The document discusses various topics related to human immunity, including:
1. It describes the two main types of immunity - innate (nonspecific) immunity which acts as the first line of defense, and acquired (specific) immunity which is adaptive and involves lymphocytes and antigen presenting cells.
2. Within acquired immunity, it distinguishes between natural active immunity gained from infection and artificial active immunity gained from vaccines.
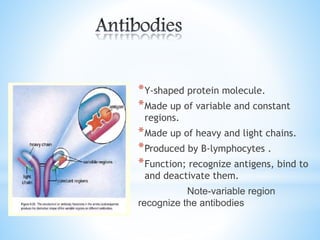
3. The two main branches of acquired immunity are humoral immunity involving antibodies, and cell-mediated immunity involving T cells that recognize antigens on cell surfaces.
4. It provides details on the structure and functions of the main antibody classes - IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD