Embed presentation
Download to read offline


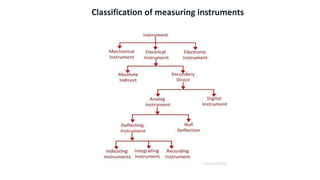







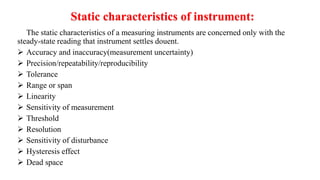

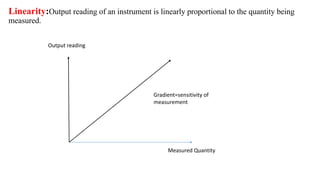

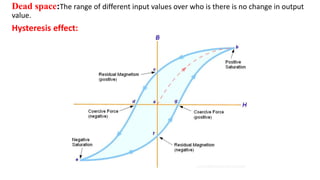
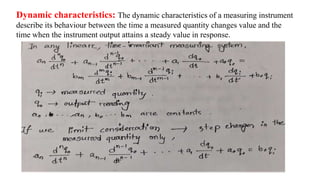

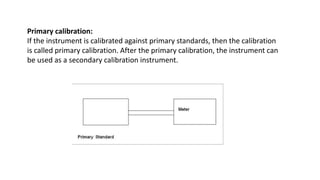

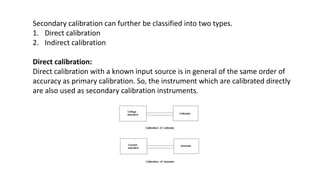
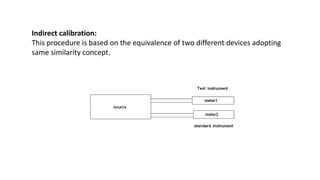

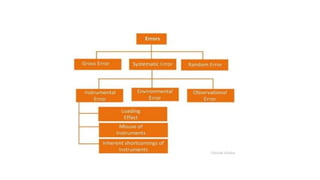





The document provides a detailed overview of measurement instruments, classifying them into mechanical, electrical, and electronic types, along with their characteristics and applications in various fields. It discusses the importance of calibration, types of errors that can occur in measurements, and distinguishes between absolute and secondary instruments, as well as analog and digital types. Additionally, it outlines key concepts such as accuracy, precision, and the characteristics of static and dynamic measurements.


























