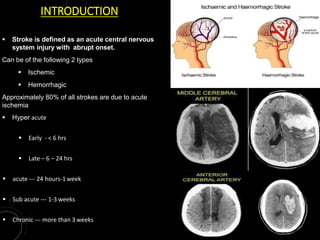
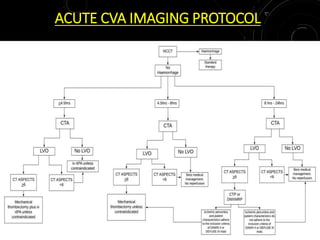
1) The document discusses imaging protocols for acute ischemic stroke, including non-contrast CT (NCCT), CT angiography (CTA), MRI, and thrombectomy procedures.
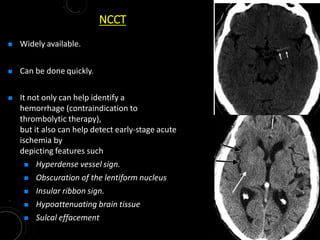
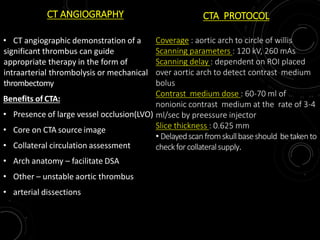
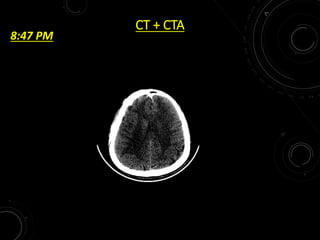
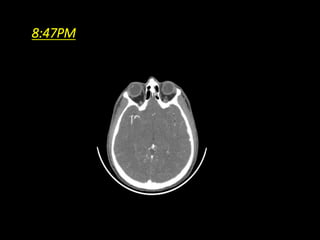
2) NCCT can help identify hemorrhage as a contraindication to thrombolysis and detect early ischemia. CTA can demonstrate thrombi to guide thrombolysis or thrombectomy and assess vessel occlusion, core infarction, and collaterals.
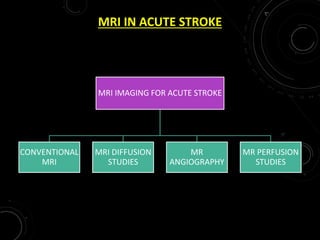
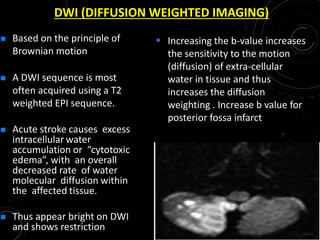
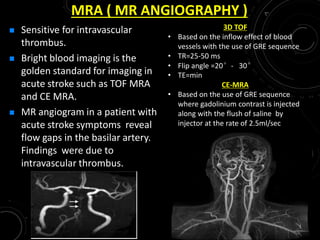
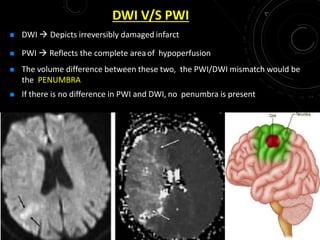
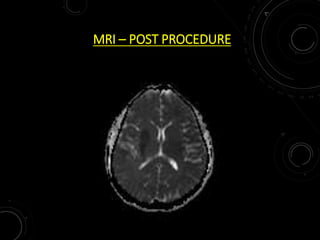
3) MRI is more sensitive than CT for acute stroke, detecting most infarcts by 24 hours. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is most sensitive in the first few hours. Perfusion imaging assesses penumbra.
4) For severe strokes,