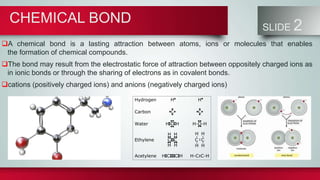
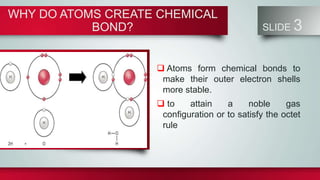
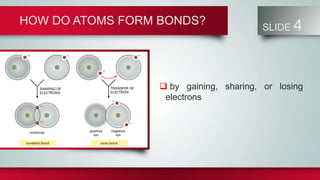
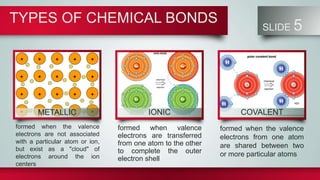
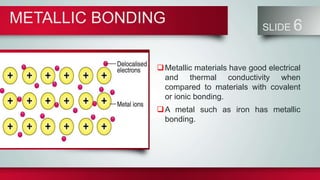
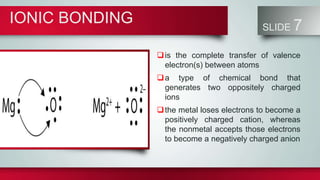
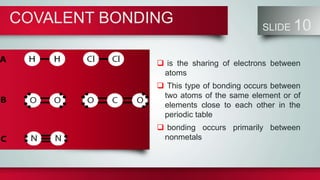
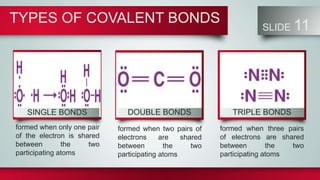
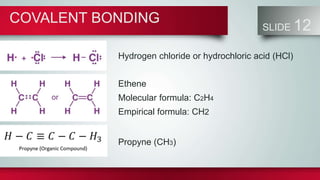
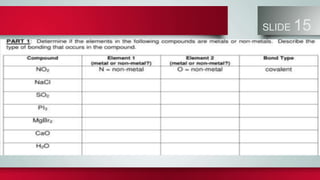
Chemical bonds form between atoms to stabilize their outer electron shells. There are three main types of bonds: ionic bonds form when electrons are transferred between atoms, covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms, and metallic bonds form from the delocalized "sea" of electrons in metal atoms. Ionic bonds result in oppositely charged ions, covalent bonds can be single, double or triple depending on electron pairs shared, and metallic bonding gives metals their conductivity. Compounds are classified as ionic, covalent or metallic based on the type of bonding between their atoms.