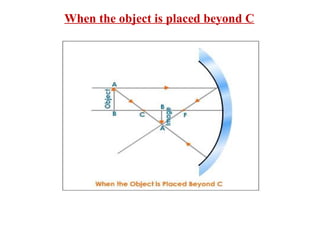
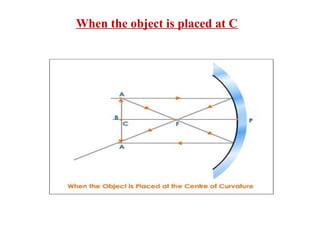
The document discusses image formation using concave mirrors. It describes 5 cases: 1) Object beyond the center of curvature C forms an inverted, reduced real image between C and the focal point F. 2) An object at C forms an inverted, same-sized real image also at C. 3) An object between C and F forms an inverted, enlarged real image beyond C. 4) No image is formed if the object is at F. 5) An object in front of F forms an upright, enlarged virtual image on the opposite side of the mirror.