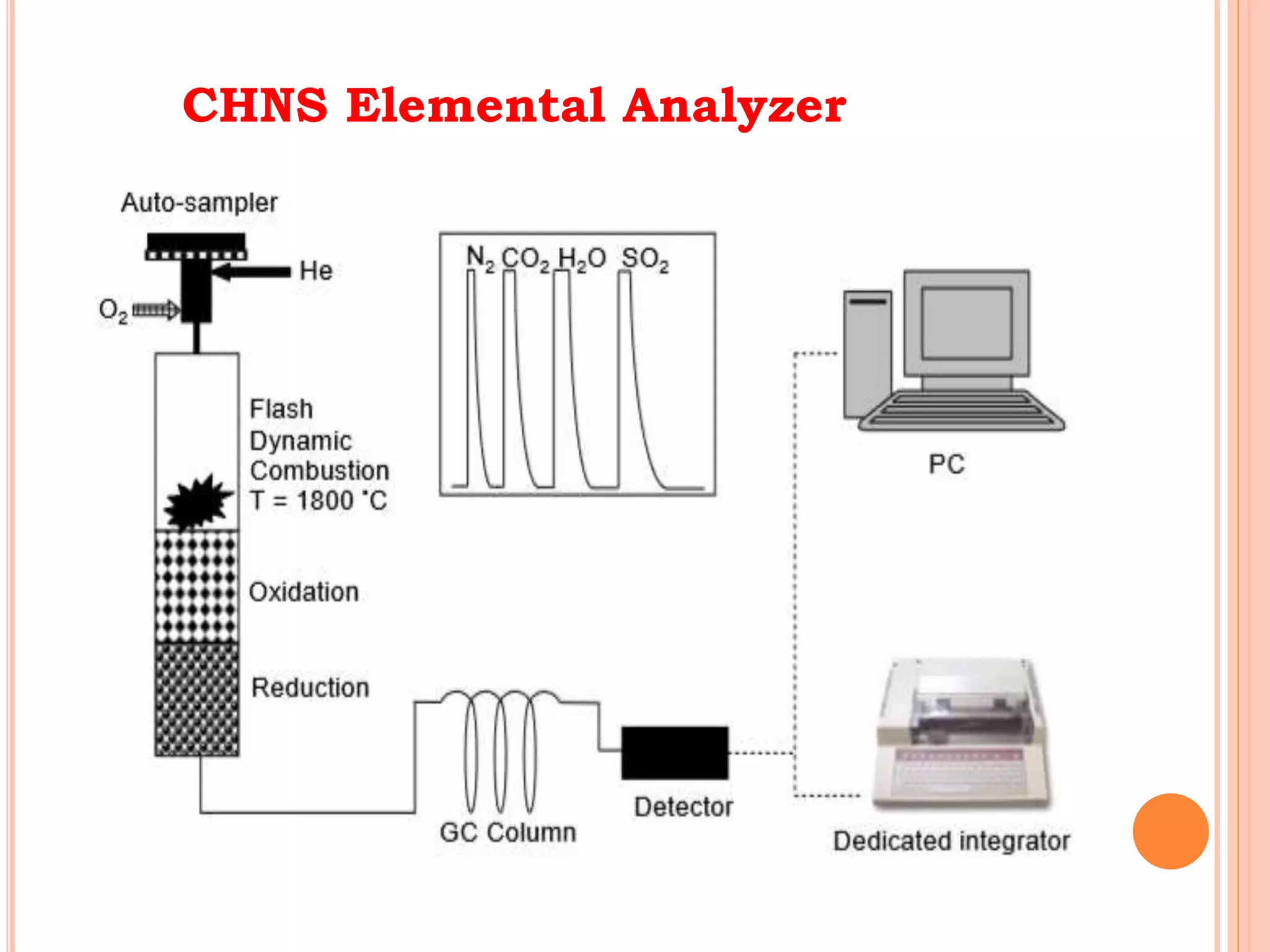
This document discusses elemental impurities in pharmaceutical products. It defines elemental impurities as traces of metals that can be introduced during manufacturing from sources like catalysts, equipment, or packaging materials. It identifies several potential sources of elemental impurities and analytical procedures that can be used to detect specific impurities. These include testing for impurities introduced during synthesis, from equipment, excipients, or container leaching. The document also describes CHNS elemental analyzers which can rapidly determine carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur content and are widely used in applications like pharmaceuticals, chemicals and food analysis.