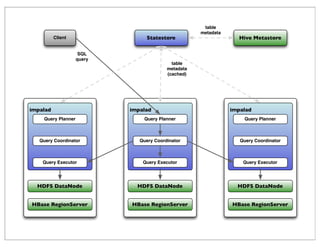
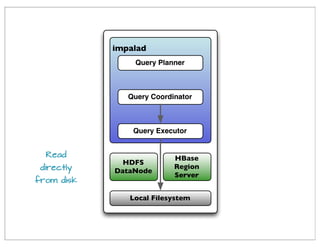
The document outlines the historical development and features of Cloudera's Impala, a distributed SQL query engine designed for low-latency data analysis on Hadoop clusters. It compares Impala's performance against Hive, emphasizing its in-memory processing capabilities and lack of reliance on MapReduce to achieve faster response times. Additionally, it discusses Impala's limitations, benchmarks, and its competitive positioning against similar technologies like Google's Dremel.