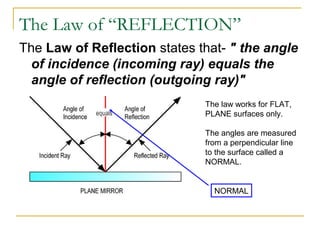
1) Light can be reflected, absorbed, or refracted. When light reflects off a flat surface, the law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
2) A mirror forms a virtual image that is located behind the mirror on the opposite side of the object. The image distance from the mirror is equal to the object distance from the mirror.
3) Spherical mirrors can be either converging or diverging. A converging mirror focuses parallel light rays to a focal point in front using ray diagrams to determine the characteristics of the real image formed.