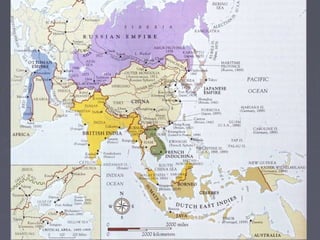
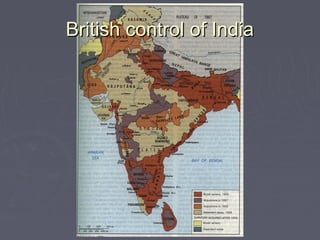
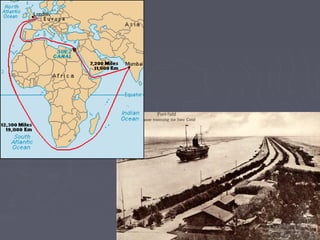
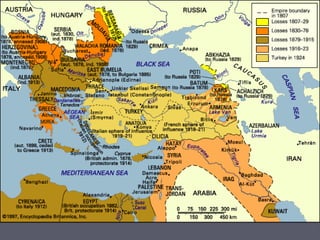
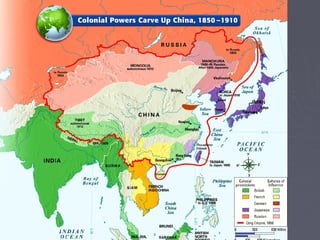
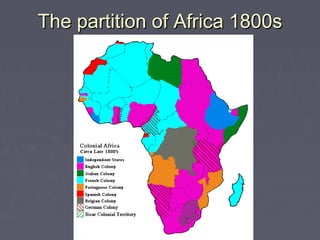
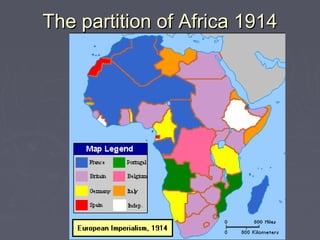
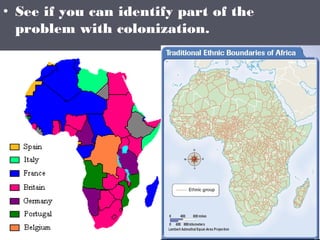
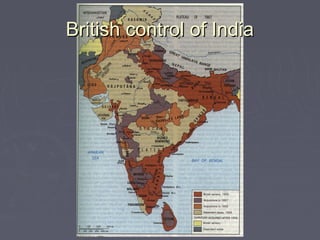
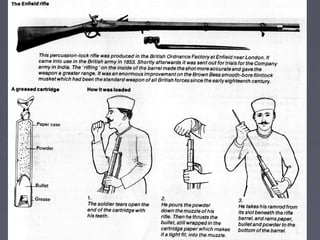
Industrialized nations in Europe and later Japan strengthened control over their colonies in the 18th and 19th centuries, establishing transoceanic empires throughout Asia, Africa, and the Pacific. They did so to gain access to raw materials, markets, and strategic locations in order to fuel their growing industrial economies. Western nations used their military and economic might to partition and dominate regions like Africa and India, often exploiting local populations and disrupting traditional ways of life, while spreading their culture and technologies. This wave of imperialism was driven by Western industrialization and notions of racial and cultural superiority.