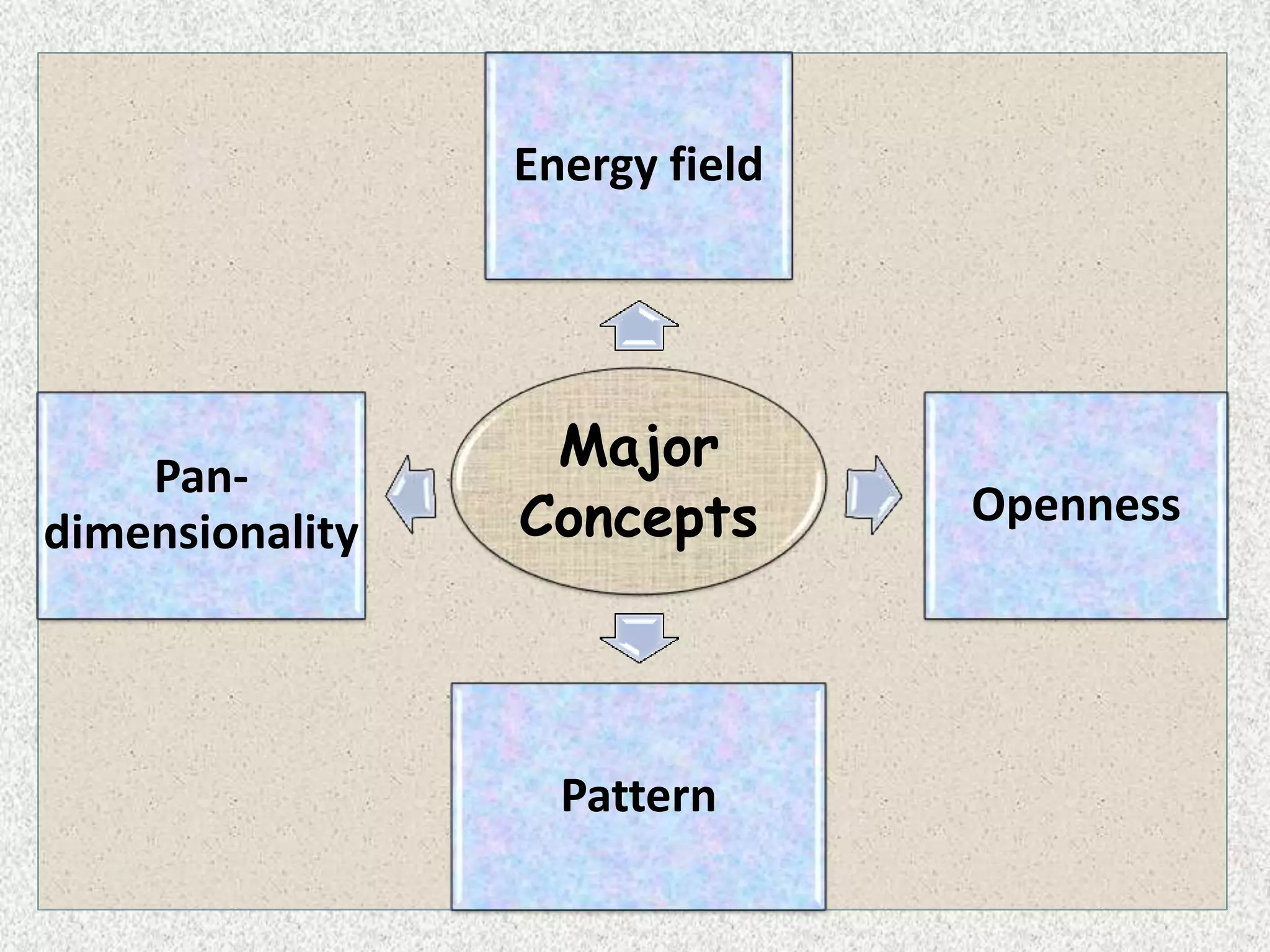
Martha Rogers presented her Science of Unitary Human Beings theory, which views humans and their environment as a unified energy field. The theory has five assumptions including that humans and environments continuously exchange energy. It also has four major concepts: energy field, openness, pattern, and pan-dimensionality. The theory's three homeodynamic principles are resonancy, helicy, and integrality. Rogers' theory emphasizes viewing patients holistically as a unified being that cannot be separated from their environment.