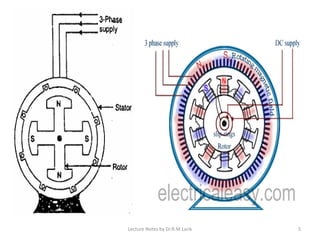
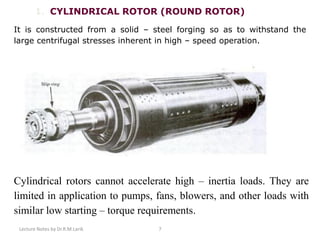
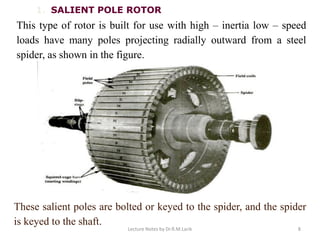
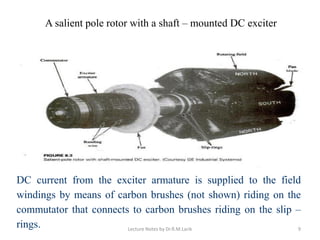
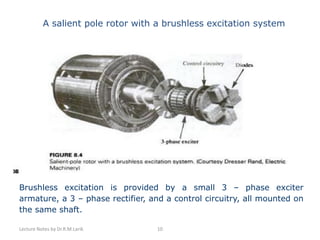
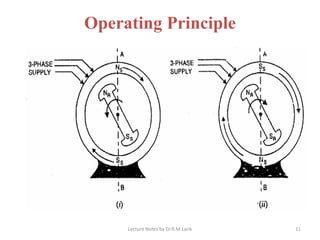
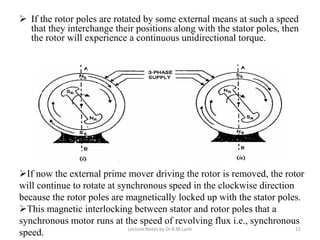
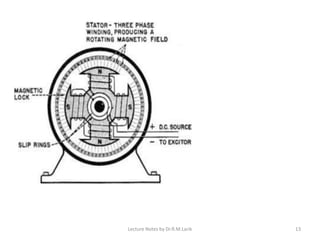
A synchronous motor operates at a constant synchronous speed determined by the supply frequency. It consists of a stator with 3-phase windings and a rotor with direct current excited poles. Synchronous motors can operate at different power factors by adjusting the rotor excitation. They are not self-starting and require an auxiliary starting method like an induction motor start or separate starting motor.