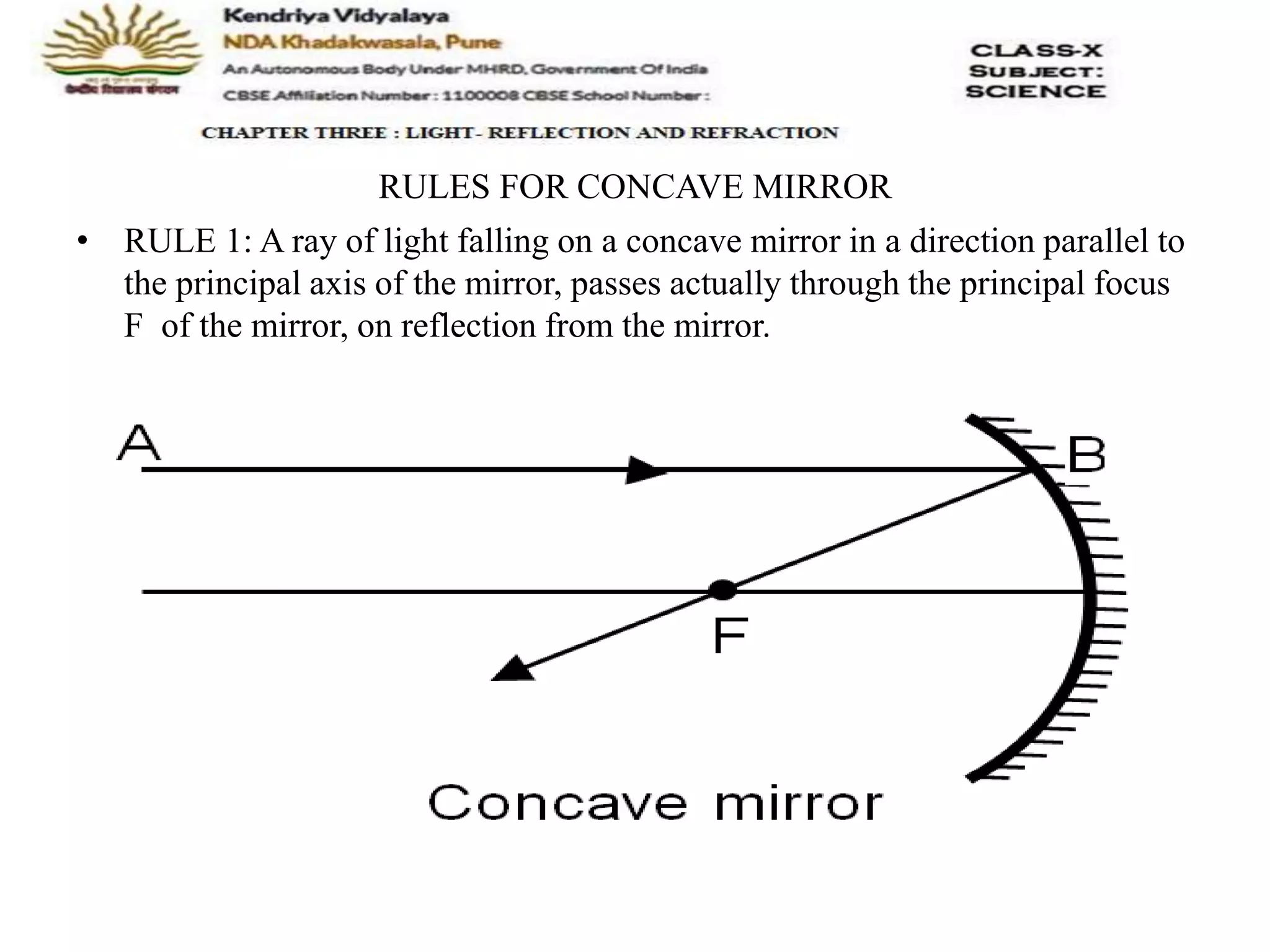
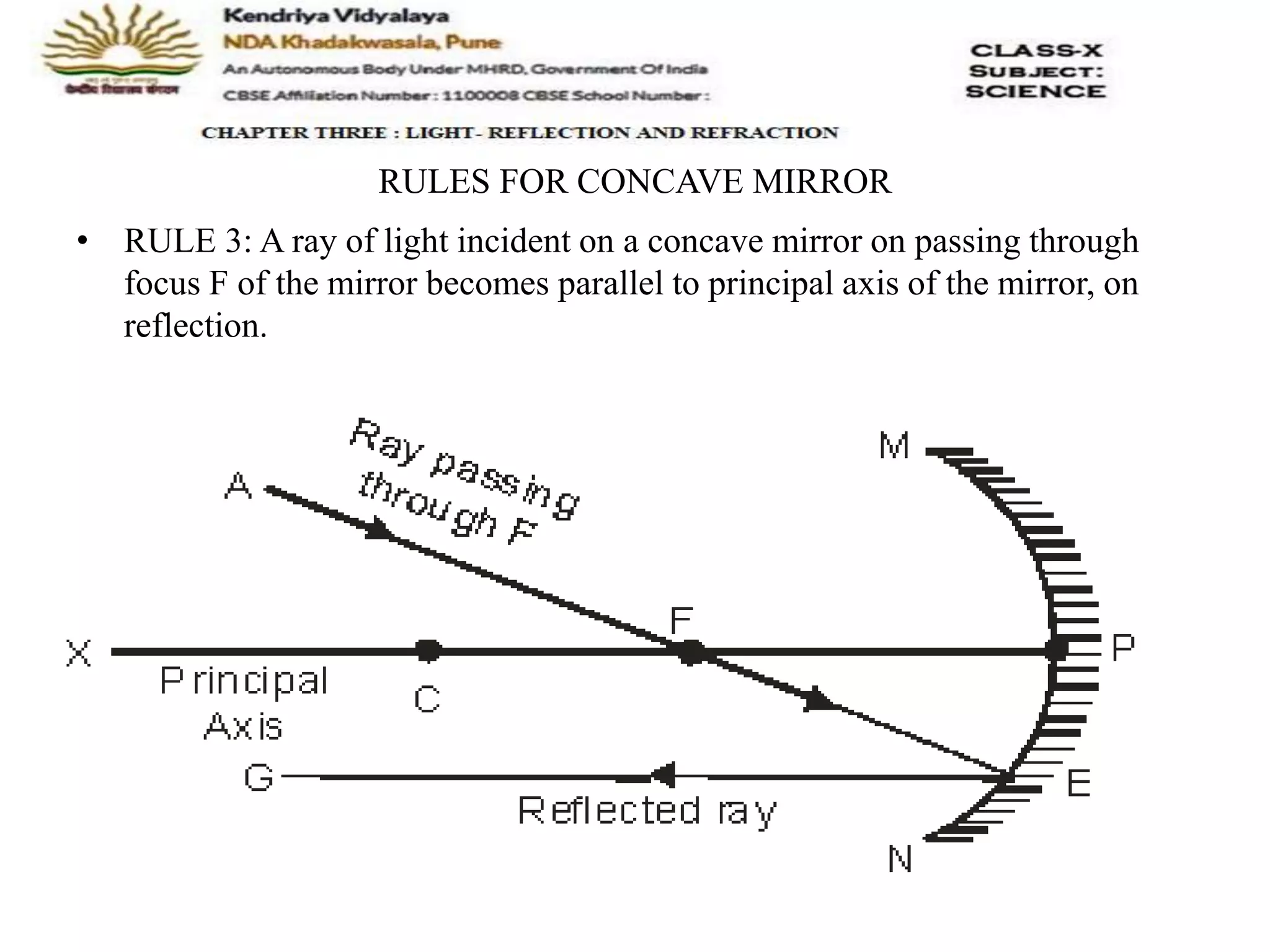
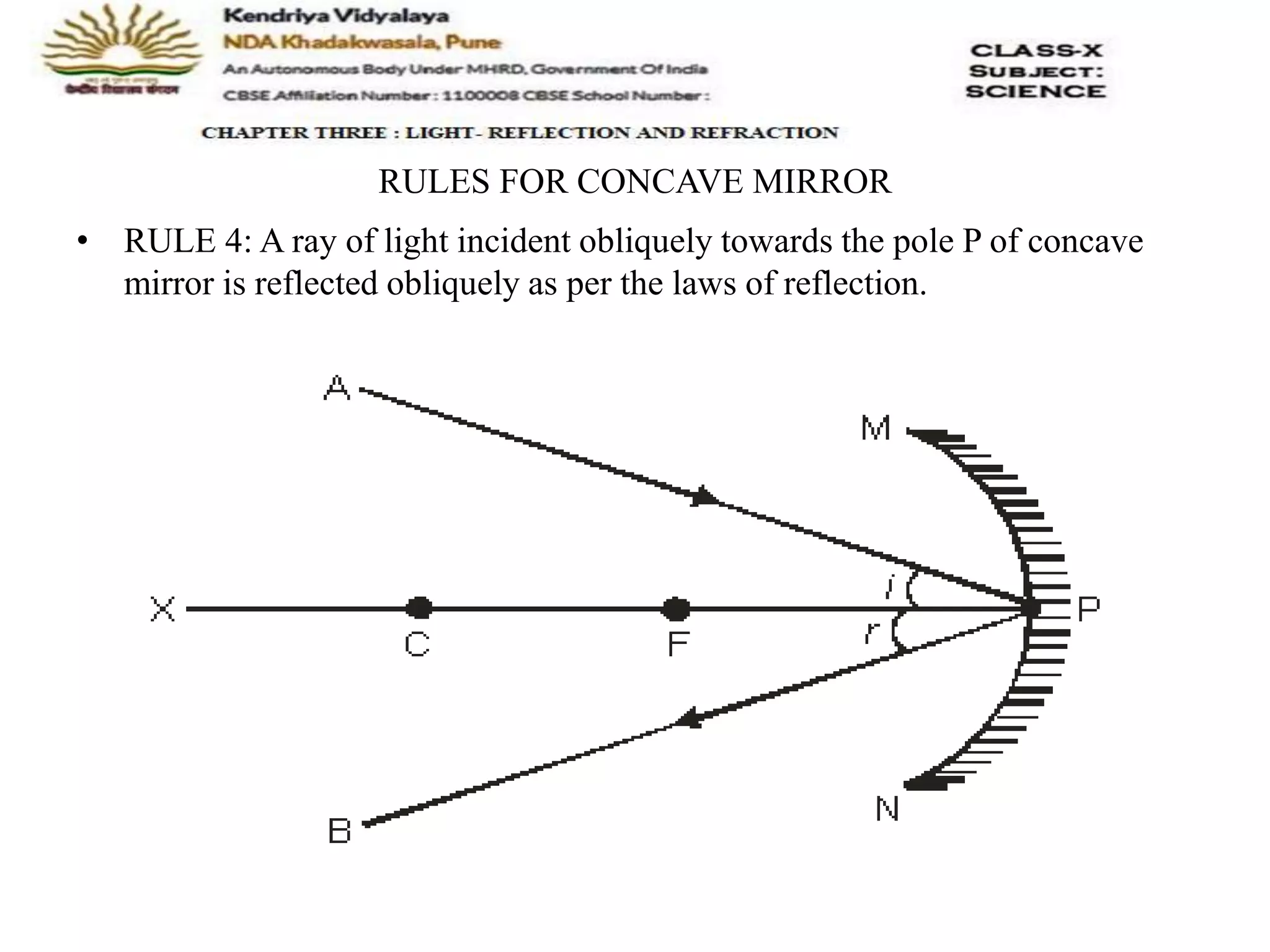
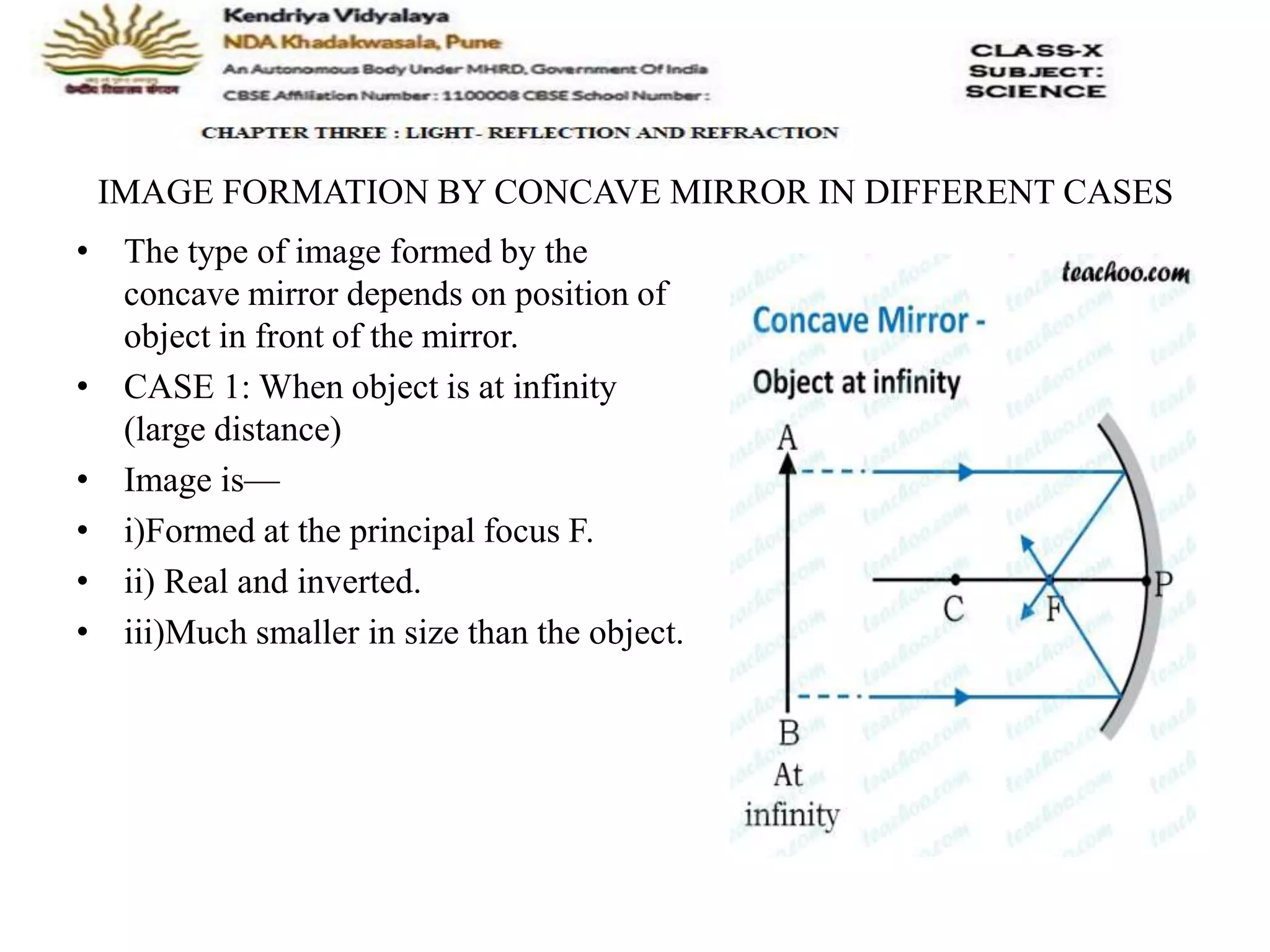
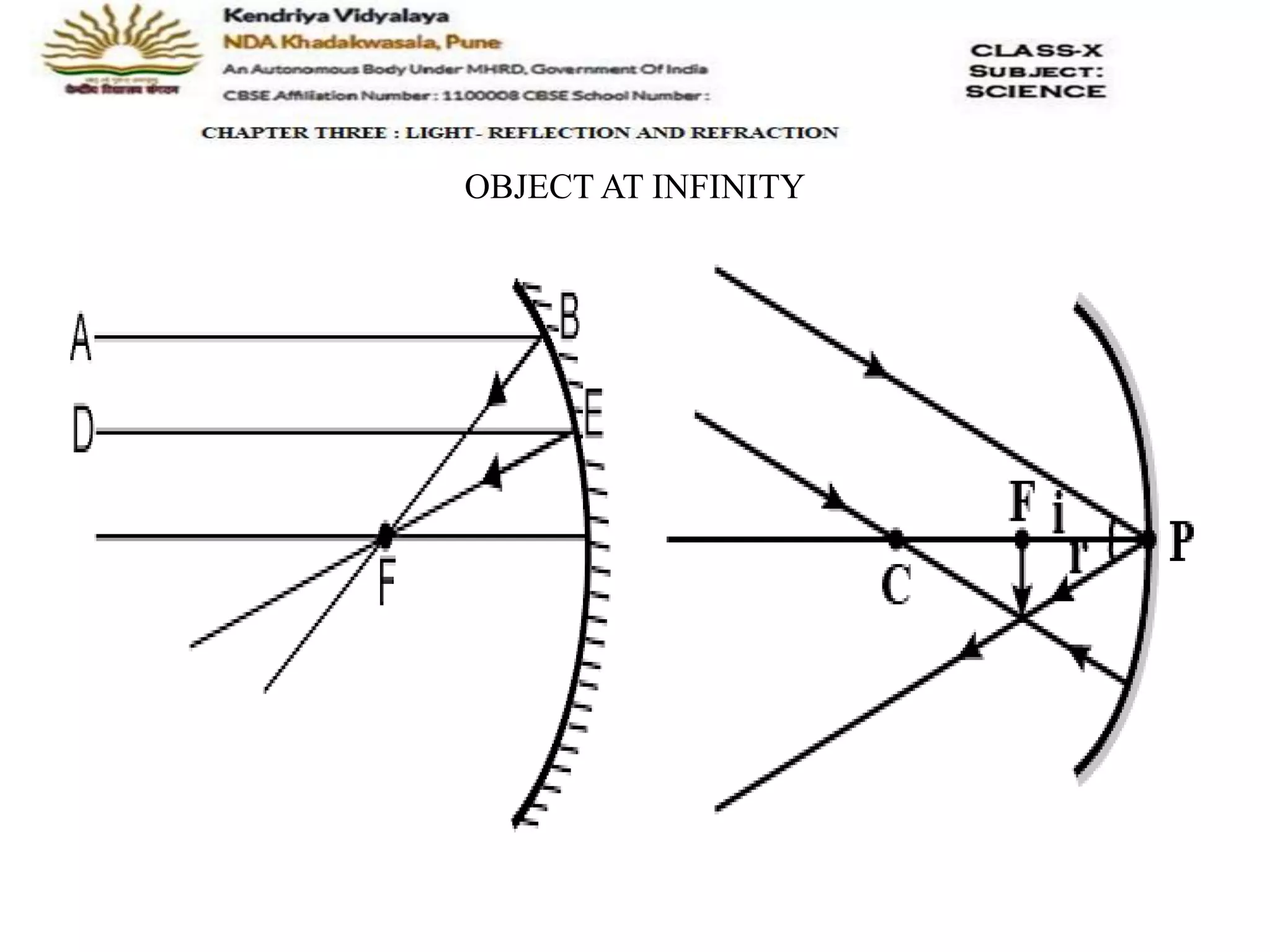
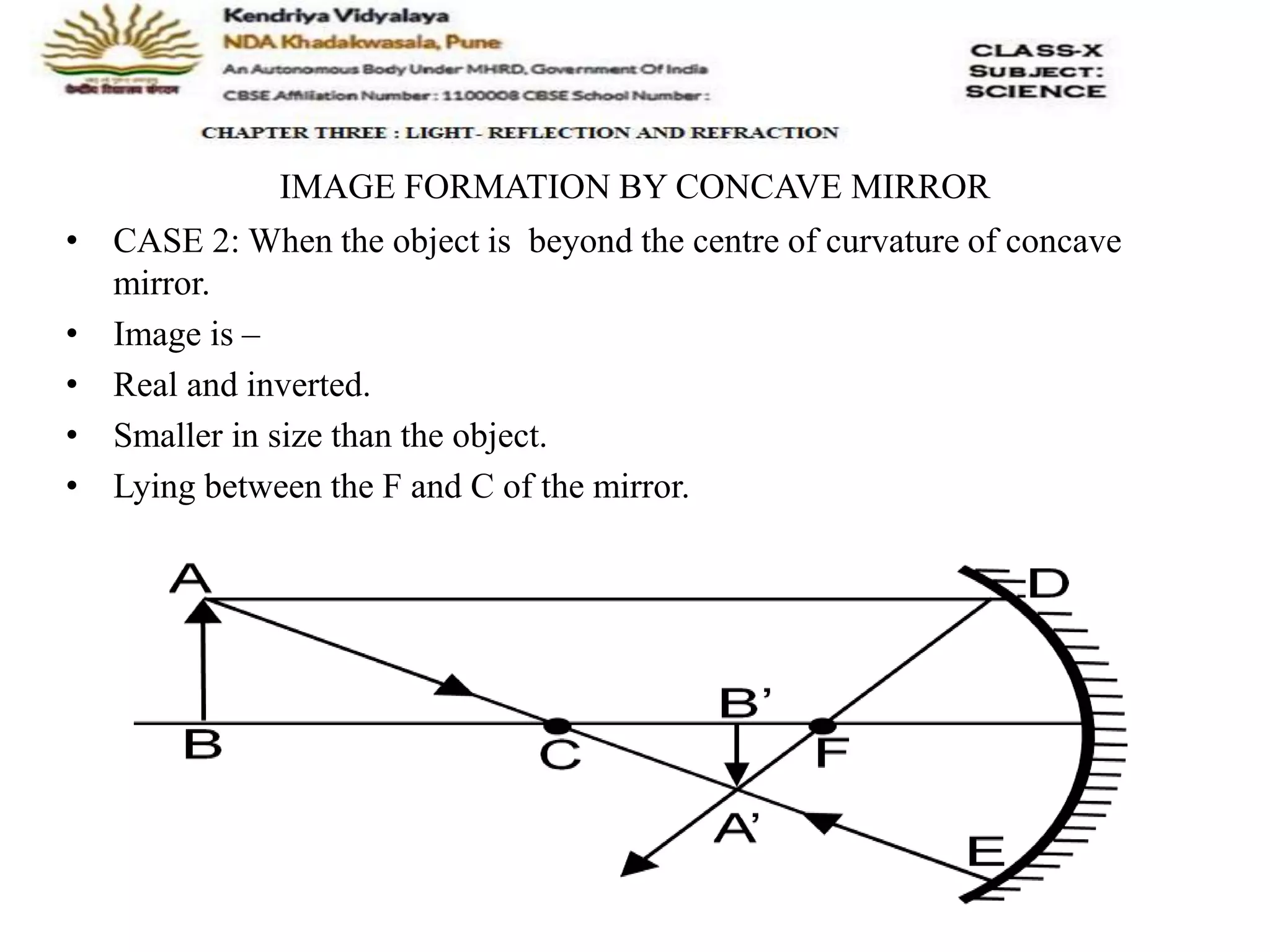
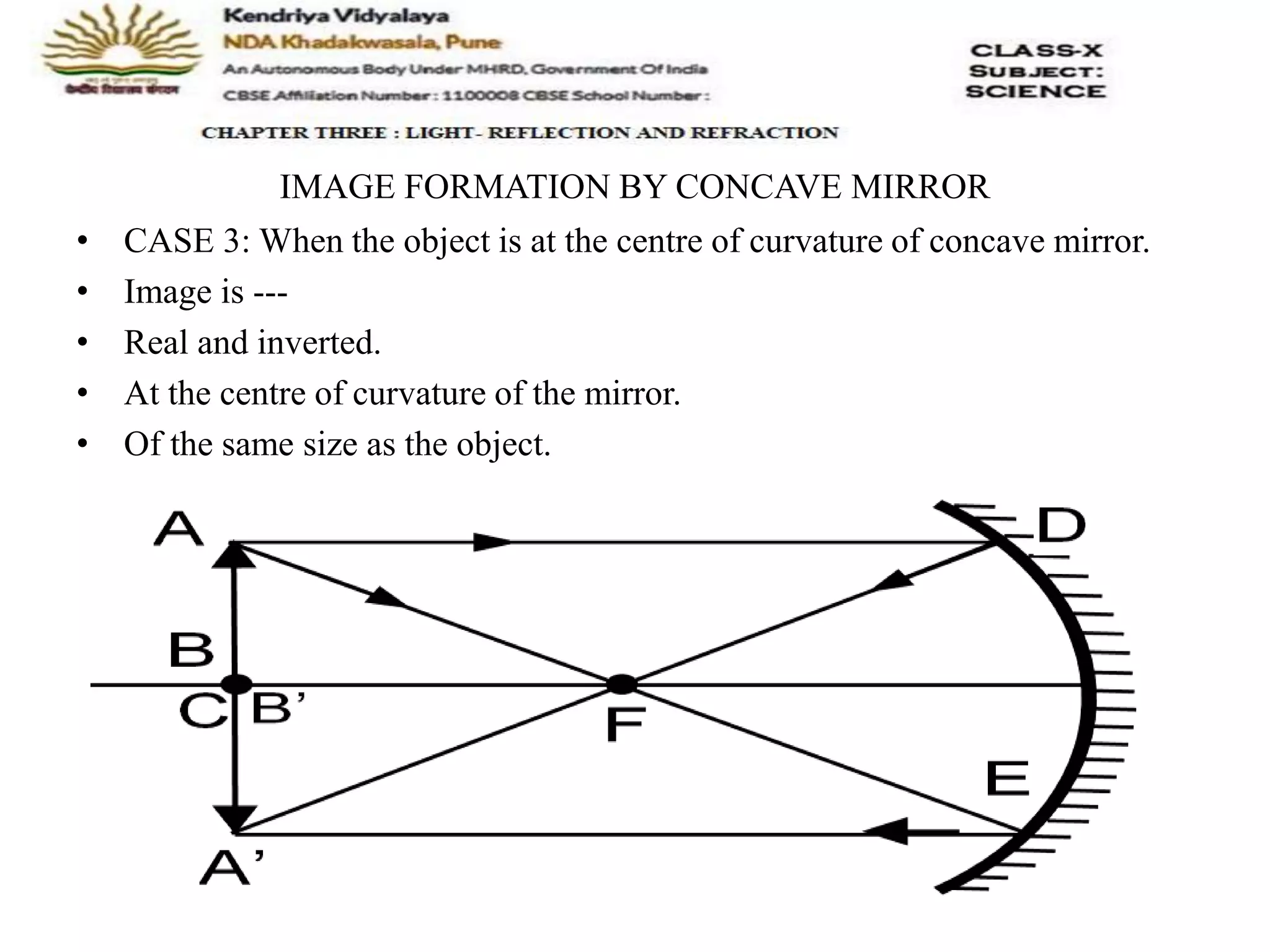
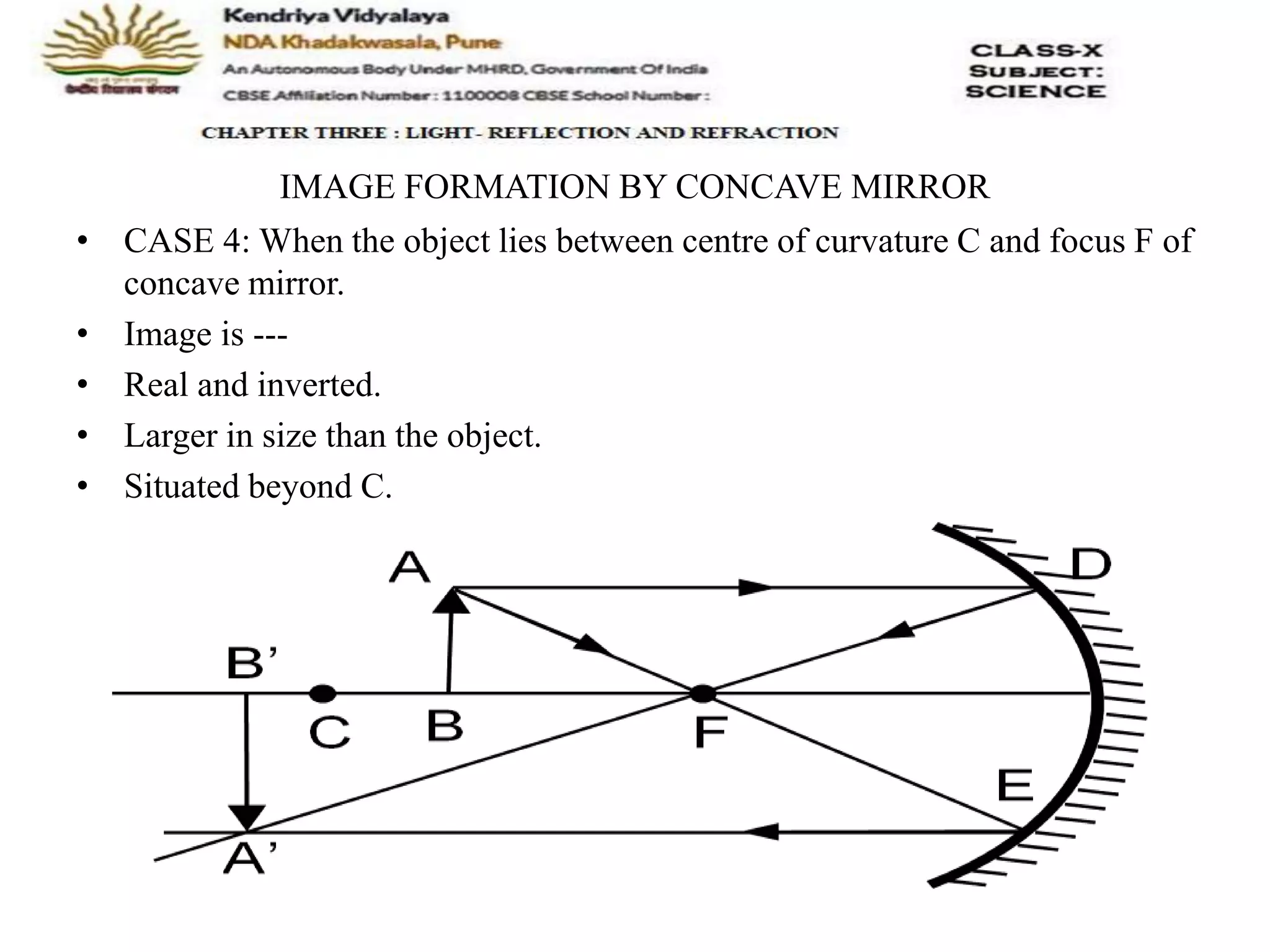
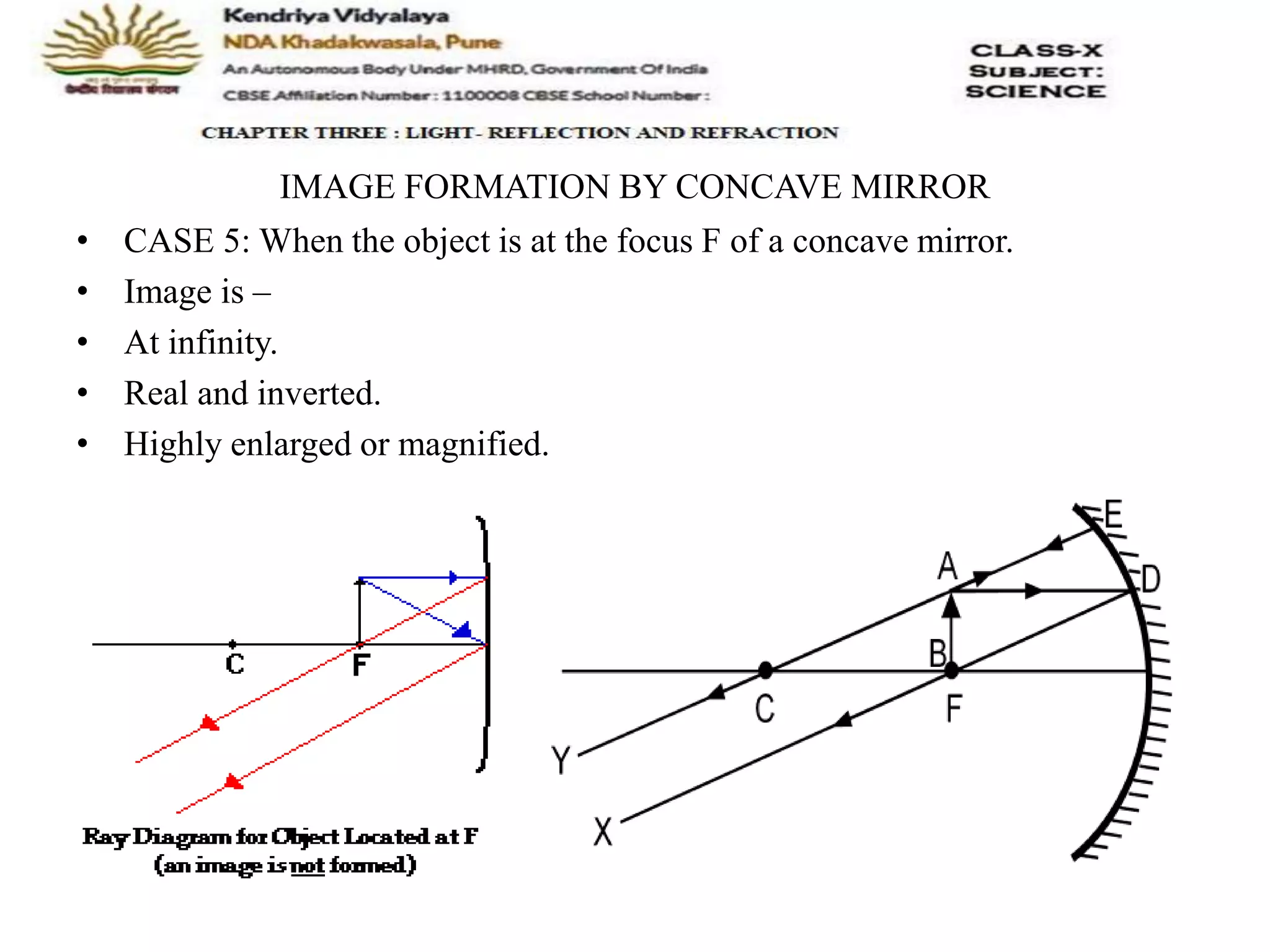
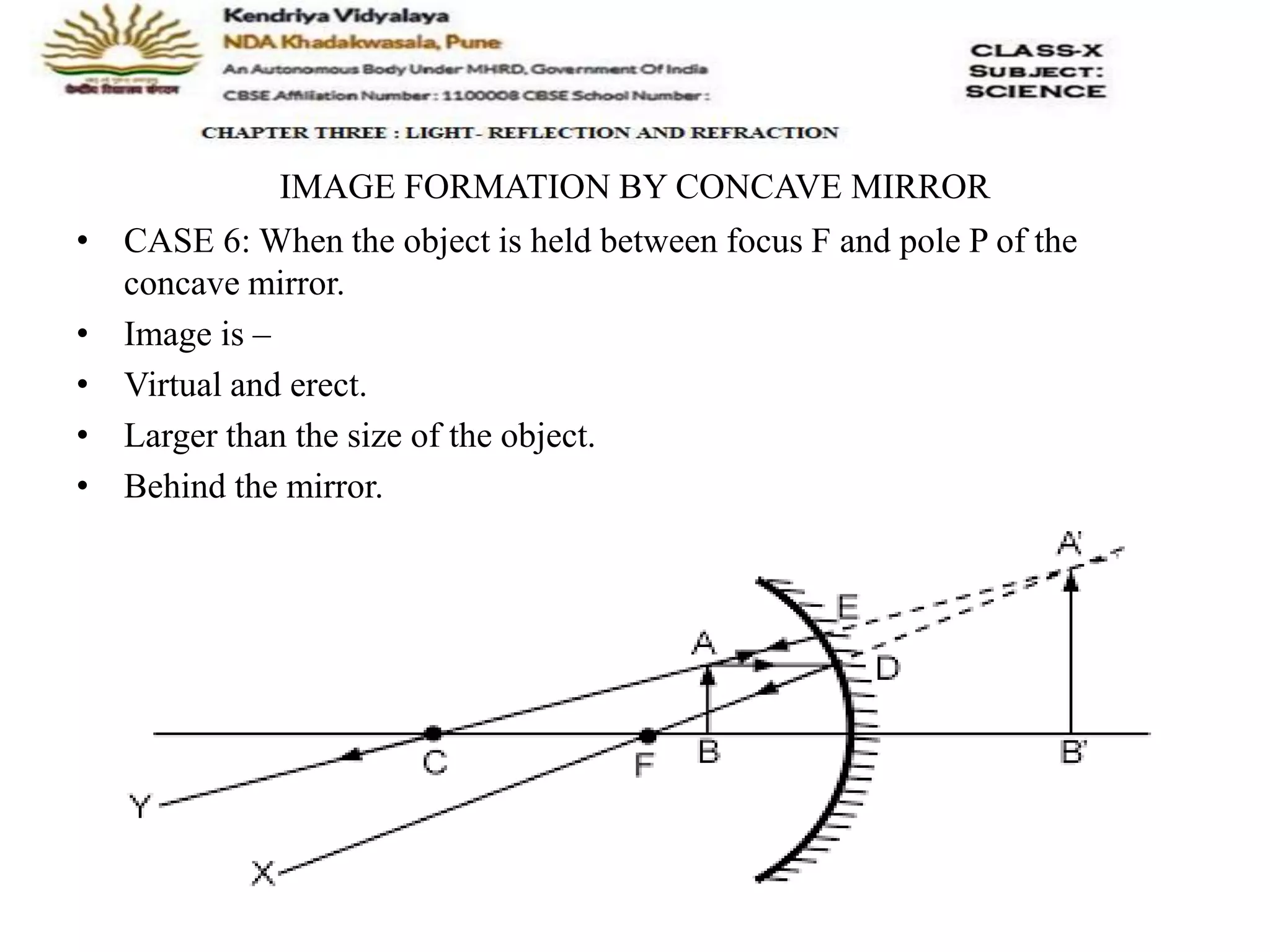
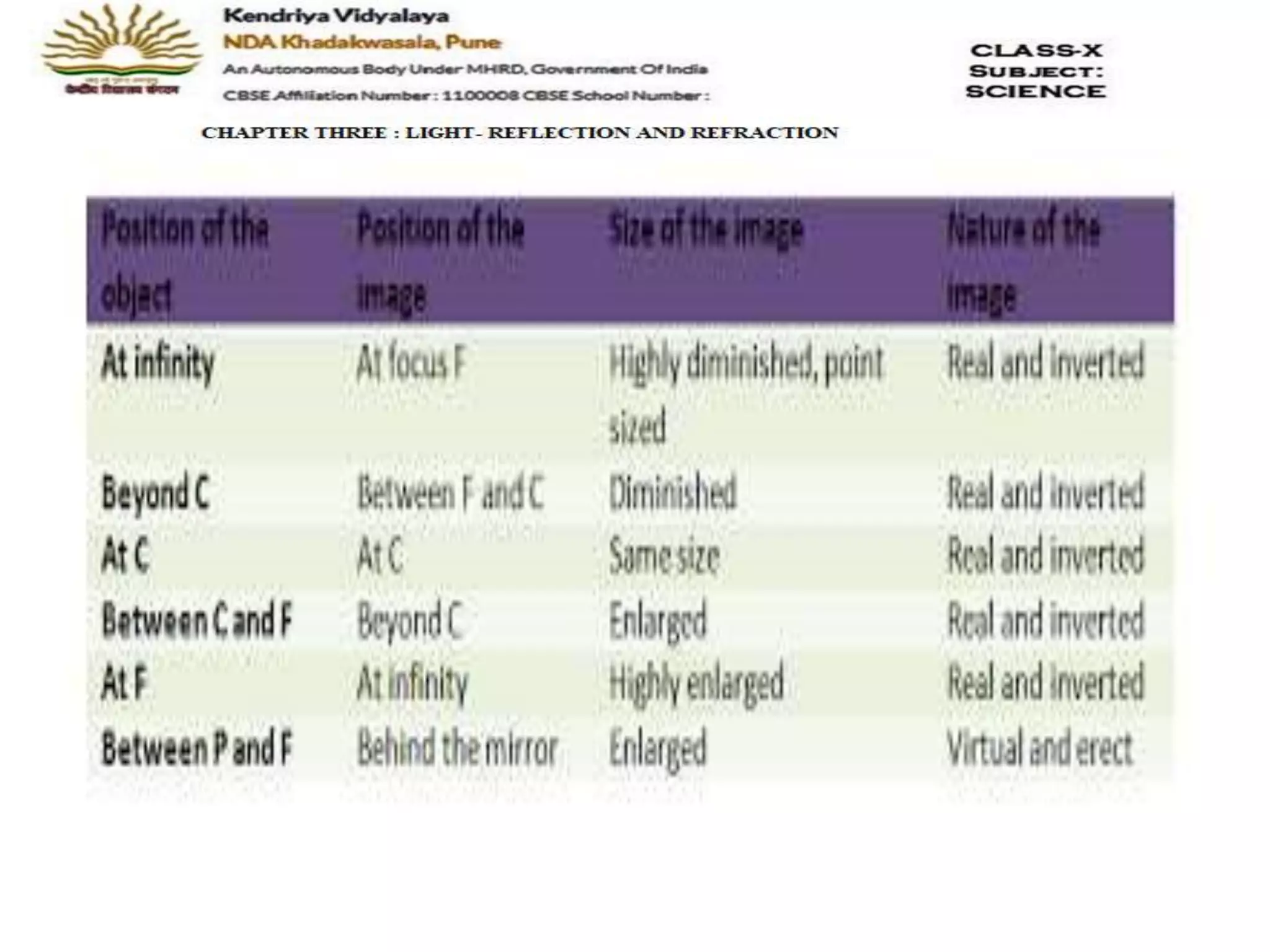
The document outlines the rules for tracing images formed by concave mirrors, including how rays of light behave upon reflection. It details various cases of image formation depending on the object's position relative to the mirror, indicating whether the image is real, virtual, inverted, or enlarged. A summary is provided of the characteristics of images formed by a concave mirror.