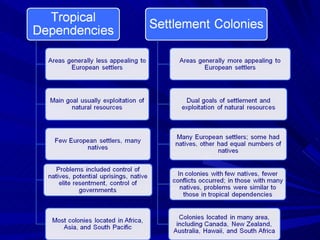
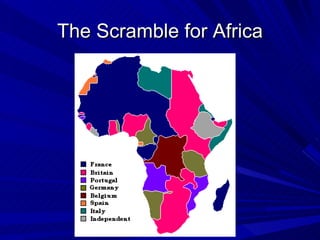
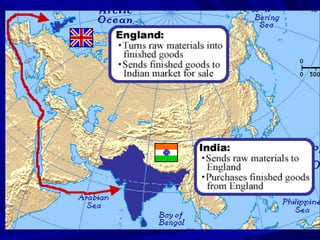
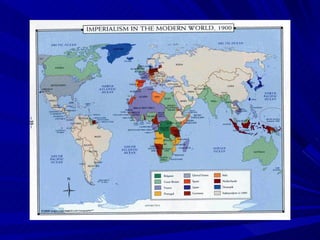
The document summarizes the key causes, forms, and effects of European imperialism between 1800-1914. The main causes included economic interests in acquiring natural resources and new markets, political and military ambitions of rising nationalism, and beliefs in racial superiority and the duty to civilize. The major European powers carved up Africa at the Berlin Conference without regard for local groups. Forms of rule included direct colonies, indirect rule through local leaders, and spheres of influence. Long term effects included the rise of a global economy with dependencies between industrialized and developing nations, as well as growing nationalist movements seeking independence in the 1900s.