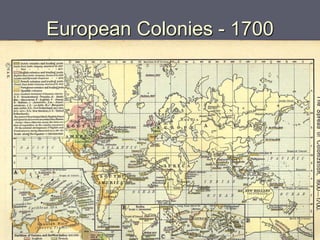
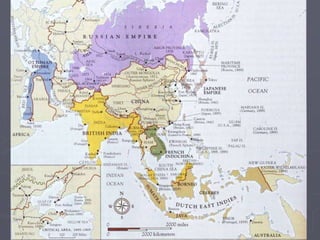
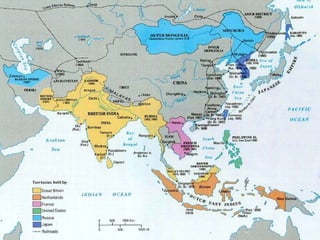
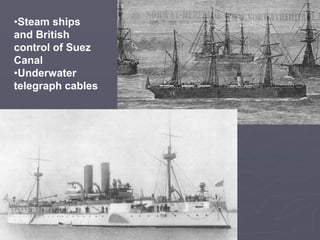
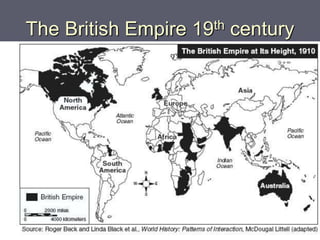
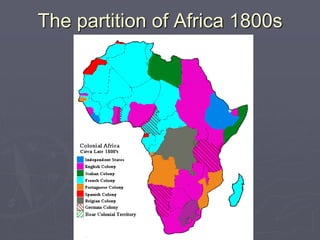
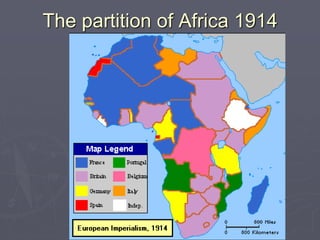
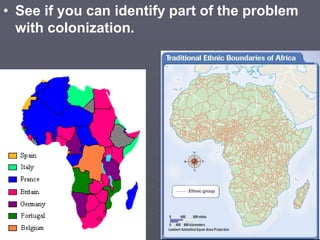
Industrialized nations like European powers, the United States, Russia, and later Japan strengthened control over their colonies and established overseas empires in Asia, Africa, and the Pacific between the 18th-19th centuries. They did so to gain profits from trade, capture markets for factory goods, absorb excess populations, and achieve national prestige. Imperialism involved the political and economic domination of weaker nations by stronger industrialized countries through military force, cooperation with local elites, and the use of new technologies like guns and steam ships.